1967 CHEVROLET CAMARO recommended oil
[x] Cancel search: recommended oilPage 180 of 659

FRONT SUSPENSION 3-16
available the following procedure may also be
used (fig. 22-Alternate Method).
1.
Support car on suitable hoist or jack (so control
arms may swing free) and remove the wheel and
tire assembly, shock absorber, and stabilizer link
at control arm.
2.
Place suitable jack stand under the lower control
arm cross shaft.
3.
Follow Steps 2-5 as outlined on previous page.
4.
Turn head of tool screw to partially compress
spring.
5. Remove the three control arm cross shaft attaching
bolts,
washers and nuts.
6. Carefully lower jack stand and if necessary increase
compression on spring and when coil spring is out of
its upper seat, relax tension on spring (fig. 22).
7. By using a pry bar to assist, if necessary, remove
the coil spring from the lower control arm.
8. Installation is the reverse of the above procedure.
Carefully follow instructions for installing spring
tool.
LOWER CONTROL ARM SPHERICAL JOINT
Chevrolet, Chevelle, Comoro and Corvette
Inspection
The lower control arm spherical joint should be re-
placed whenever wear is indicated in the upper joint
inspection.
NOTE: The lower control arm spherical joint
is a loose fit in the assembly when not connected
to the steering knuckle.
Only if inspection of each upper joint indicates them
both to be within limits, inspect each lower joint for ex-
cessive wear as follows:
1.
After reconnecting upper joints to steering knuckles,
support vehicle weight on wheels or wheel hubs.
2.
With outside micrometer or caliper, measure dis-
tance from top of lubrication fitting to bottom of ball
stud, and record the dimensions for each side.
3.
Then support vehicle weight at outer end of each
lower control arm, so that wheels or wheel hubs are
free,
then repeat Step 2.
4.
If the difference in dimensions on either side is
greater than 1/16" (.0625"), the joint is excessively
worn and both lower joints should be replaced.
If inspection of lower spherical joints does not indicate
excessive wear, inspect further as follows:
5.
On Chevrolet Only--Examine lubrication hole in each
joint assembly after cleaning out hole. Look for evi-
dence of the liner partially or fully blocking lubrica-
tion opening. Such evidence indicates that liner is
disintegrating and that both lower spherical joints
should be replaced.
Another indication of lower spherical joint excessive
wear is indicated when difficulty is experienced when
lubricating the joint. If the liner has worn to the point
where the lubrication grooves in the liner have worn
away, then abnormal pressure is required to force lubri-
cant through the joint. This is another reason to recom-
mend replacement of both lower joints.
If the above inspections do not indicate any reason for
spherical joint replacements, test the torque tightness of
Fig. 27 - Removing Lower Ball Joint - Chevelle
&
Camaro
the lower ball stud in the knuckle on each side as follows:
1.
Wire-brush off nut and cotter pin attaching spherical
joint ball stud to steering knuckle and examine for
evidence of looseness of stud in knuckle.
2.
If no evidence of looseness, remove cotter pin and
with prick punch or equivalent, mark nut stud and
knuckle to identify relative location.
3.
Tighten nut as installed and observe torque reading.
If less than 45 lbs. ft., stud may have been loose in
steering knuckle and replacement of both lower
spherical joints may be recommended.
4.
Check to see if torque of 60-94 lbs. ft. can be ob-
tained without bottoming stud or ball joint against
knuckle. If bottoming occurs, replace ball joint or
steering knuckle.
Chevrolet and Corvette
Removal
1.
Support lower control arm at outer end on floor jack,
with hoist or jack pad clear of lower ball stud nut.
2.
Remove upper and lower ball stud nuts, free ball
studs from steering knuckle and wire knuckle and
brake drum assembly up to fender skirt to preclude
interference while performing next step.
3.
Being careful not to enlarge the holes in control arm,
cut off rivets.
Installation
1.
Install new joint against underside of control arm and
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 249 of 659
BRAKES 5-16
6Y. Adjust clutch pedal travel as outlined in
Section 7.
SHOES AND LININGS
Organic Linings
NOTE:
If brake drums are worn severely, it
may be necessary to retract the adjusting screw.
To gain access to the adjusting screw star
wheel, knock out the lanced area in the web of
the brake drum using a chisel or similar tool.
Release the actuator from the star wheel by
lifting with a small screw driver and back off
the star wheel with a second screw driver (press
down on the handle to retract shoes).
CAUTION: After knocking out the metal, be
sure to remove it from the inside of the drum .
and clean all metal from the brake compartment.
A new hole cover must be installed when drum
is reinstalled.
Removal
1.
Raise the vehicle and plate on jack stands.
2.
Loosen check nuts at parking brake equalizer suffi-
ciently to remove, all tension from brake cable.
3.
Remove brake drums.
NOTE:
Since there are wheel cylinder piston
stops to prevent pistons from leaving cylinders,
it is not necessary to install wheel cylinder
clamps when brake shoes are removed; however,
brake pedal must not be depressed while drums
are removed.
4.
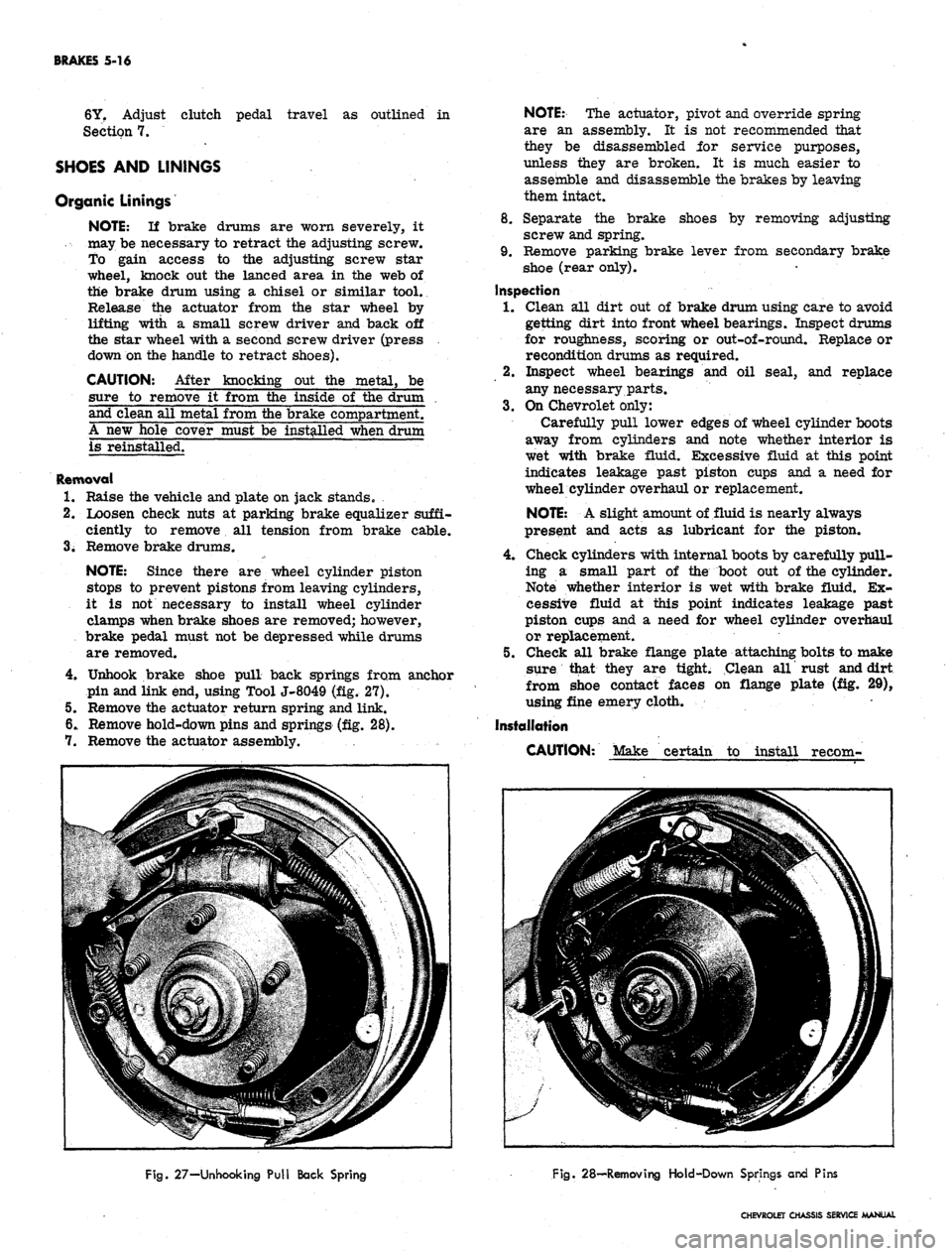
Unhook brake shoe pull back springs from anchor
pin and link end, using Tool J-8049 (fig. 27).
5. Remove the actuator return spring and link.
6. Remove hold-down pins and springs (fig. 28).
7. Remove the actuator assembly.
NOTE:
The actuator, pivot and override spring
are an assembly. It is not recommended that
they be disassembled for service purposes,
unless they are broken. It is much easier to
assemble and disassemble the brakes by leaving
them intact.
8. Separate the brake shoes by removing adjusting
screw and spring.
9. Remove parking brake lever from secondary brake
shoe (rear only).
Inspection
1.
Clean all dirt out of brake drum using care to avoid
getting dirt into front wheel bearings. Inspect drums
for roughness, scoring or out-of-round. Replace or
recondition drums as required.
2.
Inspect wheel bearings and oil seal, and replace
any necessary parts.
3.
On Chevrolet only:
Carefully pull lower edges of wheel cylinder boots
away from cylinders and note whether interior is
wet with brake fluid. Excessive fluid at this point
indicates leakage past piston cups and a need for
wheel cylinder overhaul or replacement.
NOTE:
A slight amount of fluid is nearly always
present and acts as lubricant for the piston.
4.
Check cylinders with internal boots by carefully pull-
ing a small part of the boot out of the cylinder.
Note whether interior is wet with brake fluid. Ex-
cessive fluid at this point indicates leakage past
piston cups and a need for wheel cylinder overhaul
or replacement.
5. Check all brake flange plate attaching bolts to make
sure that they are tight. Clean all rust and dirt
from shoe contact faces on flange plate (fig. 29),
using fine emery cloth.
Installation
CAUTION: Make certain to install recom-
Fig.
27-Unhooking Pull Back Spring
Fig.
28—Removing Hold-Down Springs and Pins
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 250 of 659

BRAKES 5-17
mended shoe and lining assemblies. Otherwise,
serious fade or failure may occur.
1.
Inspect new linings and make certain there are no
nicks or burrs on bonding material on shoe edge
where contact is made with brake flange plate or
on any of the contact surfaces.
NOTE: Keep hands clean while handling brake
shoes.
Do not permit oil or grease to come in
contact with linings.
2.
If working on rear brakes, lubricate parking brake
cable.
3.
On rear brakes only, lubricate fulcrum end of park-
ing brake lever and the bolt with brake lube, then
attach lever to secondary shoe with bolt, spring
washer, lock washer and nut. Make sure that lever
moves freely.
4.
Before installation make certain the adjusting screw
is clean and lubricated properly.
NOTE: Loose adjustment may occur from an
adjusting screw that is not properly operating.
If the lubrication in the adjusting screw as-
sembly is contaminated or destroyed, the ad-
justing screw should be thoroughly cleaned and
lubricated.
5.
Connect brake shoes together with adjusting screw
spring, then place adjusting screw, socket and nut
in position.
CAUTION: Make sure the proper adjusting
screw is used ("L" for left side of vehicle,
"R"
for right side of vehicle). The star wheel
should only be installed with the star wheel
nearest to the secondary shoe and the adjusting
screw spring inserted to prevent interference
with the star wheel.
6. On rear wheels connect parking brake cable to lever.
7.
Secure the primary brake shoe (short lining—faces
forward) first with the hold-down pin and spring
using a pair of pliers. Engages shoes with the wheel
cylinder connecting links.
8. Install and secure the actuator assembly and second-
ary brake shoe with the hold-down pin and spring
using a pair of needle nose pliers. On rear wheels
position parking brake strut and strut spring.
9. Install guide plate over anchor pin.
10.
Install the wire link.
NOTE: Do not hook the wire link over the
anchor pin stud with the regular spring hook
tool. This may damage the cylinder boot seals.
Fasten the wire link to the actuator assembly ;
first, then place over the anchor pin stud by
hand while holding the adjuster assembly in the
full down position.
11.
Install actuator return spring.
NOTE: Do not pry actuator lever to install re-
turn spring. Ease it in place using the end of a
screw driver or other suitable flat tool.
12.
If old brake pull back (return) springs are nicked,
distorted or if strength is doubtful, install new
springs.
13.
Hook springs in shoes using Tool J-8049 by in-
stalling the primary spring from the shoe over the
anchor pin and then spring from secondary shoe
over the wire link end.
14.
Pry shoes away from backing plate and lubricate
shoe contact surfaces with a thin coating of brake
lube (fig. 29).
CAUTION:
facings.
Be careful to keep lubricant off
Fig.
29—Backing Plate Contact Surfaces
15.
After completing installation, make certain the actu-
ator lever functions easily by hand operating the
self-adjusting feature (fig. 30).
1.6. Follow the above procedure for all wheels.
17.
Adjust the service brakes and parking brake as
outlined under "Maintenance and Adjustments" in
this section.
Metallic Linings
Metallic brake linings which use special heat resistant
brake springs are available as an option. Service opera-
tions are the same as for standard brakes; however,
when new linings are installed, the linings should be
seated as described below.
NOTE: Brake shoes with metallic linings re-
quire specially finished brake drums (honed to a
20 micro-inch finish). Metallic linings are not
recommended for service replacement on ve-
hicles with standard brake drums that have not
been honed to specified finish.
Seating Metallic Linings
After the brakes have been adjusted, the following
recommended "lining seating" is as follows:
1.
Make six to eight stops from 30 MPH with moderate
pedal pressure to aid in seating and to mbdulate
any tendency to dive.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 255 of 659

BRAKES 5-22
2.
Replace ail push rods and pull back springs.
3.
Connect hose or line to wheel cylinder.
NOTE:
If replacing front wheel cylinder, con-
nect hose and inspect installation as outlined in
"Hydraulic Brake Hose Replacement".
4.
Install drum and wheel.
5. Bleed brakes as outlined in this section.
ANCHOR PIN
Front Wheel
1.
Raise front of vehicle and place on jack stands.
2.
Remove wheel and drum as outlined in this section.
3.
Remove brake shoe pull back springs, link and guide
plate.
4.
Disengage anchor pin lock and remove anchor pin by
turning counterclockwise.
5. Place new lock plate on anchor pin and pass pin
through the hole in flange plate and screw into tapped
hole in spindle support.
6. Torque pin to 130 lb. ft. and lock by peening over
washer tabs.
7. Install brake shoe guide plate, link and pull back
springs.
8. Adjust brakes, install drum and wheel as outlined
in this section. Test brake operation.
Rear Wheel
Two type anchor pins are used in production for the
rear wheels. The riveted type is not serviced and if
failure or damage should occur to either the anchor
pin or flange plate, both parts will have to be replaced
and the threaded type anchor pin used.
Threaded Type
1.
Raise rear of vehicle and place on jack stands,
2.
Remove wheel and drum as outlined in this section.
3.
Remove brake shoe pull back springs, link and guide
plate.
4.
Remove anchor pin retaining nut and washer and
remove pin from flange plate.
5. Position anchor pin to flange plate, install lock
washer and nut, and torque pin to 80 lb. ft.
6. Install brake shoe guide plate, link and pull back
springs.
7. Adjust brakes and install drum and wheel as outlined
in this section.
8. Test brake operation.
BRAKE DRUMS
Front brake drums are the demountable type; that is,
they can be removed without removing the hub. Rear
brake drums are demountable and may be removed
wihtout removing the axle shaft.
A lanced "knock out" area (fig. 34) is provided in
the web of the brake drum for servicing purposes in
the event retracting of the brake shoes is required in
order to remove the drum.
A small screw driver or hooked wire may be inserted
to disengage the automatic adjuster actuating lever so
the star wheel may be turned.
Removal
1.
Raise vehicle and place on jack stand.
2.
Remove wheel and tire assembly, back off brake
adjustment and remove drum.
Inspection and Reconditioning
Whenever brake drums are removed they should be
thoroughly cleaned and inspected for cracks, scores,
deep grooves, and out-of-round. Any of these conditions
must be corrected since they can impair the efficiency
of brake operation and also can cause premature failure
of other parts.
Smooth up any slight scores by polishing with fine
emery cloth. Heavy or extensive scoring will cause
excessive brake lining wear and it will probably be
necessary to rebore in order to true up the braking
surface.
An out-of-round drum makes accurate brake shoe
adjustment impossible and is likely to cause excessive
wear of other parts of brake mechanism due to its
eccentric action.
A drum that is more than .008" out-of-round on the
diameter is unfit for service and should be rebored.
Out-of^round, as well as taper and wear can be ac-
curately measured with an inside micrometer fitted
with proper extension rods.
If drum is to be rebored for use with standard size
brake facings which are worn very little, only enough
metal should be removed to obtain a true smooth braking
surface.
If drum has to be rebored more than .020" over the
standard diameter, it should be rebored to .060" diameter
oversize and the brake facing should be replaced with
.030"
oversize facings.
A brake drum must not be rebored more than .060"
over the maximum standard diameter, since removal
of more metal will effect, dissipation of heat and may
cause distortion of drum. Chevrolet brake facing is
not furnished larger than .030" oversize and this will
not work efficiently in drums bored more than .060"
oversize.
Brake drums may be refinished either by turning or
grinding. Best brake performance is obtained by turning
drums with a very fine feed. To insure maximum lining
life,
the refinished braking surface must be smooth and
free from chatter or tool marks, and run-out must not
exceed .005" total indicator reading.
Cleaning
New brake drums in parts stock are given a light.
coating of rust proofing oil to prevent the formation of
rust on the critical braking surfaces during the time
that the drums are in storage.
This rust proofing oil must be carefully removed
before the drum is placed in service to prevent any
of this oil from getting on the brake shoe facings, which
might cause an extreme brake grab condition.
It is recommended that a suitable volatile, non-toxic,
greaseless type solvent be used to clean the oil from the
braking surface of the new brake drums before they are
•placed in service to insure the cleanest possible surface.
Gasoline or kerosene should not be used as there is
danger that a portion of the diluated oil substance may
be left on the braking surface that may later cause
difficulty.
Installation
1.
Make brake adjustment as outlined in this section.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 273 of 659

ENGINE
6-8
Check
and
Adjust Ignition Timing
(Fig. 13)
1.
Disconnect
the
distributor spark advance hose
and
plug
the
vacuum source opening.
2.
Start engine
and run at
idle speed
(see
tune
up
chart).
3.
Aim
timing light
at
timing
tab.
NOTE:
- The
markings
on the
tabs
are in 2°
increments
(the
greatest number
of
markings
on
the
"A"
side
of the "O"). the "O"
markings
is
TDC
of
#1 cylinder
and all
BTDC settings fall
on
the
"A"
(advance) side
of "O".
4.
Adjust
the
timing
by
loosening
the
distributor clamp
and
,
rotating
the
distributor body
as
required, then
tighten
the
clamp.
5.
Stop engine
and
remove timing light
and
reconnect
the spark advance hose.
Adjust Idle Speed
and
Mixture
(Fig. 14)
(Except when
equipped with
Air
Injection Reactor System)
1.
As a
preliminary adjustment, turn idle mixture
screws lightly
to
seat
and
back
out 2
turns.
CAUTION:
Do not
turn idle mixture screw
tightly against seat
or
damage
may
result.
2.
With engine running
at
operating temperature (choke
wide open) adjust idle speed screw
to
bring idle
speed
to
specified
rpm
(automatic transmission
in
drive, manual transmission
in
neutral).
3.
Adjust idle mixture screw
to
obtain highest steady
idle speed
(1/4
turn
out
from lean roll).
4.
Repeat Steps
2 and 3 as
needed
for
final adjustment.
5.
Shut down
the
engine, remove gauges
and
install
air
cleaner.
Adjust Idle Speed
and
Mixture
(Fig. 14)
(With
Air
Injection Reactor System)
The recommended adjustment procedure
for Air
Injec-
tion Reactor System equipped engines
is as
follows:
1.
As a
preliminary adjustment, turn idle mixture
screws lightly
to
seat
and
than back
out 3
turns.
CAUTION:
Do not
turn idle mixture screw
tightly against seat
or
damage
may
result.
2.
With engine running
at
operating temperature, choke
wide open,
and
parking brake applied, adjust idle
specified idle speed (automatic
"drive"-manual transmission
in
to
in
screw
transmission
"neutral").
;3.
Adjust idle mixture screw (turn
in) to
"lean roll"
position; then turn screw
out 1/4
turn
(1/4
turn rich
from "lean roll").
The
definition
of
"lean roll" point
is
a 20 to 30 rpm
drop
in
engine speed, obtained
by
leaning
the
idle mixture.
4.
Repeat Steps
2 and 3 as
needed
for
final adjustments.
ADDITIONAL CHECKS
AND
ADJUSTMENTS
Testing Crankcase Ventilation Valve
(Fig. 15) 0
1.
Connect tachometer
and
vacuum gauge
as for
idle
speed
and
mixture adjustment.
2.
Set
parking brake, start engine
and
adjust idle speed
and mixture.
3.
Disconnect ventilation hose
at
valve, block opening
of
valve
and
read engine
rpm
change.
4.
A
change
of
less than
50 rpm
indicates
a
plugged
ventilation valve
-
replace
the
valve.
Cylinder Balance Test
(Fig. 16)
It
is
often difficult
to
locate
a
weak cylinder.
A com-
pression test,
for
example, will
not
locate
a
leaky intake
manifold,
a
valve
not
opening properly
due to a
worn
camshaft,
or a
defective spark plug.
With
the
cylinder balance test,
the
power output
of one
cylinder
may be
checked against another, using
a set of
grounding leads. When
the
power output
of
each cylinder
is
not
equal,
the
engine will lose power
and run
roughly.
Perform
a
cylinder balance test
as
follows:
1.
Connect
the
tachometer
and
vacuum gauge.
2.
Start engine
and run at 1500 rpm.
3.
Ground large clip
of
grounding leads
and
connect
in-
dividual leads
to all
spark plugs except
the
pair being
tested.
Divide
the
firing order
in
half
and
arrange
one
half
over
the
other.
The
cylinders
to be
tested together
ap-
pear
one
over
the
other.
L4 Firing Order
V8 Firing Order
1-8-4-3-6-5-7-2
1-6, 8-5, 4-7, 3-2
1-3-4-2
= 1-3
4-2
L6 Firing Order
1-5-3-6-2-4
=
=
1-4. 3-2
1-5-3
6-2-4
1-6, 5-2, 3-4
1-8-4-3
6-5-7-2
4.
Operate engine
on
each pair
of
cylinders
in
turn
and
note engine
rpm and
manifold vacuum
for
each pair.
A variation
of
more than
1
inch
of
vacuum
or 40 rpm
between pairs
of
cylinders being tested indicates that
the cylinders
are off
balance.
Battery
The battery should
be
checked with special testing
equipment
and to the
equipment manufacturers specifica-
tions.
See
Section 6Y
for
complete information
on
battery
tests.
Ignition
The following additional ignition checks
may be
made
with
any of
several pieces
of
equipment available
for un-
covering
the
source
of
engine difficulties.
The
specific
operating instructions
of the
equipment manufacturer
should
be
followed:
Cranking voltage
Ignition switch
Distributor resistance
Secondary resistance
Ignition output
and
secondary leakage
Cranking Voltage
(Fig. 17)
1.
Disconnect coil primary lead
at the
coil negative
terminal
to
prevent engine from firing during
cranking.
2.
Connect voltmeter between primary terminal
of coi|
(resistance wire side)
and
ground.
3.
Operate starting motor.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 281 of 659

ENGINE 6-16
5.
Adjust ignition timing and carburetor idle speed and
mixture.
VALVE STEM OIL SEAL AND/OR VALVE SPRING
Replacement
1.
Remove rocker arm cover as outlined.
2.
Remove spark plug, rocker arm and push rod on the
cylinder(s) to be serviced.
3.
Apply compressed air to the spark plug hole to hold
the valves in place.
NOTE: A tool to apply air to the cylinder is
available through local jobbers or may be manu-
factured. In manufacturing this Tool a AC-46N
Spark Plug or its equivalent is recommended.
This will make the Tool universal for all
Chevrolet engines. Chisel the spark plug as
shown, then drive the porcelain out of the plug
by tapping the center electrode against a hard
block. Using a 3/8" pipe tap, cut threads in the
remaining portion of the spark ^>lug and assem-
ble as shown (fig. 3L).
4.
Using Tool J-5892 to compress the valve spring, re-
move the valve locks, valve cap, valve shield and
valve spring and damper (fig. 4L).
5.
Remove the valve stem oil seal.
6. To replace, set the valve spring and damper, valve
shield and valve cap in place. The close coiled end
of the spring is installed against the cylinder head.
Compress the spring with
Too^
J-5892 and install oil
seal in the lower groove of the stem, making sure the
seal'is flat and not twisted.
NOTE: A light coat of oil on the seal will help
prevent twisting.
7.
Install the valve locks and release the compressor
tool, making sure the locks seat properly in the
upper groove of the valve stem.
NOTE: Grease may be used to hold the locks
in place while releasing the compressor tool.
8. Install spark plug, using a new gasket, and torque to
specifications.
9. Install and adjust valve mechanism as outlined.
CYLINDER HEAD ASSEMBLY
Removal
1.
Remove manifold assembly as. outlined.
2.
Remove valve mechanism as outlined.
3.
Drain cooling system (block).
4.
Remove fuel and vacuum line from retaining clip at
water outlet then disconnect wires from temperature
sending units.
5.
Disconnect upper radiator hose at water outlet hous-
ing and battery ground strap at cylinder head.
6. Remove coil (L6 engines only).
7.
Remove cylinder head bolts, cylinder head and gas-
ket. Place cylinder head on two blocks of wood to
prevent damage.
Installation
CAUTION: The gasket surfaces on both the
head and the block must be clean of any foreign
matter and free of nicks or heavy scratches.
Cylinder bolt threads in the block and threads
on the cylinder head bolt must be cleaned. (Dirt
will affect bolt torque.) Do not use gasket sealer
on composition steel asbestos gasket.
Fig. 3L -
AIF
Adapter Tool
1.
Place the gasket in position over the dowel pins with
the bead up.
2.
Carefully guide cylinder head into place over dowel
pins and gasket.
3.
Coat threads of cylinder head bolts with sealing com-
pound and install finger tight.
4.
Tighten cylinder head bolts a little at a time in the
sequence shown on the torque sequence chart until
the specified torque is reached.
5.
Install coil (if removed).
6. Connect upper radiator hose and engine ground strap.
7.
Connect temperature sending unit wires and install
fuel and vacuum lines in clip at water outlet.
8. Fill cooling system.
•
9. Install manifold assembly as outlined.
10.
Install and adjust valve mechanism as outlined.
Fig.
4L
- Compressing Valve Spring
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 294 of 659

ENGINE 6-29
an extent that the return spring can no longer push
the plunger back up to working position. Probable
causes are:
a. Excessive varnish or carbon deposit causing ab-
normal stickiness.
b.
(Sailing or "pick-up" between plunger and bore of
lifter body, usually caused by an abrasive piece of
dirt or metal wedging between plunger and lifter
body.
2.
Moderate Rapping Noise--Probable causes are:
a. Excessively high leakdown rate.
b.
Leaky check valve seat.
c. Improper adjustment.
3.
General Noise Throughout the Valve Train-rThis
will, in almost all cases, be a definite indication of
insufficient oil supply, or improper adjustment.
4.
Intermittent Clicking—Probable causes are:
a. A microscopic piece of dirt momentarily caught
between ball seat and check valve ball.
b.
In rare cases, the ball itself may be out-of-round
or have a flat spot.
c. Improper adjustment.
In most cases where noise exists in one or more lifters
all lifter units should be removed, disassembled, cleaned
in a solvent, reassembled, and reinstalled in the engine.
If dirt, corrosion, carbon, etc. is shown to exist in one
unit, it more than likely exists in all the units, thus it
would only be a matter of time before all lifters caused
trouble.
Removal
1.
Remove intake manifold as outlined.
2.
Remove valve mechanism as outlined.
3.
Remove valve lifters.
NOTE: Place valve lifters in a rack so they
may be reinstalled in the same location.
Installation
1.
Install valve lifters.
NOTE: Whenever new valve lifters are being
installed coat foot of valve lifters with Molykote
or its equivalent.
2.
Install intake manifold as outlined.
3.
Install and adjust valve mechanism as outlined.
VALVE STEM OIL SEAL AND/OR VALVE SPRING
Replacement
1.
Remove rocker arm cover(s) as outlined.
2.
Remove spark plug, rocker arm and push rod on the
cylinders to be serviced.
3.
Apply compressed air to the spark plug hole to hold
tl*e valves in place.
NOTE: A tool to apply air to the cylinder is
available through local jobbers or may be manu-
factured. In manufacturing this Tool a AC-46N
Spark Plug or its equivalent is recommended.
This will make the Tool universal for all
Chevrolet engines. Chisel the spark plug as
shown, then drive the porcelain out of the plug
by tapping the center electrode against a hard
block. Using a 3/8" pipe tap, cut threads in the
remaining portion of the spark plug and assem-
ble as shown (fig. 6V).
Fig.
6V - Air Adapter Tool
4.
Using Tool J-5892, to compress the valve spring, re-
move the valve locks, valve cap, and valve spring and
damper (fig. 7V).
5.
Remove valve stem oil seal.
6. Remove as follows:
283, 327 and 350 eu. in.
Engines
a. To replace, set the valve spring and damper,
valve shield and valve cap in place. The close
coiled end of the spring is installed against the
cylinder head.
b.
Compress the spring with Tool J-5892 and install
oil seal in the lower groove of the stem, making
sure the seal is flat and not twisted.
NOTE: A light coat of oil on the seal will help
prevent twisting.
Fig.
7V - Compressing Valve Spring
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 344 of 659

MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
ENGINE-ELECTRICAL 6Y-19
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE
BREAKER POINT SYSTEM
The distributor breaker points and spark plugs are the
only ignition system components that require periodic
service. The remainder of the ignition system requires
only periodic inspection to check operation of the units,
tightness of the electrical connections, and condition of
the wiring. When checking the coil, test with a reputable
tester.
Breaker type distributors are equipped with cam lubri-
cator and should have the wick replaced at the same time
contact point set is replaced. It is not necessary to
lubricate the breaker cam when using a cam lubricator.
Do not attempt to lubricate the wick - Replace when
necessary. When installing a new wick, adjust its posi-
tion so the end of the wick just touches the lobe of the
breaker cam.
Distributor shaft lubrication is accomplished by a
reservoir of lube around the mainshaft in the distributor
body.
BREAKERLESS SYSTEM
Since there are no moving parts in the ignition pulse
amplifier unit mounted forward of the radiator bulkhead,
and the distributor shaft and bushings have permanent
type lubrication, no periodic maintenance is therefore
required for the breakerless ignition system. The dis-
tributor lower bushing is lubricated by engine oil through
a splash hole in the distributor housing, and a housing
cavity next to the upper bushing contains a supply of
lubricant which will last between overhaul periods. At
time of overhaul, the upper bushing may be lubricated
by removing the plastic seal and then adding SAE 20 oil
to the packing in the cavity. A new plastic seal will be
required since the old one will be damaged during
removal.
Tachometer readings for test purposes can be made on
the primary circuit of the breakerless ignition system in
the same manner as on the conventional ignition system,
however before attempting to connect a test tachometer
into the primary circuit check with your instrument
supplier to insure that satisfactory readings can be
obtained and the breakerless system will not be damaged
by the tachometer that is to be used,
IGNITION COIL CHECK (BREAKERLESS)
The ignition coil primary can be checked for an open
PULSE
AMPLIFIER
IGN. SWITCH WIRE
"("IGN" TERMINAL)
-E3 IJU
12
WHITE-
-20 BLACKf' • 12 WHITE-
Fig.
3i—
Breakerless Ignition System
condition by connecting an ohmmeter across the two
primary terminals with the battery disconnected. Pri-
mary resistance at 75
°F.
should be between .35 and .55
ohm. An infinite reading indicates the primary is open.
For the engine to run but miss at times, the primary
open may be of the intermittent type.
The coil secondary can be checked for an open by con-
necting an ohmmeter from the high tension center tower
to either primary terminal. To obtain a reliable reading,
a scale on the ohmmeter having the 20,000 ohm value
within, or nearly within, the middle third of the scale
should be used. Secondary resistance at 75°F. should be
between
8,000
and 12,500 ohms. If the reading is infinite,
the coil secondary winding is open.
A number of different types of coil testers are avail-
able from various test equipment manufacturers. When
using these testers, follow the procedure recommended
by the tester manufacturer.
tester will properly
NOTE:
Make sure the
check this special coil.
SPARK PLUGS
Should be removed, inspected cleaned and regapped at
tune-up. Defective plugs should be replaced, see Servic-
ing of Units Off the Vehicle.
SERVICE OPERATIONS
DISTRIBUTOR CONTACT POINTS
CLEANING
Dirty contact points should be dressed with a few
strokes of a clean, fine-cut contact file. The file should
not be used for other metals and should not be allowed to
become greasy or dirty. Never use emery cloth to clean
contact points. Contact surfaces, after considerable use,
may not appear bright and smooth, but this is not neces-
sarily an indication that they are not functioning satis-
factorily. Do not attempt to remove all roughness nor
dress the point surfaces down smooth; merely remove
scale or dirt.
Badly burned or pitted contact points should be re-
placed and the cause of trouble determined so it can be
eliminated. High resistance or loose connections in the
condenser circuit, oil or foreign materials on the contact
surfaces, improper point adjustment or high voltages may
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL