1959 FIAT 500 cooling
[x] Cancel search: coolingPage 23 of 128

FIG 1 :44 Cylinder head h o ld-down nuts tightening
sequence. 500 Sedan
TIMING CHAIN ENDCYLINDER No. 1 CYLINDER No. 2 FLYWHEEL END
CAMSHAFT
EXPANSION SLOT C/ROD NUMBERROTATION DIRECTION
FIG 1 :45 The correct position of connecting rod-
piston assembly on engine 120.000
30
screws and together with new lockplates tighten to a
torque wrench setting of 23.1 Ib ft. Bend down the
lockplates.
9 Slide the centrifugal oil filter mounting flange, the
oil slinger and the mounting screw together with its
lockplates onto the crankshaft and tighten the screw
to a torque wrench setting of 108.5 Ib ft. Bend down
the lockplate.
10 Assemble the clutch assembly to the flywheel and
using Fiat pilot A.62023 centralize the driven plate
to the pressure plate assembly. Secure the pressure
plate assembly using screws and toothed washers.
11 Fit new oil pan cork gasket, if necessary using a little
grease to hold in position and carefully fit the oil pan
securing with screws, toothed washers and lock-
plates. Bend down the lockplates onto the screw
heads.
12 Fit the oil cooling air conveyor on the oil pan and
secure with screws and toothed washers.
13 Carefully turn the engine over and fit the centrifugal
filter mounting flange rubber seal. Fit the oil filter
cover and secure with screws together with plain and
toothed washers to a torque wrench setting of
5.8
Ib ft.
14 Ensure t h e faces of the cylinder head and cylinders
are free from dirt and oil and carefully slide the
cylinder head gasket over the studs ensuring that it
is the correct way up. Insert the tappets in the same
order to removal together with the sleeves, pushrods,
oil delivery line to the rocker arm shaft and the casing
with its seal ring.
15 Thoroughly inspect the cylinder head to ensure that
it has been correctly reassembled, carefully slide it
over the studs and secure using the four cap nuts
internally and four standard nuts and plain washers
externally. Tighten the nuts in the order as shown in
FIG 1 :44 or 1 :46 to a torque wrench setting of
23.9 Ib ft.
16 Fit the rocker arm shaft and arm assembly together
with the two supports. Tighten the supports using
screws, plain and toothed washers to a torque
wrench setting of 15.2Ibft. Adjust the tappet-to-
rocker clearance as detailed in Section 1 :16.
17 Temporarily plug the intake duct hole to ensure that
no foreign matter finds its way into the engine.
Install the spark plugs having ensured that they are
clean and correctly adjusted.
18 Reassemble the engine cowling and air
exhaust
throttle valve assembly which should be secured on
the top side using t w o nuts, t w o plain washers and
two toothed washers, on the underside with two
screws and t w o toothed washers, and centrally using
one screw and one spring washer.
19 Fit the toothed washers on the end of the spark plug
electrode and tighten the terminals together with the
special rubber boots.
20 Refit the fan, generator and ground cable assembly
and secure the crankcase, also the warmed air intake
shrouding. Finally tighten the generator to fan nuts.
21 Fit both lower exhaust silencer mounting brackets
onto the crankcase but do not tighten fully. Fit the
air conveyor and secure to the engine cowling using
six screws, six toothed washers and one nut together
with a toothed washer. Join together the t w o
Page 38 of 128

Air cleaner—station wagon:
A pleated paper air cleaner element is housed in a
special air intake chamber connected to the front of the
engine air cooling cowling (see FIG 4 : 2) . This chamber
will be seen located towards the rear of t h e power unit
compartment. Remove the retaining wing nut, lift off the
lid and the element can be withdrawn by lifting upwards.
2:10 Blow-by-gases recirculation device
Engine 110 F.000
All the oil vapours and blow-by-gases that are formed
in the engine crankcase are drawn to the cylinder head
cover recess 1 (see FIG 2:18). From here they travel into
the pipe 5 via a breather valve 2 which is firmly attached to
the oil filler cap 3 and the strainer 4 located in the filler
neck. The oil vapours and gases are then d r a w n back into
the duct 9 from the pipe 5 which connects the air cleaner
6 to the carburetter 7. This ensures a complete closed cir-
cuit circulation.
Engine 120.000:
From engine No. 288156 the oil vapours and blow-by-
gases instead of being exhausted to the atmosphere are
conveyed to the air cleaner and from here they are drawn
back into the combustion chambers. To ensure that an
excessive of oil vapour does not pass along the piping
with the blow-by-gases a diaphragm is fitted in the duct
in front of the breather valve 2 (see FIG 2 :18), the dia-
phragm comprising a filter gauze 11 and moveable parti-
tion 10.
It should be noted that the oil vapour strainer 4 (see
FIG 2:18) and the flame trap 8 can easily be removed
from their seating for cleaning or renewal.
2 : 1 1 Fuel tank
The fuel tank is located in the front compartment as
shown in FIG 2:19, it comprises a filler union fitted with a
cap, a fuel reserve supply indicator sender unit and a con-
nection incorporating a filter for the main fuel supply pipes.
To remove the tank proceed as follows:
1 Remove the contents of the front compartment includ-
ing the spare wheel and tool bag.
2 Disconnect the main fuel line at the sender unit and also
disconnect the cable to the fuel reserve supply indicator.
3 Remove the four screws together w i t h the clips that fix
the tank to the body and carefully lift away the fuel tank.
4 Carefully drain the contents of the tank into a clean dry
container of a suitable capacity.
Fuel tank—sedan (110 F.) and station wagon (120):
The fuel tank is arranged in the front compartment as
shown in FIG 2 :20. To remove the fuel tank proceed as
follows:
1 Remove both screws which secure the front ends of the
clamping bands to the dash panel. The screws are
shown by arrows in FIG 2 :20.
Petrol tank cleaning:
The tank must be thoroughly checked for leaks espe-
cially at the joint seams. Should a leak be found it is
F50045
advisable for a garage to attend to this as it is very dange-
rous to apply heat to a petrol tank without first taking strict
precautions and a garage will be in a better position to do
this. To clean the tank interior, remove the drain plug and
spray in a jet of air or petrol so that all sediment and dirt
deposits can be loosened. Then vigorously shake the tank.
Flush the tank w i t h petrol and blow the tank dry. Repeat
this procedure until the tank is clean. Refit the drain plug.
Whilst the petrol tank is away from the car it is advisable
to disconnect the fuel feed pipes at the pump and the
carburetter and ensure that these are clear by using an air
jet to one end of the pipe.
Key t o Fig 2 :20
Note Arrows point to fuel tank clamping band screws vent valve
indicator tank unit1 Fuel tank2 Filler cap with
3 Fuel suction pipe and reserve supply
4 Tank clamping bands
FIG 2:20 Location of the fuel tank in front compart-
ment, 500F, L FIG 2:19 Fuel tank in front compartment. The fuel
reserve supply indicator (red light) glows when fuel
amount in tank is less than .8 to 1.1 Imp galls, or 5 litre FUEL TANK
FUEL LINE TO PUMP
FUEL GAUGE CABLE
Page 44 of 128

indicates the condition inside the combustion chamber
and may be used as a guide to engine tuning.
Before the spark plugs are removed b l o w away any
loose dirt from the plug recesses using a compressed air
jet or tyre pump. Store the plugs in the order of removal
ready for inspection.
Examine the gaskets and if they are about half their
thickness they may be used again otherwise they must be
replaced.
Inspect the electrode end of the plugs and note the
type and colour of the deposit. Normally it should be
powdery and range from b r o w n to a greyish tan in colour.
There will also be slight wear of the electrodes and the
general effect described is one which comes from mixed
periods of high-speed and low-speed driving. Cleaning
and resetting the gap is all that will be necessary.
If the deposits are white or yellowish they indicate long
periods of constant-speed driving or much low-speed
city driving. Again, the treatment is straightforward.
Dry, black, fluffy deposits are usually the result of
running with too rich a mixture. Incomplete combustion
of the petrol air charge may also be a cause and this might
be traced to a defect in the ignition system or excessive
idling.
Overheated sparking plugs have a white blistered look
about the centre electrode and the side electrode may be
badly eroded. This may be caused by poor cooling, wrong
ignition timing or sustained high speeds under heavy load.
To clean the sparking plugs effectively they should be
cleaned using an abrasive blasting machine and tested
under pressure once the electrodes have been reset. File
these until they are clean, bright and the faces parallel and
set the gap to .019 to .023 inch. Do not try to bend the
centre electrode.
Before replacing the plugs use a wire brush to clean the
threads taking care that the electrodes are not touched.
Thoroughly clean the spark plug in petrol, and dry using a
compressed air jet or a tyre pump. If difficulty is found in
screwing the plugs into the cylinder head by hand run a
tap d o w n the threads to clear away any carbon. If a tap is
not available use an old sparking plug with crosscuts d o w nthe threads. Finally tighten the plugs to a torque wrench
setting of 18 to 21 Ib ft.
Sparking plug leads:
The spark plug leads and the lead from the coil to the
distributor cap must be regularly checked for cracking of
the insulation and also correct seating in the distributor
cap and coil top. It is recommended that silicone grease is
smeared around the sockets before the leads are replaced
to ensure no moisture may enter causing difficult starting.
3 : 9 The distributor driving spindle (sedan and
sports engine)
If for any reason, the driving spindle has been removed
from its housing in the crankcase, it must be correctly
meshed w i t h the camshaft gear otherwise it
will be impos-
sible to set the ignition timing.
3:10 Fault diagnosis
(a) Engine w i l l not fire
1 Battery discharged
2 Distributor contact points dirty, pitted or maladjusted
3 Distributor cap dirty, cracked or tracking
4 Carbon brush inside distributor cap not touching rotor
5 Faulty cable or loose connection in low-tension circuit
6 Distributor rotor arm cracked
7 Faulty coil
8 Broken contact breaker spring
9 Contact points stuck open
(b) Engine misfires
1 Check 2, 3, 4, and 7 in (a)
2 Weak contact breaker spring
3 High-tension plug and coil leads cracked or perished
4 Sparking plug(s) loose
5 Sparking plug insulation cracked
6 Sparking plug gap incorrectly set
7 Ignition timing too far advanced
Page 46 of 128

CHAPTER 4
THE COOLING SYSTEM
4:1
4:2
4:3Description
Air outlet thermostat and shutter
Tension adjustment4:4
4:5
4:6Heating system safety device
Maintenance
Fault diagnosis
4:1Description
Sedan:
A l l the Fiat new 500 models covered by this manual are
aircooled by the forced air circulation system from a
centrifugal blower which is mounted on the generator
output shaft. The blower fan has fourteen vanes which are
arranged at various angles to reduce operating noise
during high-speed operation. A specially designed
cowling as shown in FIGS 4 : 1 and 4:2 conveys the air
from the blower and distributes it to the various parts of
the exterior of the engine.
The main components of the air cooling system are as
follows:
1 Air intake compartment at the rear end of t h e body.
2 An elbow pipe for the admittance of incoming air.
3 A flexible air pipe connecting the elbow pipe to the
conveyor.
4 A spiral air conveyor which contains the centrifugal fan.
5 Distribution ducting for directing the air flow to various
parts of the engine.
6 A bellows type thermostat is fitted to the cowling which
operates a butterfly shutter controlling the air outlet
from the engine which ensures control of the engine
operating temperature.
F50053 When the shutter is in the open position, engine heated
air is allowed to disperse to the outside of the engine
cowling. With the shutter in its closed position, the air is
recirculated in the engine cowling so ensuring a quick
engine warm-up period.
It should be noted that by operating the heater lever
which is located on the centre tunnel at the rear seat,
warmed air flowing out from the engine cowling is passed
to the inside of the car for heating and demisting purposes.
Station wagon:
Refer to FIG 4 : 2 where it will be seen that as the engine
is located on its side underneath the luggage compartment
floor the ducting has been modified and the air intakes are
located at the rear of the side windows. A linear blower is
housed in the engine baffles and cowling and is attached
to the drive end of the generator.
The thermostat 'C' (see FIG 4 : 2) is located on the
righthand side of the engine cowling and should start
opening the engine heated air outlet shutter ' D ' when the
temperature of the air rises to 1 7 8 - 1 8 5 ° F and the shutter
should be wide open when the air is at a temperature of
196-207°F.
Page 47 of 128

FIG 4 : 1 Engine cooling air circulation system
Key to Fig4:1 A Engine cooling air intake B Carburetter air suction cleaner C Centrifugal fan and air conveyor
D Oil pan cooling air passage E Warmed air admission hose to car interior F Engine air outlet control shutter, wide open
position (at 178° to 189°F — 81° to 87° C) G Air outlet thermostat
54
Page 48 of 128

55F500
FIG 4 : 2 Cooling air circulation system of engine 120.000
Key to Fig 4 : 2 A Air intakes B Fan C Thermostat, engine air draft shutter control D Shutter enqine air draft
E Carburetter air cleaner F Duct, warmed air-to-car interior G Lever, air-to-car interior valve control
Page 49 of 128
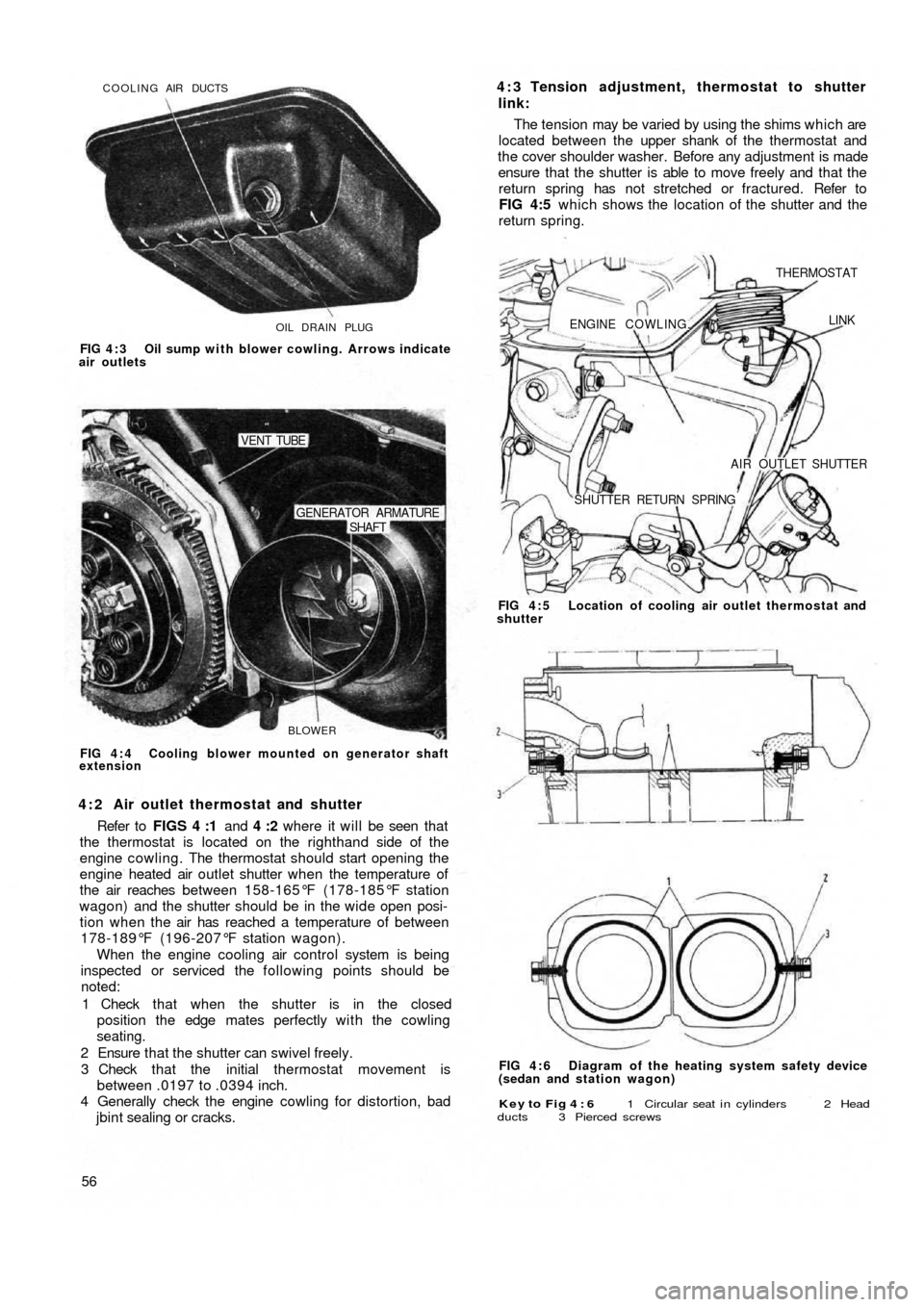
OIL DRAIN PLUG COOLING AIR DUCTS
FIG 4 : 3 Oil sump with blower cowling. Arrows indicate
air outlets
BLOWER
SHAFT GENERATOR ARMATURE
VENT TUBE
FIG 4 : 4 Cooling blower mounted on generator shaft
extension
4 : 2 Air outlet thermostat and shutter
Refer to FIGS 4 :1 and 4 :2 where it will be seen that
the thermostat is located on the righthand side of the
engine cowling. The thermostat should start opening the
engine heated air outlet shutter when the temperature of
the air reaches between 158-165°F (178-185°F station
wagon) and the shutter should be in the wide open posi-
tion when the air has reached a temperature of between
178-189°F (196-207°F station wagon).
When the engine cooling air control system is being
inspected or serviced the following points should be
noted:
1 Check that when the shutter is in the closed
position the edge mates perfectly with the cowling
seating.
2 Ensure that the shutter can swivel freely.
3 Check that the initial thermostat movement is
between .0197 to .0394 inch.
4 Generally check the engine cowling for distortion, bad
jbint sealing or cracks.
56
Key to Fig 4 : 6 1 Circular seat i n cylinders 2 Head
ducts 3 Pierced screws
FIG 4 : 6 Diagram of the heating system safety device
(sedan and station wagon) FIG 4 : 5 Location of cooling air outlet thermostat and
shutter
ENGINE COWLING.
THERMOSTAT
LINK
AIR OUTLET SHUTTER
SHUTTER RETURN SPRING
4 : 3 Tension adjustment, thermostat to shutter
link:
The tension may be varied by using the shims which are
located between the upper shank of the thermostat and
the cover shoulder washer. Before any adjustment is made
ensure that the shutter is able to move freely and that the
return spring has not stretched or fractured. Refer to
FIG 4:5 which shows the location of the shutter and the
return spring.
Page 50 of 128

4 : 4 Heating system safety device
110F series sedan engines and later station wagon
engines incorporate a modification to the cylinder head
designed so that in the event of cylinder head gasket
failure exhaust gases are expelled outside the engine and
not leaked into the heating system.
The safety device comprises a square section circular
seat 1 (see FIG 4 :6) which is formed in the upper face of
the cylinder, a special duct in the cylinder head and a
pierced screw 3 for each cylinder.
The system is so designed that the exhaust gases are
released to the atmosphere from the circular seat in the
cylinder via the duct 2 and the pierced screw 3. It should
be noted that the screw 3 is also used for securing the
conveyor.
4 : 5 Maintenance
Due to the simple design of the air cooling system
maintenance has been kept to an absolute minimum and
should consist of the following checks:1 Inspect all the air conveyor system joints and ensure
that all the joint nuts and bolts are tight and that there
is no distortion between two joint faces.
2 Check that the tension of the generator and fan drive
belt is correct: with a hand pressure of approximately
22 Ib the belt should sag 13/32 inch. Adjust if necessary
as detailed in Chapter 1.
3 Ensure that the shutter can swivel freely and that the
spring is in a serviceable condition.
4 : 6 Fault diagnosis
(a) Engine overheating
1 Generator and fan drive belt slipping
2 Shutter control thermostat defective
3 Shutter unable to swivel freely
4 Shutter return spring broken
5 Leaking joints in conveyor system
F50057