1967 FIAT 500 dimension
[x] Cancel search: dimensionPage 11 of 128

INTAKEEXHAUSTINTAKEEXHAUST
FIG 1 :18 Main specifications of intake and exhaust valves and valves guides (dimensions in mm)
head. Disconnect the t w o side exhaust manifolds.
Note the spark plug HT cables locations and dis-
connect from spark plugs.
2 Remove the rocker shaft pedestal- and lift away the
rocker gear. Extract the pushrods, making a careful
note of their location. Remove the cylinder head hold
down nuts in the order shown in FIG 1 :44 and using a
puller as shown in FIG 1 :9 lift off the head.
Dismantling the cylinder head:
1 Using Fiat valve spring compressor A.60084 or a uni-
versal spring compressor depress the valve spring as
shown in FIG 1 :14 and lift out the cotters. Release t h e
compressor and withdraw the lock cone, oil shield
(inlet valve only) upper spring cup, valve spring and
lower spring cup. Withdraw the valve from the under-
side of the head.
2 Dismantle the remaining three valve assemblies as
detailed above ensuring that all parts are kept in sets
for correct reassembly.
Inspection and servicing of the cylinder head :
1 Remove all carbon deposits from the combustion
chambers and valve ports using a rotary wire brush or a
set of scrapers.
2 Thoroughly clean the cylinder head and to test for dis-
tortion lightly coat the machined faces with 'Engineers
Blue' or lamp
black and place the cylinder head on a
surface plate. Carefully slide to and fro and any streaks
left behind will indicate a distorted surface. A distorted
head will not make a gas-tight seal with the cylinders
and must be entrusted to an expert for correction or,
in severe cases, renewed.
3 Carefully clean the valve guides as shown in FIG 1:16
using Fiat guide brush A.11417 bis. Should the guides
18Reassembly is the reverse procedure to dismantling.
During assembly utmost cleanliness must be observed as
any abrasive material could find its way to the pistons and
cylinder bores causing unnecessary wear. Check that the
cylinder barrel mating face is clean to ensure correct
gasket sealing.Reassembly of t h e cylinder head:
be worn then they should be removed using a press and
a suitable sized drift. The guides are press fitted with a
pinch fit of .00134 to .00244 inch. To install the guides
use Fiat tool A.601 53 as shown in FIG 1 :17. As the
guides have no stop ring during the press fitting, the
depth of insertion is determined by the Fiat tool. If the
tool is not available take the necessary depth measure-
ments before the old guides are removed. The normal
fit clearance between valve stem and guide is .00087 to
.00217 inch with a maximum wear limit of .0059 inch.
To check this see FIG 1:18.
4 The valve seats should always be reconditioned after
decarbonization. It is suggested that this operation be
left to a local service station with valve seat cutting
equipment. The valve seat angle for both inlet and
exhaust valves is 4 5 ° ± 5'.
5 Inspect the valves for soundness or distortion and if the
clearance between guide and stem is within the manu-
facturers wear tolerance of .0049 inch the valve may
be cleaned using a wire brush and the seating face
ground to an angle of 45°30' ± 5'. This again should
be left to the local service station.
Valve springs:
Thoroughly clean the valve springs of oil deposit and
inspect for cracks. It is advisable to check the free spring
height and if this dimension differs from the original
height, details of which are given in Technical Data, the
spring must be renewed. Any decrease in length indicates
that the spring has weakened.
Page 13 of 128

FIG 1:21 Finned cylinder. Letter A stamped on cylinder
indicates the class to which cylinder belongs, as referred
to its inside diameter
CLASS LETTER
FIG 1 :22 Cylinder measurement points
seats, gearbox companion flange and timing gear cover
mounting flange.
The cast iron cylinders are finned radially to increase the
cooling air surface and are located symmetrically on the
crankcase, each being held by four studs. The cylinders are
installed by sliding into the crankcase bores and finally
held in place by the cylinder head (see FIGS 1 :8 and
1 :21).
Inspect the cylinder bores for score marks, wear and
any other defects or damage. The clearance between the
piston maximum diameter and the cylinder bore should be
checked to ensure that it is within the maximum wear limit
of .0059 inch.
20FIG 1 :23 Checking cylinder diameter by dial gauge
C.687 brought to zero w i t h ring gauge C.672 DIAL GAUGE C 687
RING GAUGE C. 672 The cylinder height must be checked between the seat-
ing face on the crankcase and the top surface and this
dimension should be 3.5433 ±0006 inch.
If this dimension is less than specified the cylinder must
be renewed to prevent possible carbon deposits on the
piston crown and underside of combustion chamber
causing the piston to strike the cylinder head (see
FIG 1 :24). Checking cylinder height: This operation should bring the bore size to correspond
to the oversize piston sizes in order to obtain the correct
clearance between the piston and cylinder. These
limits
are given in Technical Data. It will be observed that the
cylinders are divided into three classes depending on the
bore diameter. The classes are identified by the letters 'A',
'B
1 and ' C , one of which will be stamped on the mating
face with the cylinder head as shown in FIG 1 :21. Pistons
are divided into three classes to correspond with the
cylinder bore sizes. Naturally the piston and bore must
belong to the same class. The maximum available piston
oversize is .0236 inch.
Pistons and rings for the Model 500 sports engine are
not available in oversize dimensions so if the cylinder bore
diameter is above the maximum wear limit new parts must
be fitted.Honing or reboring cylinder bores: It is essential that the diameter measurements are taken
at t w o different heights in the cylinder bore along both the
longitudinal and transverse axles as shown in FIG 1 :22.
It is recommended that to zero the internal micrometer
Fiat ring gauge C.672 is used (see FIG 1 :23).
If bore wear or ovality is between .0059 and .0079 inch
the cylinder bore may be honed. Should however the
wear limit of .0079 inch be exceeded then the bores must
be recut.
Page 34 of 128

FIG 2:12 illustrates the starting device fitted to
26.IMB.4 and later carburetters. It differs from earlier
units in detail, principally in having fewer starting mixture
orifices 30 and 32 into the mixture duct 26.
2 : 8 Carburetter operation and adjustment,
Weber 26. OC
The new 500 station wagon is fitted with the Weber
26.OC carburetter which is of a horizontal draft design to
suit the engine which is fitted in the horizontal position.
The carburetter is fitted with a progressive action starting
device which enables the driver to adjust the mixture rich-
ness to the most arduous of starting conditions, and will
enable the engine to run eyenly until it reaches normal
operating temperature.
A dampened needle valve ensures a smooth running
engine as it is not affected by engine vibrations and there-
fore giving a constant fuel level in the carburetter bowls.
A secondary venturi is incorporated in the single casting
of the carburetter body.
Carburetter operation, starting device:
The petrol from bowl 23 (see FIG 2:13) reaches the
starting jet 37 through the duct 35. By operating the choke
lever 31 to the end of its stroke, the valve 30 is lifted from
its seat and brought to the 'fully open' position as shown
in diagram 'A' (FIG 2:13). Under these conditions the
valve 30 uncovers both the starting mixture ducts 28 and
29. With the throttle set in the idling speed position the
engine vacuum created by the operation of the starter
motor causes the fuel contained in the recess of j e t 37 in
the jet and the reserve
well 36 to be mixed with the air
coming from the air jet 38.
The mixture arrives through the ducts 28 and 29 at the
same time as air from holes 34, past the throttle so per-
mitting easy starting of the engine.
A
B
C
FIG 2:12 Section of later starting device
Key to Fig 2:12 A Cold starting position B Warming up position C Normal running position
2 Air inlet 21 Primary venturi 24 Secondary venturi 26 Mixture duct 27 Air bleed 30,32 Starting mixture orifices
33 Valve 34 Mixture duct 35 Air orifices 38 Rocker 39 Lever return spring 40 Control lever 41 Control wire screw
42 Cover and cable support 43 Valve spring 44 Spring guide and retainer 45 Starting jet emulsion air duct 46 Emulsion
air reserve well duct 47 Reserve well 48 Starting jet
F50041 Once the engine has initially fired the starting device will
deliver a mixture whose petrol/air ratio is such that the
engine will run regularly even though it is cold. As soon as
the engine warms up this rich charge would be excessive
and therefore it becomes necessary to gradually ease back
the operation of the starting device. As this is occurring,
the valve 30 gradually covers up the mixture duct orifice 28
so as to weaken the mixture while by closing the duct 29
gradually. It also reduces the amount of mixture delivered
by the carburetter as shown in diagram ' B ' (FIG 2:13). FIG 2:11 Mounting flange modification: A earlier, B
later (dimensions in mm)
Page 53 of 128
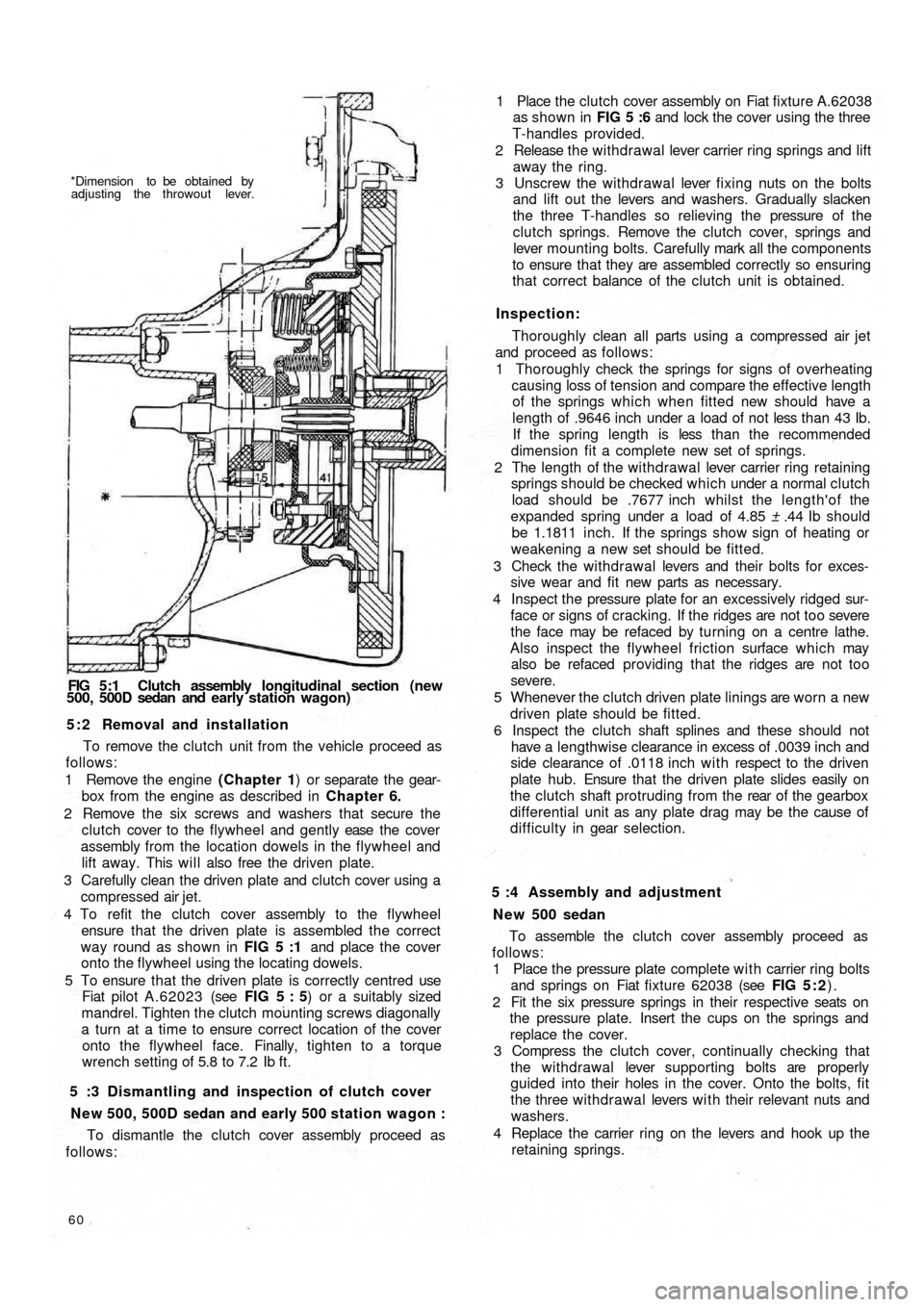
*Dimension to be obtained by
adjusting the throwout lever.
FIG 5:1 Clutch assembly longitudinal section (new
500, 500D sedan and early station wagon)
5 : 2 Removal and installation
To remove the clutch unit from the vehicle proceed as
follows:
1 Remove the engine (Chapter 1) or separate the gear-
box from the engine as described in Chapter 6.
2 Remove the six screws and washers that secure the
clutch cover to the flywheel and gently ease the cover
assembly from the location dowels in the flywheel and
lift away. This will also free the driven plate.
3 Carefully clean the driven plate and clutch cover using a
compressed air jet.
4 To refit the clutch cover assembly to the flywheel
ensure that the driven plate is assembled the correct
way round as shown in FIG 5 :1 and place the cover
onto the flywheel using the locating dowels.
5 To ensure that the driven plate is correctly centred use
Fiat pilot A.62023 (see FIG 5 : 5) or a suitably sized
mandrel. Tighten the clutch mounting screws diagonally
a turn at a time to ensure correct location of the cover
onto the flywheel face. Finally, tighten to a torque
wrench setting of 5.8 to 7.2 Ib ft.
5 :3 Dismantling and inspection of clutch cover
New 500, 500D sedan and early 500 station wagon :
To dismantle the clutch cover assembly proceed as
follows:
60
To assemble the clutch cover assembly proceed as
follows:
1 Place the pressure plate complete with carrier ring bolts
and springs on Fiat fixture 62038 (see FIG 5 : 2).
2 Fit the six pressure springs in their respective seats on
the pressure plate. Insert the cups on the springs and
replace the cover.
3 Compress the clutch cover, continually checking that
the withdrawal lever supporting bolts are properly
guided into their holes in the cover. Onto the bolts, fit
the three withdrawal levers w i t h their relevant nuts and
washers.
4 Replace the carrier ring on the levers and hook up the
retaining springs. 5 :4 Assembly and adjustment
N e w 500 sedan1 Place the clutch cover assembly on Fiat fixture A.62038
as shown in FIG 5 :6 and lock the cover using the three
T-handles provided.
2 Release the w i thdrawal lever carrier ring springs and lift
away the ring.
3 Unscrew the withdrawal lever fixing nuts on the bolts
and lift out the levers and washers. Gradually slacken
the three T-handles so relieving the pressure of the
clutch springs. Remove the clutch cover, springs and
lever mounting bolts. Carefully mark all the components
to ensure that they are assembled correctly so ensuring
that correct balance of the clutch unit is obtained.
Inspection:
Thoroughly clean all parts using a compressed air jet
and proceed as follows:
1 Thoroughly check the springs for signs of overheating
causing loss of tension and compare the effective length
of the springs which when fitted new should have a
length of .9646 inch under a load of not less than 43 Ib.
If the spring length is less t h a n t h e recommended
dimension fit a complete new set of springs.
2 The length of the withdrawal lever carrier ring retaining
springs should be checked which under a normal clutch
load should be .7677 inch whilst the length'of the
expanded spring under a load of 4.85 ± .44 Ib should
be 1.1811 inch. If the springs show sign of heating or
weakening a new set should be fitted.
3 Check the withdrawa l levers and their bolts for exces-
sive wear and fit new parts as necessary.
4 Inspect the pressure plate for an excessively ridged sur-
face or signs of cracking. If the ridges are not too severe
the face may be refaced by turning on a centre lathe.
Also inspect the flywheel friction surface which may
also be refaced providing that the ridges are not too
severe.
5 Whenever the clutch driven plate linings are worn a new
driven plate should be fitted.
6 Inspect the clutch shaft splines and these should not
have a lengthwise clearance in excess of .0039 inch and
side clearance of .0118 inch w i t h respect to the driven
plate hub. Ensure that the driven plate slides easily on
the clutch shaft protruding from the rear of the gearbox
differential unit as any plate drag may be the cause of
d i f f i c u l t y in gear selection.
Page 64 of 128

of wear, distorting or unevenness of the surfaces as this
part is very heavily pressed when the vehicle is negotia-
ting a corner. If the clearance to the idle pinions exceeds
.0059 inch the shaft must be renewed.
2 Inspect the ring gear and pinion seat, the side gears.and
the idle pinions for correct meshing. This will be shown
up by white marks on the sides of the gear teeth. Check
that none of the teeth are broken, chipped or exces-
sively worn and if any part is suspect then it must be
renewed not forgetting that the ring gear and pinion
come as a matched pair.
3 Inspect the condition of the ball and roller bearings, the
rollers and balls and working faces must not show signs
of pitting wear or cracking and if any part is suspect then
the race must be renewed.
4 Check that there is not any undue wear on the faces of
the thrust rings. Any slight indentations may be evened
out using a fine oil stone but if the damage is excessive
then new rings or oversize rings must befitted as neces-
sary. Thrust rings are supplied as service spares in the
following thicknesses.
Standard .0394 inch
Oversize .0512-.0591 inch
6:6 Reassembly—differential unit
To reassemble the differential case proceed as follows:
1 Press onto the differential half housing which carries
the ring gear one differential bearing inner race ensuring
that it is pushed fully home onto its seating. Install the
thrust ring and side gear (see FIG 6 : 7).
2 From t h e inside of the case insert the axle shaft com-
plete with pivot and runners that form the slip joint.
Also install the idle pinions and carrier shaft. Position
the ring gear onto the housing half and install the
differential pinion shaft retainer ring.
3 Press the other differential bearing inner race onto its
seating on the left differential housing half and replace
the left axle shaft complete with slip joint.
4 J o i n the t w o case halves together and tighten the
retaining screws and also the retaining screws of the
ring gear to a torque wrench setting of 23.1 Ib ft. Secure
all screws by bending up the lockplates.
5 Press t h e differential bearing outer races into their
seatings in the bearing housings and also f i t the o i l seals.
Also install the bearing housings over the driving shafts
together with the adjuster rings.
6 Install the differential unit assembly into the final drive
housing front half and bolt the rear
half onto it. Tighten
the six mounting nuts to a torque wrench setting of
27.5 Ib ft. Finally place the bearing housings in their
seats and tighten the mounting nuts to a torque wrench
setting of 13 lb ft.
It should be noted that after the gearbox has been over-
hauled the complete differential unit should only be in-
stalled after the drive pinion depth adjustments has been
carried out.
6 : 7 Final drive gear set adjustment
The installation and adjustment of the final drive gear
set requires special care otherwise the unit may have to be
dismantled again for further adjustment. So as to establish
the correct mesh of the t w o gears, their relative position is
accurately set during initial assembly at the factory.
F50071 Refer to FIG 6 :8 where it will be seen that t w o numbers
are stamped on the pinion shaft near to the threaded end,
the upper number is the matching number which should
also appear on the crownwheel. The lower number indi-
cates the positive or negative deviation from the theoretical
distance between the centre line of the ring gear and the
pinion face. It is this number which must be taken into
account when calculating the adjusting shim thickness
which has to be fitted between the rear roller bearing and
the fourth-speed gear on the layshaft.
The formula from which the adjusting shim thickness
can be calculated is as follows:
S=A—(B + C)
Where S=shim thickness.
A= distance between the front bearing inner
race and the centre line of the ring gear.
B = distance of the drive pinion face to the ring
gear centre line.
C = t h e total of the widths of the third-speed
gear bush, third- and fourth-speed hub,
fourth-speed gear bush and rear roller
bearing inner race fitted onto the mainshaft
It should be noted that 'A' is the total of half the diameter
of the differential bearing housing seat which is in actual
fact 41.00 mm, and the distance measured between the
front bearing inner race and the differential bearing housing
seat. The last
dimension will have a minimum manufactu-
ring limit of 150.54 mm. Any deviation from this value
must be determined and considered when determining
the total shim thickness 'S'.
A= 150.54 + 41.00 + a (deviation)
To determine deviation 'a' Fiat tool A.62036 should be
assembled to the gearbox casing as shown in FIG 6 : 9
and to take the reading proceed as follows:
1 Assemble the front ballbearing and its retainer into the
gearbox housing and tighten the retainer bolts.
2 Hold the gearbox housing in the vertical position with
the differential side upwards and insert Fiat tool
A.62036 carefully from above into the bearing bore and
lock it firmly by tightening the knurled nut.
3 Using Fiat dial gauge C.689 which has been previously
zeroed on a surface plate should next be mounted
onto the t o p of Fiat tool A.62036 with its pointer resting
on the lowest position of the differential bearing hous-
ing bore as shown in FIG 6:10. To obtain the lowest
point move the pointer to both sides of the bottom dead
centre position so as to obtain the maximum reading.
The distance ' B ' in the formula for calculating the shim
thickness is designed to have a lower manufacturing limit
of 75 mm. Any deviation ' b ' is stamped on the drive pinion.
Therefore to calculate the value of ' B '
B = 7 5 + b (deviation)
The distance 'C' in the formula for calculating the shim
thickness is designed to have a lower manufacturing limit
FIG 6 : 8 Layshaft w i t h final drive pinion. The arrow
points to the number (14) for correct mating with ring
gear and to the centesimal figure (—10) for accurate
mating position of pinion and gear
Page 99 of 128

FIG 10:5 Section view of right side rear brake assembly
(500 Station Wagon)
FIG 10:6 Sectional view of a self-adjusting device for
automatic brake shoe-to-drum clearance take-up (500
Sedan)
Key to Fig 1 0 : 6 1 Pin 2 Friction washers 3 Load spring
4 Bushing 5 Shoe 6 Self-adjustment slot 7 Stud
2 Make a note of the location of the shoe return springs
and gently ease t h e shoes away from the backplate
(see FIG 10:4)
3 Disconnect the hydraulic line from the rear of t h e
wheel cylinder and also the shoe operating lever return
spring, the pin, washer and clevis from the lever so
releasing the handbrake inner operating cable.
4 Remove the t w o cylinder retaining bolts and lift away
the hydraulic cylinder.
106
Brake shoe linings:
Refer t o Section 10:3.
Brake drums:
Refer to Section 10:3.
Reassembly of rear brakes:
This is the reverse procedure to dismantling. Ensure
that the pull-off springs are correctly fitted to the holes
in the webs of the brake shoes and that the shoes
register in the slotted ends of the pistons and the side
mounting plate.
Carefully retract the position of the brake shoes and
ease t h e d r u m towards the hub ensuring that the four
bolt holes line up correctly. Replace the four bolts
together with their spring washers, reconnect the hand
brake cable. Refit road wheel and wheel trim.
10:5 Master cylinder
Operation:
Hydraulic fluid is admitted to the master cylinder
through hole 8 (see FIG 10:7), it seeps through the gap
between the valve carrier ring 17 and the master cylinder
dowel and flows through the valve carrier ring holes 15
so reaching the hydraulic lines, therefore filling the
system w i t h fluid. When the brake pedal is depressed the
plunger is moved forwards by the pushrod 12. This
forward action of the plunger 9 and valve carrier 17 brings
the valve 16 to rest against the valve front face. The
forward movement is continued so causing the valve ring
16 to pass over the compensation hole 5 and cutting off
communication with the fluid reservoirs. From this point
compression of the hydraulic fluid commences.
Hydraulic fluid acting on the front and inner faces of
the valve enables perfect valve sealing even under high
operation pressures. When the pressure reaches the fluid
in the wheel cylinders (see FIG 10:8) , it forces the
plungers 3 apart and through the plungers stems so
operating the brake shoes.
After releasing the brake pedal, the combined action
of the brake shoe and master cylinder plunger return
springs sends the fluid back to the master cylinder and
all parts resume their original position. The connection
between the hydraulic
system and the reservoir is
restored.
As there are no conventional valves fitted in the master
cylinder and the communication orifice between the
system a n d the reservoir is amply dimensioned the
bleeding operation is very straightforward.
Master cylinder removal:
1 Disconnect the stoplight cables from the pressure
operated switch.
2 Using a tapered w o o d plug of suitable size blank t h e
hole in the brake f l u i d reservoir.
3 Screw out the four front and rear cylinder brake fluid
delivery line connections at the master cylinder.
4 Remove the t w o master cylinder retaining nuts and
spring washers and carefully ease the hydraulic
cylinder from the body.