1957 FIAT 500 diagram
[x] Cancel search: diagramPage 40 of 128

3:1
3:2
3:3
3:4
3:5Description
Operation
Routine maintenance
Ignition faults
Removing and dismantling distributor (sedan
and sports)
CHAPTER 3
THE IGNITION SYSTEM
3:6
3:7
3:8
3:9
3:10
Removing and dismantling
(station wagon)
Timing the ignition
Sparking plugs
The distributor drive spindle
Fault diagnosisdistributor
3 :1 Description
The ignition system fitted to all the models covered by
this manual consists of an ignition coil, ignition distributor
fitted with contact breaker points, a centrifugal automatic
advance system, condenser, low- and high-tension
wiring, spark plugs and a power supply provided by a
generator and battery. The wiring diagram is shown in
FIG 3 : 1
1 The low-tension circuit which is sometimes called the
primary circuit includes the power supply, contact
breaker points, condenser and ignition coil primary
winding.
2 The high-tension circuit which is sometimes called the
secondary circuit includes the ignition coil secondary
winding, distributor rotor, distributor cap with terminals
and the central brush, high-tension cables and the spark
plugs.
3 : 2 Operation
The contact breaker unit in the distributor interrupts
the primary circuit by the points opening. The sudden stop
in the flow of current in the primary winding, does not cause
arcing at the contact breaker points because it discharges
into the condenser connected in parallel w i t h the contact
F50047
breaker points. With the sudden collapse of the primary
circuit, the intensity of the magnetic field drops causing
an induced high-tension current in the ignition coil
secondary winding. The high EMF is distributed to the
sparking plugs by the ignition distributor rotor.
The automatic advance mechanism comprises a plate
carrying t w o weights which are symmetrically pivoted on
the plate at one end. Also attached to the weights at
opposite ends to the pivots is the cam carrier shaft with
special tension return springs. Under the action of centri-
fugal force as the rotational speed increases, the weights
move outwards causing the cam carrier shaft to move
angularly compared to the distributor drive shaft thus
causing advancement of the ignition timing.
The contact breaker assembly comprises the cam on the
drive shaft and t w o contact points, one of which is
stationary while the other is under the influence of the
cam, the action of which is transmitted by a rubbing block.
The cam has t w o lobes to control the opening and closing
of contact points. The stationary contact point is mounted
on an adjustable support to enable the contact breaker
point gap to be adjusted.
The HT current reaches the distributor cap central
terminal, from the ignition coil and is distributed to each
of the spark plugs at the correct time by the rotor arm.
Page 41 of 128

FIG 3 : 1 Ignition system wiring diagram
BATTERY
SWITCHBREAKER COIL
SPARK PLUG
CONDENSER
FIG 3 : 2 Ignition distributor in place on engine with
cap lifted offCURRENT CONTACT
TO SPARK PLUG
BREAKER A R M
STATIONARY
CONTACT
CARRIER
ADJUSTING
SCREW
CONTACT POINTS HIGH TENSION)
CARBON CONTACT
3 : 3 Routine maintenance
Refer to FIG 3: 2 and remove the distributor cap and lift
off the rotor arm. Lubricate the cam spindle felt pad using
Fiat VS oil. There is provision for the oil to make its way
downwards. Squirt a few drops of oil into the distributor
shaft lubrication fitting, the location being shown in FIG
3:3 Smear a little grease on the cam and a small drop of
oil to the contact breaker point pivot.
Adjusting the contact breaker points:
Refer to FIG 3 : 2 and slacken the stationary contact
carrier adjusting screw. Slowly rotate the engine until one
one of the t w o cams has opened the points to the fullest
48
extent so that the gap is measured at the position of the
maximum opening. Reset the gap to a correct clearance of
.0185 to .0209 inch and tighten the contact carrier screw.
Cleaning the contact points:
If the contact points are dirty or pitted they must be
cleaned by polishing them with a fine carborundum stone
taking very great care to ensure that the contact faces are
flat and square. Afterwards wipe away all dust with a cloth
moistened in petrol. The contacts may be removed from
the distributor body to assist refacing and cleaning refer-
ring to Section 3:5. If the moving contact is removed
from its pivot, check that its operation is not sluggish. If it is
tight, polish the pivot pin with a strip of fine emery cloth,
clean off all dust and apply a tiny spot of oil to the top of
the pivot pin. If a spring testing gauge is available the
contact breaker spring should have a tension of 16.8± 1.8
oz. measured at the points.
3 :4 Ignition faults
If the engine runs unevenly set it to idle at a fast speed.
Taking care not to touch any metal part of the sparking
plug leads, pull up the insulator sleeve and short each
plug in turn, using a screwdriver with an insulated handle.
Connect the screwdriver blade between the plug top and
the cylinder head. Shorting a plug which is firing properly
will make the engine uneven running more pronounced.
Shorting a plug in a cylinder which is not firing will make
no difference.
Having located the
faulty cylinder, stop the engine and
remove the plug lead. Start the engine and hold the lead
carefully to avoid shocks so that the metal end is about
3/16 inch away from the cylinder head. A strong regular
spark shows that the fault might be with the sparking plug.
Remove and clean it according to the instructions in
Section 3 :8. Alternatively substitute it with a new plug.
If the spark is weak and irregular, check that the lead is
not perished or cracked. If it appears to be defective,
renew it and try another test. If there is no improvement,
remove the distributor cap and wipe the inside clean and
dry. Check the carbon brush located as shown in FIG 3 : 2 .
It should protrude from the cap moulding and be free to
move against the pressure of the internal spring. Examine
the surface inside the cap for signs of 'tracking' which can
be seen as a thin black line between the electrodes or to
some metal part in contact with the cap. This is caused by
sparking, and the only cure is to fit a new cap.
Testing the low-tension circuit:
Before carrying out electrical tests, confirm that the
contact breaker points are clean and correctly set, then
proceed as follows:
1 Disconnect the black low-tension cable from the
ignition coil and from the side of the distributor.
Connect a test lamp between the t w o terminals. Turn
the engine over slowly. If the lamp lights when the
contacts close and goes out when they open, the
low-tension circuit is in order. If the lamp fails to light
the contacts are dirty or there is a break or loose con-
nection in the low-tension wiring.
2 If the fault lies in the
low-tension circuit, switch on
the ignition and turn the crankshaft until the contact
breaker points are fully open. Refer to the wiring
diagram in Technical Data and check the circuit with
Page 49 of 128
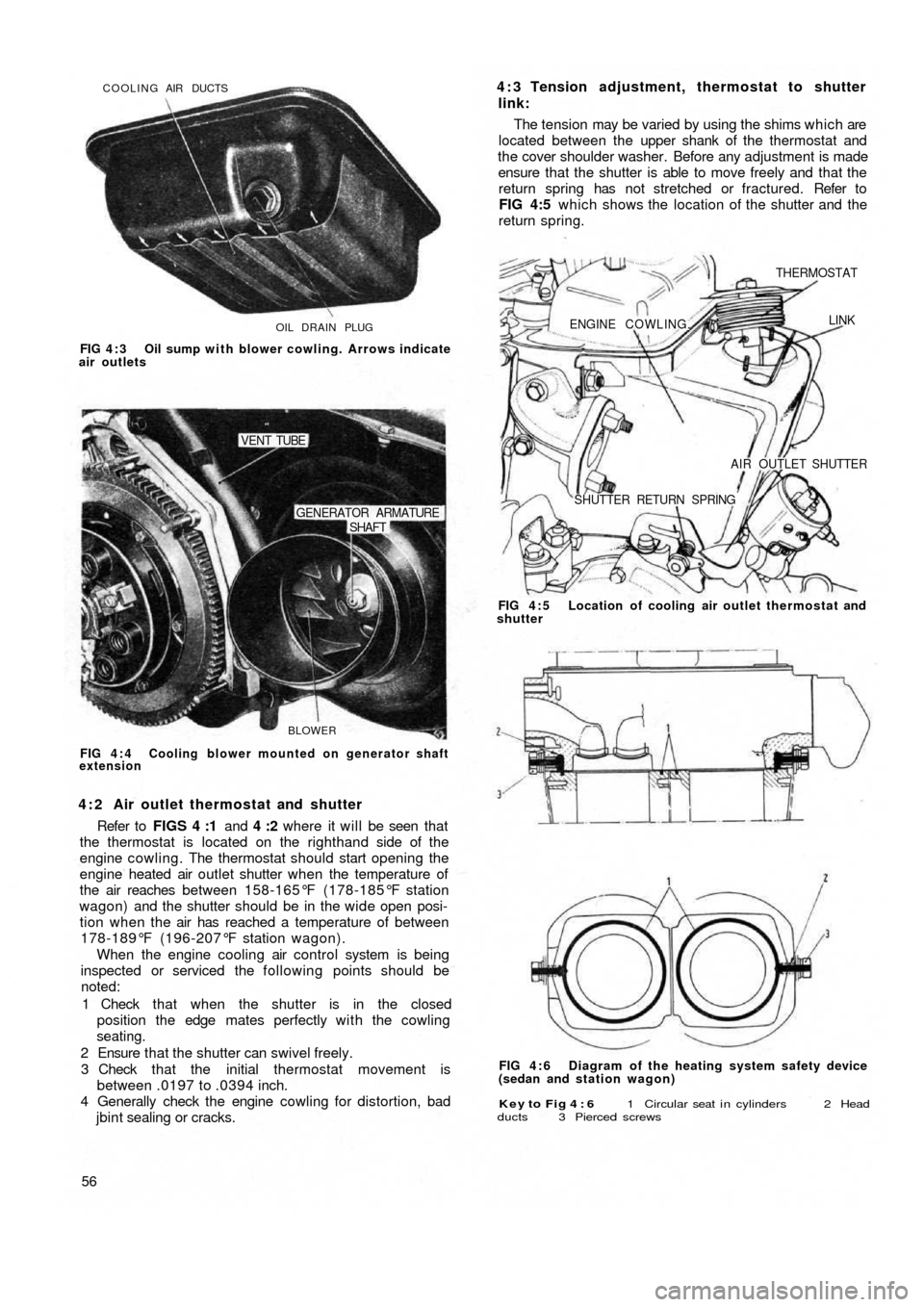
OIL DRAIN PLUG COOLING AIR DUCTS
FIG 4 : 3 Oil sump with blower cowling. Arrows indicate
air outlets
BLOWER
SHAFT GENERATOR ARMATURE
VENT TUBE
FIG 4 : 4 Cooling blower mounted on generator shaft
extension
4 : 2 Air outlet thermostat and shutter
Refer to FIGS 4 :1 and 4 :2 where it will be seen that
the thermostat is located on the righthand side of the
engine cowling. The thermostat should start opening the
engine heated air outlet shutter when the temperature of
the air reaches between 158-165°F (178-185°F station
wagon) and the shutter should be in the wide open posi-
tion when the air has reached a temperature of between
178-189°F (196-207°F station wagon).
When the engine cooling air control system is being
inspected or serviced the following points should be
noted:
1 Check that when the shutter is in the closed
position the edge mates perfectly with the cowling
seating.
2 Ensure that the shutter can swivel freely.
3 Check that the initial thermostat movement is
between .0197 to .0394 inch.
4 Generally check the engine cowling for distortion, bad
jbint sealing or cracks.
56
Key to Fig 4 : 6 1 Circular seat i n cylinders 2 Head
ducts 3 Pierced screws
FIG 4 : 6 Diagram of the heating system safety device
(sedan and station wagon) FIG 4 : 5 Location of cooling air outlet thermostat and
shutter
ENGINE COWLING.
THERMOSTAT
LINK
AIR OUTLET SHUTTER
SHUTTER RETURN SPRING
4 : 3 Tension adjustment, thermostat to shutter
link:
The tension may be varied by using the shims which are
located between the upper shank of the thermostat and
the cover shoulder washer. Before any adjustment is made
ensure that the shutter is able to move freely and that the
return spring has not stretched or fractured. Refer to
FIG 4:5 which shows the location of the shutter and the
return spring.
Page 55 of 128
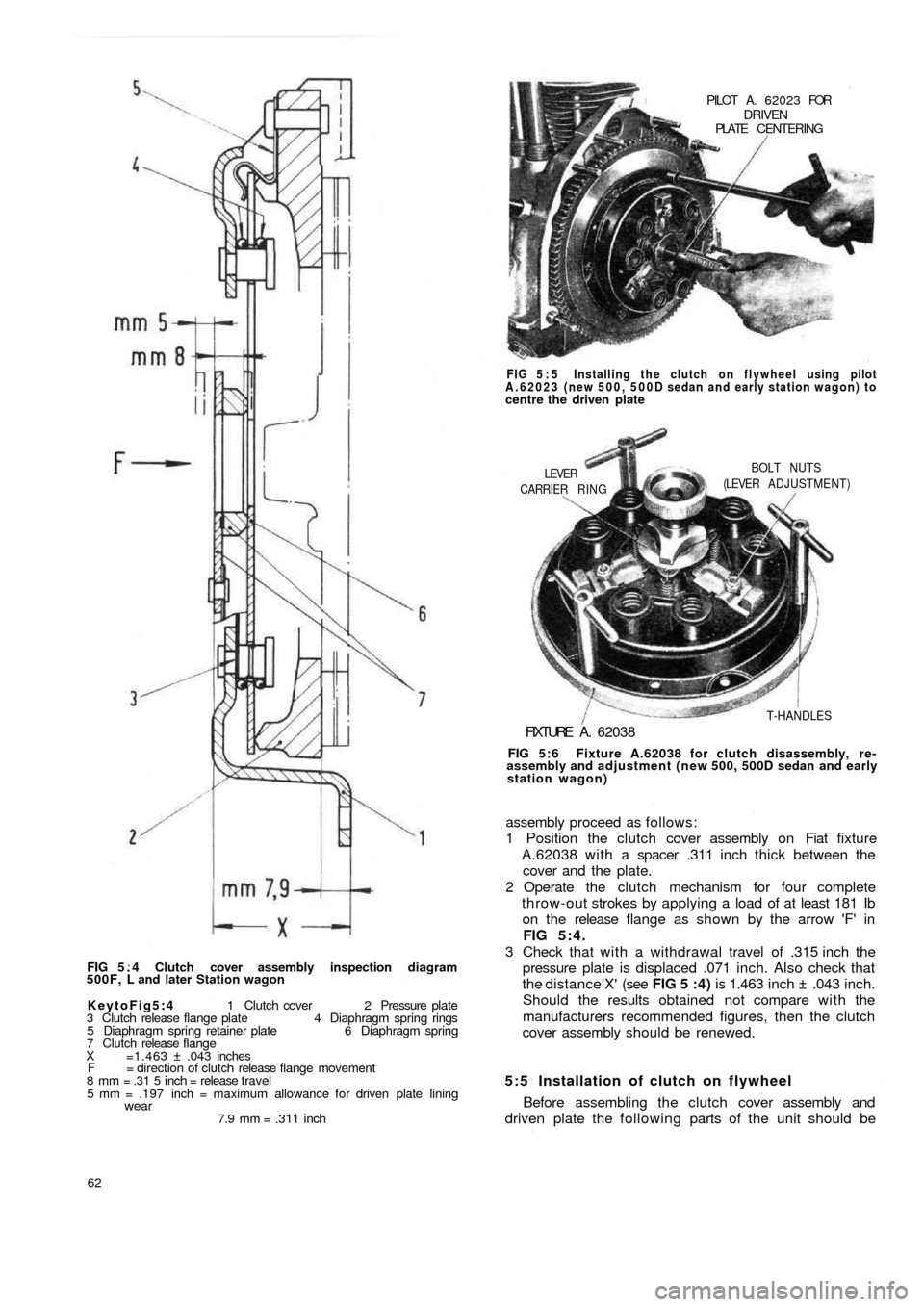
FIG 5 . 4 Clutch cover assembly inspection diagram
500F, L and later Station wagon
KeytoFig5:4 1 Clutch cover 2 Pressure plate
3 Clutch release flange plate 4 Diaphragm spring rings
5 Diaphragm spring retainer plate 6 Diaphragm spring
7 Clutch release flange
X =1.463 ± .043 inches
F = direction of clutch release flange movement
8 mm = .31 5 inch = release travel
5 mm = .197 inch = maximum allowance for driven plate lining
wear7.9 mm = .311 inch
62
5:5 Installation of clutch on flywheel
Before assembling the clutch cover assembly and
driven plate the following parts of the unit should be assembly proceed as follows:
1 Position the clutch cover assembly on Fiat fixture
A.62038 with a spacer .311 inch thick between the
cover and the plate.
2 Operate the clutch mechanism for four complete
throw-out strokes by applying a load of at least 181 Ib
on the release flange as shown by the arrow 'F' in
FIG 5:4.
3 Check that w i t h a withdrawal travel of .315 inch the
pressure plate is displaced .071 inch. Also check that
the distance'X' (see FIG 5 :4) is 1.463 inch ± .043 inch.
Should the results obtained not compare w i t h the
manufacturers recommended figures, then the clutch
cover assembly should be renewed.
FIG 5:6 Fixture A.62038 for clutch disassembly, re-
assembly and adjustment (new 500, 500D sedan and early
station wagon)
FIXTURE A . 62038
T-HANDLES CARRIER RING
LEVERBOLT NUTS
(LEVER ADJUSTMENT) FIG 5 : 5 Installing the clutch on flywheel using pilot
A.62023 (new 500, 500D sedan and early station wagon) to
centre the driven platePILOT A. 62023 FOR
DRIVENPLATE CENTERING
Page 66 of 128

FIG 6:12 Graphic demonstration of C and c
Key to Fig 6:12 1 Bevel pinion rear roller bearing inner
race 2 Bush, fourth-speed driven gear 3 Hub,
third- and fourth-speed engagement sleeve 4 Bush,
third-speed driven gear
'C Total height of items 1, 2, 3 and 4 which must be mounted
on final drive pinion
'c' Difference between actual height C and the minimum
drawing call-out 4.5527 inch represented by tool A.62037
that the new Fiat tools are used to determine shim thick-
ness as detailed below:
S = 0.90 + a — (b + c)
Where S = shim thickness
0.90 = standard coefficient
a = value of reading on the dial indicator
A.95690 applied to fixture A.70036 as
shown in FIG 6:13.
b = value stamped on pinion stem as shown in
FIG 6:8.
c= value read o n the dial indicator corres-
ponding to the difference between height
of Tool A.70037 as shown in FIG 6:14,
and the sum of the thicknesses of the items
to be installed in pinion and included
between front bearing inner shoulder and
rear bearing outer shoulder.
Ring gear clearance and differential bearing pre-
load :
To enable the correct ring gear tooth clearance to be
ascertained use Fiat tool A.62039 together with a dial
gauge. The support for dial gauge should be fixed into
the t w o lower bolt holes of the flywheel housing and the
pointer of the dial gauge adjusted so that it is located
through the clutch shaft hole in the final drive housing
so resting on a ring gear tooth (see FIG 6:15). Then
proceed as follows:
1 During reassembly the differential bearing nuts should
not have been screwed fully home to the differential
F50073
bearing outer races w h e n installing into the f i n a l drive
unit. These should now be carefully screwed in until
they are in gentle contact with the bearing races.
2 Slide Fiat tool A.62040 over one of the drive shafts
and using Fiat tool A.62041 lock the drive shaft to
the differential housing thus preventing the drive
pinion from rotating.
3 Gently turn the drive shaft which should now be
locked to the ring gear and note the movement of the
dial gauge indicator. This will show the tooth clear-
ance. When the clearance is correctly adjusted the
FIG 6:14 Reading value c on dial indicator Key to Fig 6:13 1 Dummy pinion, tool A.70036
2 Support with dial gauge, tool A.95690 FIG 6:13 Diagram showing the position of tools for
determining the value of a
Page 94 of 128

reassembling and during assembly liberally lubricated
using Fiat W90/M oil (SAE90 EP).
2 The pitman arm nut should be correctly positioned on
reassembly to the sector shaft and both are marked
with notches or a master tooth on the sector will mate
with a double tooth on the pitman arm which will
prevent incorrect reassembly.
3 The pitman arm nut must be tightened to a torque
wrench setting of 72 Ib/ft.
4 Fill the box up to the level and filler plug with SAE90 EP
gear oil.
Refitting the steering box:
To refit the steering box to the vehicle proceed as
follows:
1 Engage the w o r m screw f r o m the steering shaft by
gently manipulating the steering box.
2 Replace the steering box to body nuts and tighten to a
torque wrench setting of 14 to 18 Ib/ft.
3 Replace the t w o track rod pins in their seatings in the
pitman arm and tighten the self-locking nuts to a
torque wrench setting of 18 to 21 Ib/ft.
4 Replace the steering shaft to worm screw mounting
bolt, lock washer and nut.
9 :5 Relay lever and support
The steering idler arm is secured to the body by means
of a support bracket and a rubber bushed pivot bolt. This
is shown in FIG 9 : 7. When this unit is being serviced
the following points should be noted.
1 If there is excessive play between the pin and the
bushes the bushes must be renewed. Also check the
condition of the pin and if there are signs of excessive
wear it must be renewed.
2 To eliminate torsional stresses in the rubber bushes
during assembly the pin nut must be tightened to
torque wrench setting of 39 to 43 Ib/ft, once the
front wheel toe-in has been correctly adjusted w i t h the
wheels set in the straight ahead position.
3 The relay lever support to body mounting nuts must
be tightened to a torque wrench setting of 14 to 18
Ib/ft.
9 : 6 Steering rods (tie rods)
The steering rod is connected to the idler arm and the
drop arm by means of non-adjustable ball joints. The
track rods are connected to the right and left steering
arms by non-adjustable ball joints and comprise t w o
sleeves which are split and having internally threaded
ends. The ball joints are clamped to either end of the
sleeves. To facilitate adjustment one ball joint end has a
lefthand thread and the other a righthand thread.
Adjustment is made by loosening both the clamping bolts
and turning the central sleeve.
To remove the steering rods from the pitman arm, the
relay lever and knuckle arms Fiat pullers A.46006 and
A.6473 or universal ball joint removers should be used.
If excessive play is evident in the ball joint linkage or
the pin is damaged the complete ball joint assembly must
be renewed.
Upon reassembly the tie rod to ball pin knuckle arm
nuts must be tightened to a torque wrench setting of
18 to 21 Ib/ft.
F500101
FIG 9:7 Relay lever support section
FIG 9:8 Front wheel toe-in checking diagram
Key to Fig 9:8 A—B = 000 inch to .079 inch
It is important that all steering linkages are thoroughly
checked at regular intervals and if any parts are suspect
then they must be renewed.
9 : 7 Front wheel toe-in
To check and adjust the front wheel toe-in proceed as
follows:
1 Ensure that the tyres are inflated to the recommended
pressures. Ensure that the steering wheel is in its
Page 97 of 128

FIG 10:1 Diagrammatic view of service and rear wheel parking brake system
Key to Fig 10:1 1 Bleeder connections 2 Brake fluid reservoir 3 Service brake pedal 4 Hand lever, mechanical
parking brake on rear wheels 5 Hand lever travel adjustment stretchers 6 Stop lamps 7 Mechanical brake operating lever,
controlled from lever 4 8 Shoe clearance self-adjusting device 9 Wheel cylinders 10 Master cylinder 11 Stoplight
pressure-operated switch
FIG 10:2 Left front wheel brake assembly (500 Sedan)
SHOE
RETURN
SPRINGSHOE MOUNTING
BRACKET SHOE
RETAINING
PLATE SHOES
DEVICESHOE
SELF-ADJUSTING
WHEEL CYLINDERSHOE RETURNSPRING
2 Check that the hydraulic flexible hoses are not con-
taminated with oil or grease which would destroy the
rubber.
3 Ensure that all pipeline fastening clips are secure
otherwise hydraulic line failure could occur due to
cracking caused by excessive vibration.
104
4 Carefully clean all connections and inspect for
hydraulic fluid leaks. Should any leaks be detected
then the connections should be tightened taking very
great care not to twist the pipes during this operation.
5 Ensure that the hydraulic fluid level in the reservoir is
correctly filled up to the top of the filter using Fiat
special 'Blue Label' brake fluid. Extra care must be
taken to ensure that no fluid is spilled over the body
paintwork, as this acts as a strong solvent.
6 Ensure that the play between the brake pedal pushrod
and the master cylinder plunger is .019 inch. This will
correspond to approximately .098 inch free pedal
travel.
Never use any fluid but the recommended hydraulic
fluid. Do not leave it in unsealed containers as it will
absorb moisture which can be dangerous. It is best to
discard fluid drained from the system or after a bleeding
operation. Observe absolute cleanliness when working
on all parts of the hydraulic system.
10:3 Front brakes
Front brake drum removal:
1 Remove the wheel trims and carefully slacken the road
wheel retaining bolts. Using a garage hydraulic jack
raise the front of the vehicle and place on firmly
based stands. Remove the road wheels.
Page 104 of 128

CHAPTER 11
THE ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT
11:1 Description
11:2 Battery
11:3 The generator
11:4 The starter
11:5 The control box
1 1 : 6 Fuses
1 1 : 7 Flasher unit
11:1 Description
All models covered by this manual have 12 volts
electrical systems in which the negative battery terminal
is earthed. There are three units in the regulator box to
control the charging circuit; a cut-out, a current regulator
and a voltage regulator. These are adjustable but it must
be stressed that accurate moving coil meters are required
when checking or altering the settings. Cheap and
unreliable instruments will make accurate adjustments
impossible.
There are wiring diagrams in Technical Data at the end
of this manual to enable those with electrical experience
to trace and correct wiring faults.
For t h e U.K. Market the headlamps are of the double
filament dipping renewable bulb type with adjustments
for individual beam settings.
The battery is located in the front compartment
forward of the petrol tank and the fuses to the rear o f the
petrol tank.
Detailed instructions for servicing the electrical equip-
ment will be found in this chapter, but it must be pointed
out that it is not sensible to try to repair that which is
seriously defective, electrically or mechanically. Such
equipment should be replaced by new units which can
be obtained on an exchange basis.
F500111
11 :8 Windscreen wipers
1 1 : 9 The lighting system
11:10 Panel and warning lights
11:11 The horn
11:12 Lighting and flasher switch
1 1 : 1 3 Fault diagnosis
11.2 The battery
This of the 12-volt lead/acid type and has to meet
heavy demands for current particularly in the winter. To
maintain the performance of the battery at its maximum
it is essential to carry out the following operations.
Keep the top of the battery and surrounding parts dry
and clean, as dampness can cause leakage between the
securing clamps and the battery terminals. Clean off any
corrosion from the metal parts of the battery mounting
with diluted ammonia and paint them with an anti-
sulphuric paint. If the terminal posts are corroded,
remove the cables and clean w i t h diluted ammonia.
Smear the posts w i t h petroleum jelly before remaking the
connections and fit the terminals securely. High electrical
resistance due to corrosion at the terminal posts is often
responsible for lack of sufficient current to operate the
starter motor.
Ensure t h a t the filler plugs are in good condition and
show no signs of cracks. This may cause leakage of
electrolyte and consequent corrosion. Test the condition
of the cells after topping-up the electrolyte level with
distilled water to just above the tops of the separators as
shown in FIG 11 :2 . Never add neat acid. If it is
necessary to make a new electrolyte due to loss by
spillage add sulphuric acid to the
distilled water.
It is highly dangerous to add water to acid.