1959 FIAT 500 oil filter
[x] Cancel search: oil filterPage 2 of 128

CHAPTER 1
THE ENGINE
1 :1
1 :2
1 :3
1 :4
1 :5
1 :6
1 :7
1 :8
1:9
1 :10
1 :11Description
Engine removal (sedan—all versions)
Engine removal (station wagon)
Engine disassembly (sedan—all versions)
Engine disassembly (station wagon)
Cylinder head removal, servicing and
replacement
Timing gear overhaul
Crankcase and cylinders
Piston assembly
Connecting rods
Crankshaft and main bearings
1 :1 Description
The 'New 500' two-cylinder aircooled engine operates
on the four-stroke 'Otto Cycle' and is fitted directly to
the transmission unit which incorporates the rear drive
assembly as shown in FIG 1 :1 and FIG 1 :2.
With the power unit fitted at the rear several advantages
are obtained including better load distribution to the
wheels when the vehicle is loaded, elimination of propeller
shaft reducing the size of centre tunnel and better use of
available space.
The cylinder block comprises t w o cast iron cylinder
barrels w i t h cooling fins. The bottom of the cylinders fit
into machined seats in the aluminium crankcase.
The aluminium crankcase carries eight studs on which
are located the t w o cylinder barrels w i t h the aluminium
cylinder head on the top.
A two bush crankshaft of special cast iron is fitted into
the lower half of the crankcase. The crankshaft is
F5009 provided with a counterweight and is hollow to allow for
lubrication.
The steel connecting rods have thin wall bearing halves
on the big-end, and bronze bushes in the small-end. The
offset piston pin is of steel and retained in the piston by
two circlips.
Light alloy pistons are used and are of the taper-oval-
shaped type with a maximum diameter at the base of the
skirt, along an axis perpendicular to the piston pin. Pistons
are fitted with four rings as follows, one compression at
the top, two standard oil scraper rings and one side slotted
oil scraper ring.
The one-piece aluminium cylinder head is finned to
provide a larger cooling surface and carries the inlet and
exhaust manifolds.
The inlet passages merge into a single centralized
flange onto which is mounted the carburetter. The exhaust
passages run almost parallel to the axis of the engine. 1 :12
1 :13
1 :14
1 :15
1 :16
1 :17
1 :18
1 :19
1 :20
1 :21
1 :22Flywheel and starter ring gear
The oil pump
Lubrication, oil filter, relief valve
Valve timing
Valve stem to rocker clearance
Engine assembly (sedan—all versions)
Engine assembly (station wagon)
Power plant mounting
Adjustment of generator and fan belt drive
Modifications
Fault diagnosis
Page 3 of 128

FIG 1:1 Left side view of the power plant to suit
500 Sedan
10
FIG 1:2 Right side rear three-quarter view of the power plant for 500 Station Wagon Mounted on the top of the cylinder head is the overhead
valve rocker mechanism that is operated by a chain driven
camshaft through tappets and vertical pushrods.
The carburetter is of the downdraft type fitted with a
starting device that is controlled by a lever on the central
floor tunnel. A pleated paper element air cleaner and
silencer is fitted to the carburetter air intake. A mechanical
diaphragm type fuel pump operated from the camshaft by
a pushrod, supplies petrol to the carburetter from a fuel
tank located at the front of the vehicle.
Engine lubrication is provided by a gear pump driven
from the camshaft and mounted within the timing cover
drawing oil from the engine sump. The oil is cleaned by a
centrifugal filter situated at the rear end of t h e crankshaft
and pressure is controlled by a valve mounted on the
pump body. Crankcase ventilation is provided for through
a rubber hose connected to the top of the rocker cover.
The engine is cooled by air from a centrifugal blower
mounted on the generator shaft and housed in a specially
designed cowling conveying air to and around the engine.
The air temperature is governed by a special thermostat
fitted in the engine cowling.
Page 6 of 128

The interior of the car can be heated by the engine
warmed air being ducted into the front compartment and
controlled by a lever on the heating system tunnel.
Engine ignition is by a battery, ignition coil and distribu-
tor which is driven by a gear on the camshaft. The engine
is started by an electric starter motor which is mounted on
the gearbox casing and is controlled by a lever located
behind the gearchange lever.
The complete power unit is mounted by a spring support
at the centre of the rear b o d y crossmember and by t w o
rubber pads mounted laterally to the gearbox.
1 :2 Engine removal (sedan—all versions)
To remove the engine from the car proceed as follows:
Raise t h e rear of t h e car and place on firmly based
stands placed under suitable brackets on the underside
of the body.
Disconnect the battery positive terminal clamp from the
battery terminal post. Release the clip securing the main
petrol pipe to the tank sender unit and ease t h e pipe
from the unit. Drain the oil from the engine sump into
a suitably sized container.
D i s c o n n e c t t h e rear number plate light wire (see
FIG 1 : 6) . Release t h e engine compartment lid check
strap from its slot and separate the lid from the body by
sliding the hinge apart.
Remove the cables attached to the ignition coil, also
to the generator and the starter motor. Remove the
starter motor control tie rod.
Release the oil pressure
indicator cable, the main petrol pipeline at the pump,
the accelerator and starting device controls.
Remove the t w o hoses of the heating and cooling
system which are the input hose to the blower and the
hose for the car heating system. Release and lift out the
engine apron. Remove the starter motor mounting bolts
and carefully lift away the motor.
Using a garage hydraulic jack with suitable cradle (see
FIG 1 : 7) or a rope sling relieve the engine weight
from its mountings. Remove the nuts securing the
gearbox to the engine and the flywheel protection
apron.
Remove the bolts fixing the elastic support to the cross-
member. Remove the rear crossmember mounting nuts
noting that the engine earth cable is held by one
mounting nut and lift away the crossmember.
Carefully ease t h e engine away from the gearbox
ensuring that there is no strain placed on the clutch
shaft. Lower the engine to the floor taking care that no
weight is allowed on any of the attachments. 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1 :3 Engine removal (station wagon)
To remove the engine from the station wagon proceed
as follows:
1 Raise t h e rear of the vehicle and place on firmly based
stands placed under suitable brackets on the underside
of the body.
2 Disconnect the battery positive terminal clamp from
the battery terminal post. Release the clip securing the
main petrol pipe to the tank sender unit and ease the
pipe from the unit. Drain the oil from the engine sump
into a clean dry container of suitable size.
3 H o l d t h e rear door open and secure using string to stop
it swinging to the closed position. Secure the luggage
compartment floor panel in its upright position.
F50013 4 Remove the cables attached to the ignition coil, also
to the generator and starter motor. Remove the starter
motor control tie rod. Release the o i l pressure indicator
cable, the main petrol pipeline at the pump, the accele-
rator and starting device controls. Disconnect the air
filter housing.
5 Remove the hose connecting the car heating system
to the engine cowling. Disconnect the clip holding the
air pipe to the blower and carefully disconnect the pipe
from the blower cowling. Remove the starter motor
mounting bolts and carefully lift away the motor. FIG 1:5 120.000 engine assembly: cross-section view
through a cylinder
Page 8 of 128

6 Release the ignition distributor support retaining nut
and lift away the distributor together w i t h its support.
7 Remove all the mounting bolts of the engine cooling
cowling and lift away the assembly. Release the t w o
carburetter retaining nuts and carefully remove the
carburetter together with its drip tray.
8 Lift away the valve rocker assembly having first
released the t w o retaining nuts together with the plain
washers and lock washers. Carefully lift out the valve
rocker pushrods noting their relevant positions.
9 Slacken the four central cylinder head cap nuts and
the four conventional nuts in the order, shown in
FIG 1 :44 or 1 :46. Lift the cylinder head from the
barrels. If difficulty is experienced it is essential to use
Fiat tool A.40014 or a similar drilled plate, otherwise
serious damage could be caused if other means are
used (see FIG 1:9).
10 Remove the four pushrod sleeves and the casing
containing the oil ducting to the overhead valve gear.
11 Remove the fuel pump retaining nuts and washers
and lift away the pump. Carefully pull out the pump
control pushrod from the crankcase.
12 Remove the six screws holding the centrifugal oil filter
pulley cover and lift away the cover. Remove the
centrifugal filter mounting flange by unscrewing the
crankshaft central bolt. Also remove the timing cover
containing the oil pump gears and the oil pressure
regulating valve. Note the position of the nuts,
toothed and plain
washers for correct reassembly.
13 Release t h e four camshaft sprocket retaining bolts and
lift away the sprocket and timing chain. Using Fiat
pulley A.46020 or a large universal two-leg puller as
shown in FIG 1 :10 remove the crankshaft sprocket
and its body.
14 Carefully lift out the rocker pushrod tappets making a
note of their location and gently pull out the camshaft
making sure the front bearing bore is not damaged by
the cam lobes or distributor drive gear.
15 Mark the flywheel and crankshaft to ensure correct
reassembly and release the six f l y w h e e l retaining bolts
together w i t h the lockwashers and lift away the fly-
wheel.
16 Using Fiat tool A.60156 on the two central studs, lock
the two cylinder barrels in place as shown in FIG 1 : 1 1.
TOOL A. 40014
FIG 1:9 Tool A.40014 for cylinder head removal
F50015
17 Turn the engine upside down ensuring that no weight
is placed on the studs and remove the oil sump and the
oil suction scoop.
18 Mark the connecting rods and end caps to ensure
correct reassembly and remove the end caps. Place the
engine on its side and remove the cylinder barrels
clamp. Ensure that the studs are clean and carefully
slide off the connecting rod-piston-cylinder assem-
blies from the crankcase.
19 Remove the six screws holding the rear main bearing
housing to the crankcase and lift away the housing.
Remove the six screws holding the front main bearing
housing to the crankcase and lift away the housing.
20 Carefully ease the crankshaft from the crankcase
moving it diagonally to assist withdrawal. FIG 1:11 Cylinder hold-down tool A.601 56 TOOL A.60156 FIG 1 :10 Removing crankshaft sprocket w i t h puller
A.46020
PULLER A.46020
Page 9 of 128

STUD REMOVAL
PULLER 40010
FIG 1 :12 Removal of stud from crankcase by puller
A.40010
FIG 1 :13 Engine without blower cowling and cylinder
head cover.SPACER A N D CONNECTION
FOR ROCKER SHAFT
LUBRICATION TUBE
OILVAPOR
.VENT PIPE
CASINGS FOR PUSHRODS
(AND OIL RETURN
TO CRANKCASE
21 To ensure no damage occurs to the long cylinder
barrel mounting studs these may be removed using
Fiat puller A.40010 or a universal stud removal as
shown in FIG 1 :12.
1 :5 Engine disassembly (station wagon)
To dismantle the engine proceed as follows:
1 Remove the exhaust silencer and manifold by releasing
the four nuts holding the two flanges from the cylinder
head. Also disconnect the two silencer mounting
brackets and lift away the exhaust system (see
FIG 1 : 2).
2 Place the engine on a firm wooden top bench. Release
the clip holding the tappet cover and lift away together
with the drip tray. Disconnect the fuel line and throttle
linkage at the carburetter and carefully lift away the
carburetter together with its insulator joint and gaskets.
3 Remove the generator drive belt by releasing the three
nuts so splitting the semi-pulley. Lift away the drive
belt.
16
FIG 1 :14 Tool A.60084 for valve and valve springremoval
TOOL A . 60084
4 Remove all the bolts securing the air conveyor ducting
to the cylinder head and to the crankcase, carefully
separate the panels and lift away the separate panels
ensuring no damage is caused to the mating faces.
5 Release the ignition distributor retaining bolt and lift
away the distributor.
6 Remove the fuel pump retaining bolts and also the
three fuel pipe retaining clips and lift away the fuel
pump assembly together with the insulator, gaskets
and control rod.
7 Release the t w o valve rocker retaining nuts, note the
order of assembly of washers and ease away the rocker
shaft assembly from the top of the cylinder head.
Carefully lift out the valve rocker pushrods noting
their relevent positions for correct reassembly.
8 Slacken the four cylinder head cap nuts and the four
conventional nuts in the order shown in FIG 1 :46. Lift
the cylinder head away from the barrels. If difficulty is
experienced it is essential to use Fiat tool A.40014 or a
similar drilled plate as shown in FIG 1 :9, otherwise
serious damage could be caused if other means are
used.
9 Remove the four pushrod sleeves and the casing con-
taining the oil ducting to the overhead valve gear.
10 Remove the six screws holding the centrifugal oil filter
pulley cover and lift away the cover. Remove the
centrifugal filter mounting flange by unscrewing the
crankshaft central bolt. Also remove the timing cover
f r o m t h e rear of t h e crankcase. Note carefully the posi-
tion of the nuts, toothed and plain washers for correct
reassembly.
11 Release the four camshaft sprocket retaining bolts
and lift away the sprocket and timing chain. Using
Fiat puller A.46020 or a large universal two-leg puller
as shown in FIG 1 : 1 0 remove the crankshaft
sprocket and its key
12 Carefully lift out the rocker pushrod tappets making a
note of their location and gently pull out the camshaft
making sure that the front bearing bore is not
damaged by the cam lobes.
Page 17 of 128
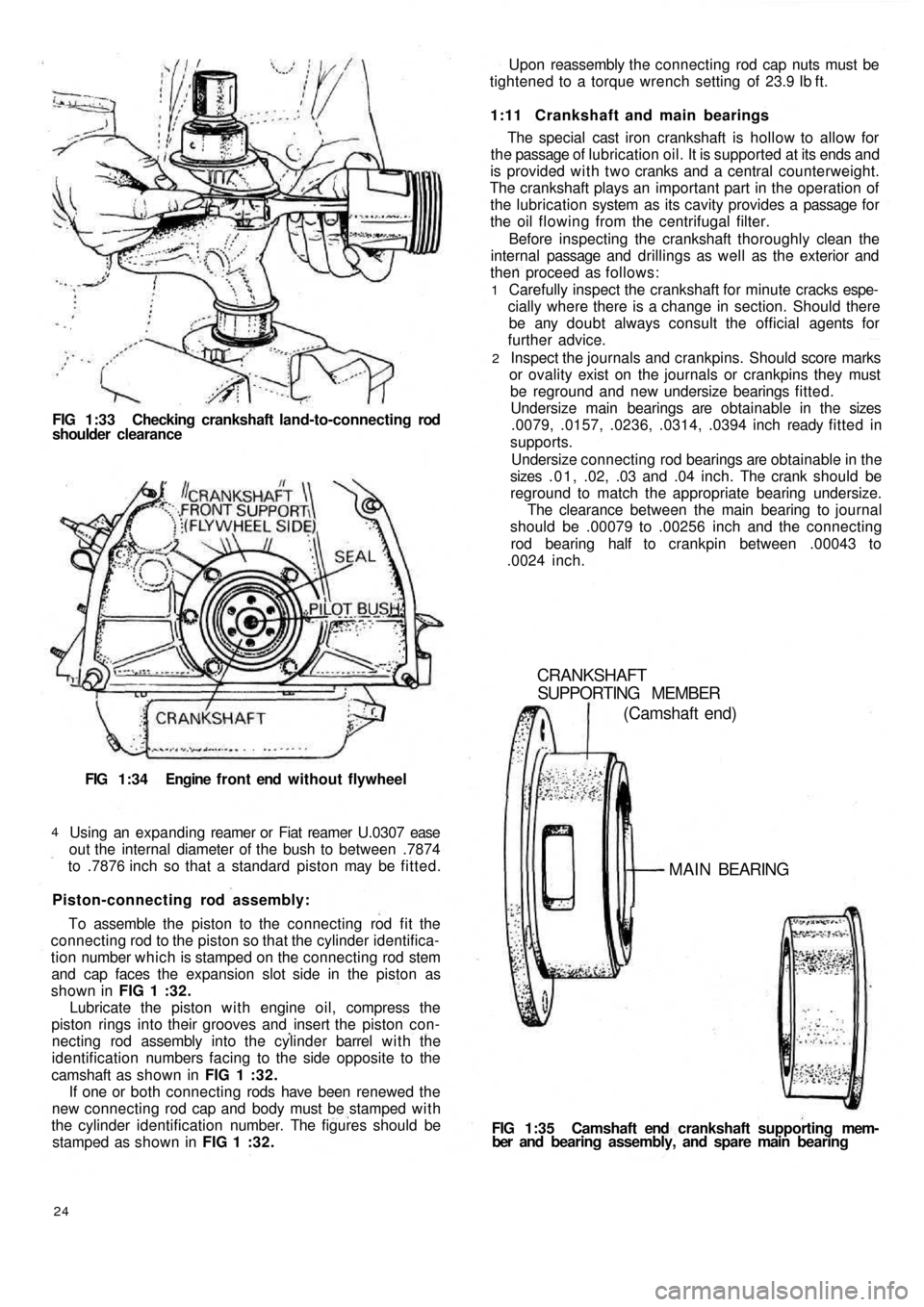
FIG 1:33 Checking crankshaft land-to-connecting rod
shoulder clearance
FIG 1:34 Engine f r o n t end without flywheel
Using an expanding reamer or Fiat reamer U.0307 ease
out the internal diameter of the bush to between .7874
to .7876 inch so that a standard piston may be fitted.
4
Piston-connecting rod assembly:
To assemble the piston to the connecting rod fit the
connecting rod to the piston so that the cylinder identifica-
tion number which is stamped on the connecting rod stem
and cap faces the expansion slot side in the piston as
shown in FIG 1 :32.
Lubricate the piston with engine oil, compress the
piston rings into their grooves and insert the piston con-
necting rod assembly into the cylinder barrel w i t h the
identification numbers facing to the side opposite to the
camshaft as shown in FIG 1 :32.
If one or both connecting rods have been renewed the
new connecting rod cap and body must be stamped w i t h
the cylinder identification number. The figures should be
stamped as shown in FIG 1 :32.
24
FIG 1:35 Camshaft end crankshaft supporting mem-
ber and bearing assembly, and spare main bearing
CRANKSHAFT
SUPPORTING MEMBER
(Camshaft end)
MAIN BEARING
Carefully inspect the crankshaft for minute cracks espe-
cially where there is a change in section. Should there
be any doubt always consult the official agents for
further advice.
Inspect the journals and crankpins. Should score marks
or ovality exist on the journals or crankpins they must
be reground and new undersize bearings fitted.
Undersize main bearings are obtainable in the sizes
.0079, .0157, .0236, .0314, .0394 inch ready fitted in
supports.
Undersize connecting rod bearings are obtainable in the
sizes .01, .02, .03 and .04 inch. The crank should be
reground to match the appropriate bearing undersize.
The clearance between the main bearing to journal
should be .00079 to .00256 inch and the connecting
rod bearing half to crankpin between .00043 to
.0024 inch.
2 1
The special cast iron crankshaft is hollow to allow for
the passage of lubrication oil. It is supported at its ends and
is provided with two cranks and a central counterweight.
The crankshaft plays an important part in the operation of
the lubrication system as its cavity provides a passage for
the oil flowing from the centrifugal filter.
Before inspecting the crankshaft thoroughly clean the
internal passage and drillings as well as the exterior and
then proceed as follows: 1:11 Crankshaft and main bearings Upon reassembly the connecting rod cap nuts must be
tightened to a torque wrench setting of 23.9 Ib ft.
Page 18 of 128

After the crankshaft has been reground it is important
that all traces of swarf are removed by constant washing
and then drying with a non-fluffy rag.
The clearance between the main bearings and journals
must be checked before installing the crankshaft in the
engine. It should also serve as a recheck after the
crankshaft has been reground.
Measure the maximum main bearing internal
diameter and the minimum journal diameter using
accurate measuring equipment. The clearance must not
exceed .0039 inch otherwise the journals must be
reground and undersize bearings fitted.
Undersize bearings w i t h .0394 inch stock on the
internal diameter are also supplied unmounted. They
must be press fitted in the supports, the recommended
interference fit being .00039 to .00197 inch. After
pressing the bearing into the support, a hole is drilled in
the bearing in line with the location dowel hole in the
support. The hole is finished with a suitable expanding
reamer, such as Fiat U.0334, and the dowel pressed i n ,
noting that the hollow dowel fits in the flywheel end
support.
The next stage is to heat the assembly in an oven or
oil bath for a period of one hour at 150°C (302°F).
When the assembly has cooled to room temperature,
the bearing is reamed in a lathe to match the crankshaft
journal size.
3
Crankshaft oil seals:
Two inner spring rubber oil seals are located, one in a
special seat in the timing gear cover and the other in the
flywheel end of the crankshaft support and provide oil
tightness. These seals are shown in FIGS 1 :3 and 1 :34.
Whenever the engine is dismantled for overhaul these
seals should be carefully inspected for correct seating and
that the inner seal surface is not worn and that the contact
area is perfect both on the crankshaft and on the fan and
generator drive pulley hub.
Clutch shaft pilot bushing:
A self-lubricating bronze bush is fitted in the end of the
crankshaft as shown in FIG 1 :34 and provides a bearing
for the clutch shaft. Should the bush be worn use Fiat
puller A.40006/1 /2 to remove the worn bush. A new bush
should be fitted using a suitably sized drift.
1:12 Flywheel and starter ring gear
The flywheel should be inspected for wear at the clutch
driven plate contact area. It should be flat and have a
smooth finish.
The ring gear teeth should be cheeked for damage
which if evident, the ring gear must be replaced. To facili-
tate the fitting of a new ring gear on the flywheel, the new
ring gear should be heated in an oil bath to a temperature
of 80°C (176°F). Using a press gently ease the
expanded
ring gear over the flywheel and press fully home.
1:13 The oil pump
Sedan :
A helical-spur gear type oil pump is driven by the cam-
shaft through a front dog drive coupling. The gears are
F50025 To remove the pump from the engine proceed as
follows:Pump removal and reassembly:
Remove the engine rear central support from the timing
gear casing. Remove the filter cover pulley and lift
away the drive belt.
Release the hollow screw attaching the slinger and the
mounting flange of the filter on the crankshaft. Also
release the nuts fixing the timing gear cover to the
crankcase.
Remove the timing gear cover together with the oil
pump assembly and the pressure relief valve.
Lift out the oil pump suction scoop with the filter
screen attached from the sump.
Reassembly of the pump to the engine is the reverse
procedure to dismantling. 1
2
3
4
5 located in a special housing in the timing gear cover and
held in place by a cover plate. The oil pressure relief valve
is mounted on the drive gear shaft guide.
A pump suction scoop fitted with a filter screen is
secured in the crankcase and connects to a duct in the
timing gear case as s h o w n in FIG 1 :36.
2
4
6Key t o Fig 1 :36
Rocker shaft
Ducts, cylinder head oil drain
Oil pressure relief valve
to centrifugal filter
9
with central oil gallery
12Sump cooling air conveyor
indicator sending unitOil filler with vent valve
Line, oil delivery to rocker shaft
Level indicator rod 31
5
7Gear pump
8 Oil duct
Centrifugal oil fitter
1110
Crankshaft
Oil pump intake screen filter
13 Low oil pressure FIG 1:36 Engine lubrication diagram
Page 19 of 128

FIG 1:37 Lubrication diagram of engine 120.000
Key to Fig 1:37 1 Oil dipstick 2 Oil filler with vent valve 3 Centrifugal oil filter
4 Crankshaft, with central oil gallery 5 Low oil pressure indicator sending unit 6 Oil pressure relief valve 7 Gear pump
8 Camshaft, with central oil gallery 9 Oil suction filter from sump 10 Oil sump drain plug
11 Oil delivery line to rocker shaft 12 Rocker shaft 13 Head cover
Pump dismantling, inspection and reassembly:
Remove the lock ring and withdraw the pressure relief
valve and spring. Remove the oil pump cover plate and
ease o u t t h e gears and shaft.
Thoroughly clean all the parts and blow clean using a
compressed air jet. Inspect the timing gear cover for
cracks or distortion. Check that the inner duct for oil
delivery to the pump is clear of obstruction. Use a
compressed air jet to clean the passage.
Check the oil pump gear teeth for damage or excessive
wear and fit new gears if necessary. The recommended
backlash is .0059 inch w i t h a maximum wear limit
giving a backlash of .0079 inch. Check the clearance
between the gear teeth and the housing walls in the
timing gear cover. The recommended clearance is .0012
to .0035 inch w i t h a maximum of .0047 inch. Ensure
that the drive gear is firmly attached to its shaft. Upon
assembly there is a pinch fit of .0016 to .0031 inch
between the t w o parts.
The driven gear to shaft clearance upon assembly is
.00079 to .00236 inch with a maximum wear limit of
.0039 inch. Also check the width of the drive and driven
gears which when new should be .3937 to .3928 inch
with a minimum width of .3917. In service a spare drive
gear is supplied complete with its shaft.
26 4 3 2 1
Station wagon:
A helical-spur gear type oil pump is driven from the
lower end of the distributor drive spindle which is in mesh
w i t h the camshaft. The gears are located in a special
housing in the bottom of the timing gear housing and are
held in place by a cover plate. The oil pressure relief valve
is located at the driven end of the camshaft.
A pump suction oil filter is fitted in the sump and this
connects to a duct in the timing gear case so supplying oil
to the pump (see FIG 1 : 3 7 ) .
Pump gears removal, inspection and reassembly:
To remove the pump gears from the timing gear cover
proceed as follows:Inspect the filter screen on the end of the pump suction
scoop and remove any obstruction. If the screen is
damaged it must be renewed.
Check that the pump drive dog is a good fit on the cam-
shaft and that the dogs are not badly worn so as to
impair the pump operation.
Reassembly of the pump is the reverse procedure to
dismantling. Ensure that the pump cover piate is
correctly located by means of the dowel on the timing
gear cover. 5
6
7