1953 JEEP CJ torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 66 of 376

D
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
FIG.
D-40—TIMING
GEARS Be
sure
to install a new rubber oil
seal
ring on each
intake
valve stem before installing the retainer
locks.
With
the retainer and spring compressed position a
seal
ring
on the valve stem just above the
lock
recess, then install the locks and release the
spring.
Adjust
the valve tappets to the proper specified
clearance.
Refer to Par. D-108, and specifications
at the end of this section for specifications and
adjustment procedure.
D-91.
Install
Camshaft
Timing
Gear
Turn
the camshaft or crankshaft as necessary so
that the timing marks on the two gears
will
be
together
after the camshaft timing gear is installed.
Refer
to Fig. D-40.
Install
the woodruff key in the key way on the front end of the camshaft.
Start
the large timing gear on the camshaft with the timing
mark
facing out. Do not drive on the camshaft gear, or the camshaft may
dislodge
the plug at the
rear
of the cylinder block causing an oil leak.
Install
the camshaft gear retaining screw and
torque it 30 to 40 lb-ft. [4,1 a 5,5 kg-m.] drawing
the gear
onto
the camshaft in the process. Standard
running
tolerance
between
the timing gears is .000" to .002" [0 a 0,051 mm.] which should be
checked with a
dial
indicator.
D-92.
Install
Timing
Gear
Oil Jet
Install
the timing gear oil jet in the tapped
hole
in
the front of the cylinder block. Position the oil
hole
in the side of the oil jet so that it
will
direct the
oil
stream against the camshaft driven gear just
ahead
of the point of
engagement
with the
crank
shaft drive gear.
D-93.
Install
Oil Pump
The
oil pump is driven from the camshaft by means of a
spiral
(worm) gear. The distributor, in
turn,
is driven by the oil pump by means of a
tongue
on the end of the distributor shaft which
engages
a slot in the end of the oil pump shaft.
Because the
tongue
and the slot are both machined off center, the two shafts can be meshed in only
one position. Since the position of the distributor shaft determines the timing of the engine, and is
controlled by the oil pump shaft, the position of the oil pump shaft with respect to the camshaft is
important.
Turn
the crankshaft to bring
together
the timing
marks
on the crankshaft and camshaft gears. See
Fig.
D-4 0.
Install
the oil pump mounting gasket on
the pump.
With
the wider side of the shaft on top
(nearer
the top of the cylinder block), start the
oil
pump drive shaft into the opening in the left side of the cylinder block with the mounting
holes
in
the body of the pump in alignment with the
holes
in
the cylinder block. Insert a long-blade screw
driver
into the distributor shaft opening in the
opposite
side of the block and
engage
the slot in the oil pump shaft.
Turn
the shaft so that the slot is positioned at what would be roughly the nine-
thirty
position on a clock face. Remove tne screwdriver and, looking down the
distributor
shaft
hole
with a flashlight, observe the position of the slot in the end of the oil pump shaft
to make certain it is properly positioned. Replace the screwdriver and, while turning the screw
driver
clockwise to guide the oil pump drive shaft
gear into
engagement
with the camshaft gear, press
against the oil pump to force it into position. Remove the screwdriver and again observe the
position of the slot. If the installation was properly made, the slot
will
be in a position roughly equiva
lent to eleven o'clock position on a clock face with
the wider side of the shaft
still
on the top. If the
slot is improperly positioned, remove the oil pump
assembly and repeat the operation.
Coat
the threads of the capscrews with gasket
cement and secure the oil pump in place with two
lockwasher-equipped capscrews installed through the body of the oil pump and into the cylinder block
and
one lockwasher-capscrew installed through
the oil pump mounting flange.
D-94.
Install
Timing
Gear
Cover
Apply
a thin coat of gasket paste to the timing
gear cover. Position the gasket on the cover and
carefully
locate the cover on the front of the front mounting plate. Attach the cover and timing
indicator
and tighten the bolts.
D-95.
Install
Pistons and Connecting Rods
Before installing each piston and connecting rod assembly in the cylinder block, generously lubricate
the entire assembly with
engine
oil. Space the ring
gaps
around the piston so that no two
gaps
are
aligned vertically and are not located over the
T-slot
in the piston
skirt.
Insert the assembly in
the correct cylinder with the connecting rod
identifying number toward the camshaft side of
the cylinder block. When installing each assembly, rotate the crankshaft so that the
crankpin
is in
the down position. Fit a piston ring compressor
tightly around the piston rings. Reach up from the
bottom
of the cylinder block and guide the end of
the connecting rod over the crankshaft
journal
as
the piston is tapped down into the cylinder bore
with
hammer handle. 66
Page 67 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
D
Lubricate
the connecting rod bearing surfaces
generously with
engine
oil and install the bearing
cap with the numbered side matched to the num
bered side of the connecting rod. Torque the nuts
evenly 35 to 45 lb-ft. [4,8 a 6,2 kg-m.]. The con
necting rod cap nuts are locked with stamped nuts.
Used
stamped nuts should be discarded and re
placed with new
ones.
These locking stamped nuts
should be installed with the flat face toward the
connecting rod nut.
Turn
the locking nut finger
tight and then 34
turn
more with a wrench. Refer
to Par. D-36 for detailed information on fitting pistons and rings in the cylinder bores.
D-96.
Install
Crankshaft
Pulley
Align
the keyway in the pulley with the woodruff key installed in the crankshaft. Drive the pulley
onto
the crankshaft and secure it in place with
the crankshaft pulley nut. Insert a block of wood
between
one of the counterweights on the
crank
shaft and the side of the cylinder block to prevent the crankshaft from turning, then tighten the nut.
D-97.
Install
Oil Pan
Before installing the oil pan, make a final internal
inspection particularly making certain that the
inside of the cylinder block is clean. Apply a thin
coat of gasket paste on the oil pan. Place the new
oil
pan gasket in position. Set the oil pan in posi
tion on the cylinder block and install the oil pan.
Torque
the attaching
bolts
12 to 15 lb-ft. [1,7 a 2,1
kg-m.].
Install
the oil pan
drain
plug and gasket
and
tighten the plug securely.
D-98.
Install
Cylinder
Head
Make
certain that the entire top of the cylinder
block
assembly, the lower surface of the cylinder
head,
and the cylinder head gasket are clean. Blow
all
dirt
or carbon out of the blind tapped bolt
holes
in
the cylinder block before the cylinder head and gasket are installed. Using aerosol spray sealer
Part
No. 994757, spray a thincoat on both surfaces
of the head gasket, position the new cylinder head gasket with the crimped
edges
of the gasket metal down (See Fig. D-31).
This
gasket position allows a
positive seal along the narrow surfaces of the
cylin
der
head
between
the combustion chambers and
eliminates the possibility of burning combustion
10102
FIG.
D-41—CYLINDER
HEAD
BOLT
TIGHTENING
SEQUENCE
gases
reaching
an
asbestos
portion of the cylinder
head gasket.
Install
the cylinder head bolts. Tighten
the
bolts
with a torque wrench to 60 to 70 lb-ft. 8,3 a 9,7
kg-m.]
in the sequence shown in
Fig.
D-41.
Do not overlook installing the cylinder head bolt
in
the intake
manifold
directly under the
car
buretor
opening.
D-99.
Install
Rocker Arm Assembly
a.
Insert
ball
ends of the intake valve push rods through the cylinder head and cylinder block and
seat them in the cupped head of the intake valve
tappets.
b.
Install
the
rocker-arm
assembly on the 'four
rocker-arm-mounting
studs. Align the rocker arms
so that the
ball
ends of the intake valve tappet
adjusting
screws fit into the cup ends of the push
rods.
c.
Install
the four rocker-arm-attaching nuts.
Thread
each nut down evenly in sequence, one
turn
at a time, until the torque is 30 to 36 lb-ft. [4,1 a 5,0 kg-m.].
d.
Cement a new gasket on the rocker arm cover.
Install
the cover placing an oil seal then a flat
washer
and nut on each cover stud. Cement a new gasket on the exhaust valve cover.
Install
the cover and crankcase ventilation fittings using a
new gasket back of the vent cover and new copper
ring
gaskets under the attaching screw heads.
Torque
the valve tappet cover nuts 7 to 10 lb-ft. [1,0 a 1,4 kg-m.].
D-100.
Install
Distributor and
Spark
Plugs
To
correctly install the distributor, it
will
be neces
sary
to place No. 1 piston in the firing position.
To
locate the firing position of No. 1 piston, first
turn
the
engine
until No. 1 piston is moving up on
the compression stroke as indicated by compression
pressure
being forced through the
spark
plug open
ing.
Turn
the
engine
slowly until the 5° before top
center
mark
on the timing gear cover is in align
ment with the
mark
on the crankshaft pulley. Oil
the distributor housing where it bears on the
cylin
der
block and install the distributor. Mount the
rotor
on distributor shaft and
turn
the shaft until
the rotor points towards No. 1
spark
plug terminal
tower position (when cap is installed, about 5
o'clock) with the contact points just breaking.
Move the rotor back and forth slightly until the
driving
lug on the end of the shaft enters the slot cut in the oil pump gear and slide the distributor
assembly down into place. Rotate the distributor body until the contact points are just breaking.
Install
the hold down screw.
Connect
the core
primary
wire to the distributor.
Clean
and adjust the
spark
plugs, setting the elec
trode
gaps
at .030" [0,762 mm.].
Install
the plugs
to prevent any foreign matter entering the com
bustion chambers during the remaining operations.
Torque
the
spark
plugs 25 to 30 lb-ft. [3,5 a 4,6
kg-m.].
Install
spark
plug cables, placing them in the dis
tributor
cap terminal towers starting with No. 1
and
installing in a counter clockwise direction of
the firing order sequence (1-3-4-2). 67
Page 68 of 376

D
HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE
D-101.
Install
Manifold
If
manifold studs were removed for replacement,
apply sealer on the stud threads
before
installing
a
new stud.
See Section Fl for exhaust emission controlled
engines.
Make
certain that no foreign objects are inside the manifold and that all
passages
are clear. Place a
new set of manifold
gaskets
in position on the side
of the cylinder block.
Then,
carefully slide the manifold
onto
the studs and against the cylinder block being careful not to damage the gaskets.
Torque
all manifold attaching nuts evenly 29 to
35 lb-ft. [4,0 a 4,8 kg-m.].
D-102.
Install
Oil
Filler
Tube
When
installing the oil filler tube, be sure that the
beveled lower end is away from the crankshaft.
Place a
piece
of
hard
wood
over the top of the
tube
to prevent damage to the cap gasket seat.
D-103.
Install
Water Pump
Make
certain that the mating surfaces of the water pump and the cylinder block are clean and smooth.
Install
the gasket on the
flange
of the pump and
install
the pump in position on the cylinder block.
Torque
the water pump attaching
bolts
alternately
and
evenly 12 to 17 lb-ft. [1,7 a 2,3 kg-m.].
D-104.
Install
Water Outlet Fitting
Install
the thermostat and the water
outlet
fitting.
Torque
the water
outlet
fitting attaching
bolts
20
to 25 lb-ft. [2,8 a 3,4 kg-m.].
FIG.
D-42—INSTALLING HURRICANE F4 ENGINE
IN
VEHICLE
1—
Lifting
Sling
2— Hoist
Cable
3—
Hurricane
F4 Engine
4— Dowel Bolt
5—
Flywheel
Housing
D-105.
ENGINE INSTALLATION
a.
Install
lifting sling to
engine
and using suitable hoist raise the
engine
from its blocking or stand
and
then slowly lower it
into
the
engine
compartment of the vehicle.
Note:
When installing the
Hurricane
F4 Engine,
two % x 4 inch
guide
bolts
or
dowels
should be
used to properly
guide
and align the
engine
to the
flywheel housing (See Fig. D-42).
b. Slightly tilt the
engine
downward and at the
same time slide the
engine
rearward
while lining up the transmission main gear shaft with the clutch
throw-out bearing and disc spline.
Note
:The
engine
crankshaft may have to be turned
slightly to align the transmission main gear shaft
with the clutch disc spline.
c. Remove the
guide
bolts
or
dowels
and secure
the
engine
to the housing.
d.
Secure the front
engine
mounts to the frame brackets and
bolt
ground cable to
engine.
e. Remove lifting sling from
engine.
f. Connect exhaust pipe to
engine
manifold flange.
g. Connect throttle and choke cables to carburetor.
h.
Install
fan to water pump pulley.
i.
Connect fuel pump line to main fuel line,
j.
Replace starting motor assembly. k. Connect
engine
wiring harness connectors at
front of cowl.
I.
Connect wires to starting motor assembly, water
temperature and oil pressure sending units and alternator.
NOTE:
ON
ENGINES EQUIPPED WITH EX
HAUST
EMISSION CONTROL,
REPLACE
THE
AIR
PUMP,
AIR
DISTRIBUTOR
MANI
FOLD,
AND
ANTI-BACKFIRE (DIVERTER)
VALVE.
SEE
SECTION
Fl.
m. Replace radiator and radiator grille support
rods and connect coolant
hoses
to
engine.
Note:
Replace heater
hoses
if vehicle is equipped
with hot water heater.
n. Fill
radiator with coolant and
engine
with oil
(see
Lubrication
Chart).
o.
Install
air cleaner and connect carburetor air
hose.
p. Connect battery cables and start
engine,
q.
Install
hood
and road
test
vehicle.
D-103.
FINAL
IN-VEHICLE
ADJUSTMENTS
a.
Clean
battery terminals and check battery. b.
Check
ignition terminals and check battery.
c. Service carburetor air cleaner.
d.
Service positive crankcase ventilation valve.
e.
Check
fuel lines. f. Gap and install new
spark
plugs.
g.
Check
distributor
points
and capacitor; replace
if
necessary. 68
Page 69 of 376

'Jeep9
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
h.
Check
ignition (distributor) timing; reset if
necessary.
i.
Check
carburetor
adjustments; reset if necessary,
j.
With
engine
fully warmed up, tighten cylinder
head and manifold
bolts
and nuts to specified
torque.
Check
cylinder head gaskets and
bolts
for
air
or coolant leaks.
Note:
Tightness of cylinder head
bolts
should be
checked and corrected after 500 to 600 miles [800
a
960 km.] of normal operation.
k.
Check
fan belt tension; adjust if necessary.
I.
Check
for and correct any oil leak, fuel leak or
coolant leak.
D-107.
VALVE
ADJUSTMENT
Proper
valve adjustment is important to prevent
burning
of valves and poor
engine
performance.
This
adjustment consists of obtaining a specified
lash
in the valve mechanism. The exhaust valve
tappets and the intake valve rocker arms should be adjusted to the proper clearance with the
engine
cold (at room temperature). Valve clearance can
be properly adjusted only when the tappet is on the
heel or low portion of the cam.
INTAKE
OPENS
9°
BTC?
FIG.
D-43-
10270
-VALVE
TIMING
D-108. Valve Adjustment Procedure
The
exhaust valve tappets are adjusted by turning
the adjusting screw in or out of the tappet as neces
sary
to obtain the proper clearance. Where special
wrenches can be obtained, they should be used to facilitate the adjustment. The proper clearance is .016" [0,406 mm.]
between
the end of the adjusting
screw and the
bottom
of the exhaust valve.
Crank
the
engine
over to
close
a valve and check
the clearance with a feeler
gauge.
To adjust, hold
the tappet with one wrench and
turn
the adjusting
screw,
with the other.
Check
and adjust each of
the tappets in proper sequence.
Adjust
each intake valve by adjusting the rocker
arm
screw at the push rod to obtain .018" [0,457 mm.] clearance
between
the rocker arm and the
valve stem with tappet on the heel of the cam.
D-109.
Check
Valve
Timing
To
check the valve timing, carefully set the intake
valve rocker arm adjustment for No. 1 cylinder to .026"
[0,6604
mm.]
between
the rocker arm and the
valve stem. Rotate the crankshaft clockwise until
the piston in No. 1 cylinder is ready for the intake stroke. The intake valve
opens
9° before top center
(BTC).
Note
the distance
between
the
"TC"
and
"5°"
marks on the indicator on the timing gear
cover and estimate the 9° before top center position.
See
Fig.
D-43.
With
the crankshaft in this position, timing is correct if the rocker arm is just tight
against the intake valve stem. Do not overlook resetting the rocker arm adjustment to the correct
running
clearance.
D-110. Positive
Crankcase
Ventilation
Be
sure there are no air leaks at the tube connec
tions
between
the air cleaner and the oil filler tube,
and
that the oil filler tube cap gasket is in
good
condition. Always keep the cap locked securely in
place. When tuning the
engine
or grinding valves, remove the control valve and clean it thoroughly.
If
the valve is blocked with carbon, the ventilating
system
will
not operate and, should the valve
fail
to seat, it
will
be impossible to make the
engine
idle satisfactorily. Refer to Par. C-6 for servicing.
D-111. Oil
Filter
The
engine
is equipped with a throw-away type
oil
filter.
This
oil filter must be serviced periodi
cally
as outlined in the
Lubrication
Section. 69
Page 71 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
D D-l 13. HURRICANE
F4
ENGINE SPECIFICATIONS
MODEL:
ENGLISH
ENGINE:
Type
Number of Cylinders
Bore
Stroke
Piston Displacement...........
Bore
Spacing (center to center): 1 and 2, 3 and 4
2 and 3
Firing
Order Compression Ratio Compression Pressure... .
Number of Mounting Points:
Front
Rear
Horsepower (SAE)
Horsepower (Max Brake) Maximum Torque @
2000
rpm.
PISTONS:
Material
Description
Length
,.
Diameter (near
bottom
of
skirt).
Weight.
Clearance
Limits:
Piston-To-Cylindcr
Bore
Ring
Groove Depth:
No. 1 and 2 Ring No. 3 Ring
Ring
Groove Width:
No. 1 Ring No. 2 Ring
No. 3 Ring
Piston Pin Hole Bore
Cylinder
Bore — Standard.....
—
max. out of round
F-Head
4
W
134.2 cu. in.
3.437"
4.938"
1-3-4-2
6.7:1
120 to 130 psi.
2
1
15.63
@
4000
rpm. 114 lb-ft. 75
-
max. taper..
-
max. rebore.
PISTON RINGS:
Function:
No. 1 and 2 No. 3. .
Material:
No. 1. .
No. 2 and 3
Width;
No. 1 and 2
No. 3. . . .
Gap
(Std. to .009 Cyl. Bore).
Thickness:
No. 1 and No. 2 Rings....
No. 3 Ring
Side Clearance in Groove:
No. 1 Ring No. 2 Ring
No. 3 Ring
PISTON
PINS:
Material
Length
Diameter
Type
Clearance
in Piston
(selective
fit).
Aluminum
Alloy
Gam
Ground, T-slot, Tin Plated
3.1225*
to
3.1245*
13.5 oz.
Selective Feeler Fit
.1593" to .1655"
.1693" to .1755"
.0955" to .0965" .095" to .096"
1875" to .1885" .760" to .770"
3.125"
to
3.127"
.005" .005" .040"
Compression
Oil
Cast
Iron,
Chrome-plated Face
Cast
Iron
.007" to .017"
.134" to .144" .115" to .125"
.002" to .004"
.0015" to .0035" .001" to .0025"
SAE
1016 Steel
2.781"
.8119"
Locked
in Rod
.0001"
to .0003"
METRIC
7,937
cm.
11,112
cm. 2199 cm*
8,729
cm.
12,542
cm.
8,4 a 9,2 kg-cm2
15,77 kg-m.
9,525
cm.
7,9311
a
7,9362
cm.
382,7
gr.
4,046
a
4,203
mm.
4,300
a
4,457
mm.
2,4257
a
2,4511
mm. 2,413 a
2,438
mm.
4,7625
a
4,7879
mm.
19,304
a
19,558
mm.
7,9375
a
7,9425
cm.
0,1270
mm.
0,1270
mm.
1,0160
mm.
2,38 mm.
4,76 mm.
0,178 a
0,432
mm.
3,403
a
3,657
mm. 2,821 a 3,175 mm.
0,051 a 0,102 mm.
0,038
a
0,088
mm.
0,025
a
0,063
mm.
70,637
mm.
20,6223
mm.
0,0025
a
0,0076
mm. 71
Page 79 of 376
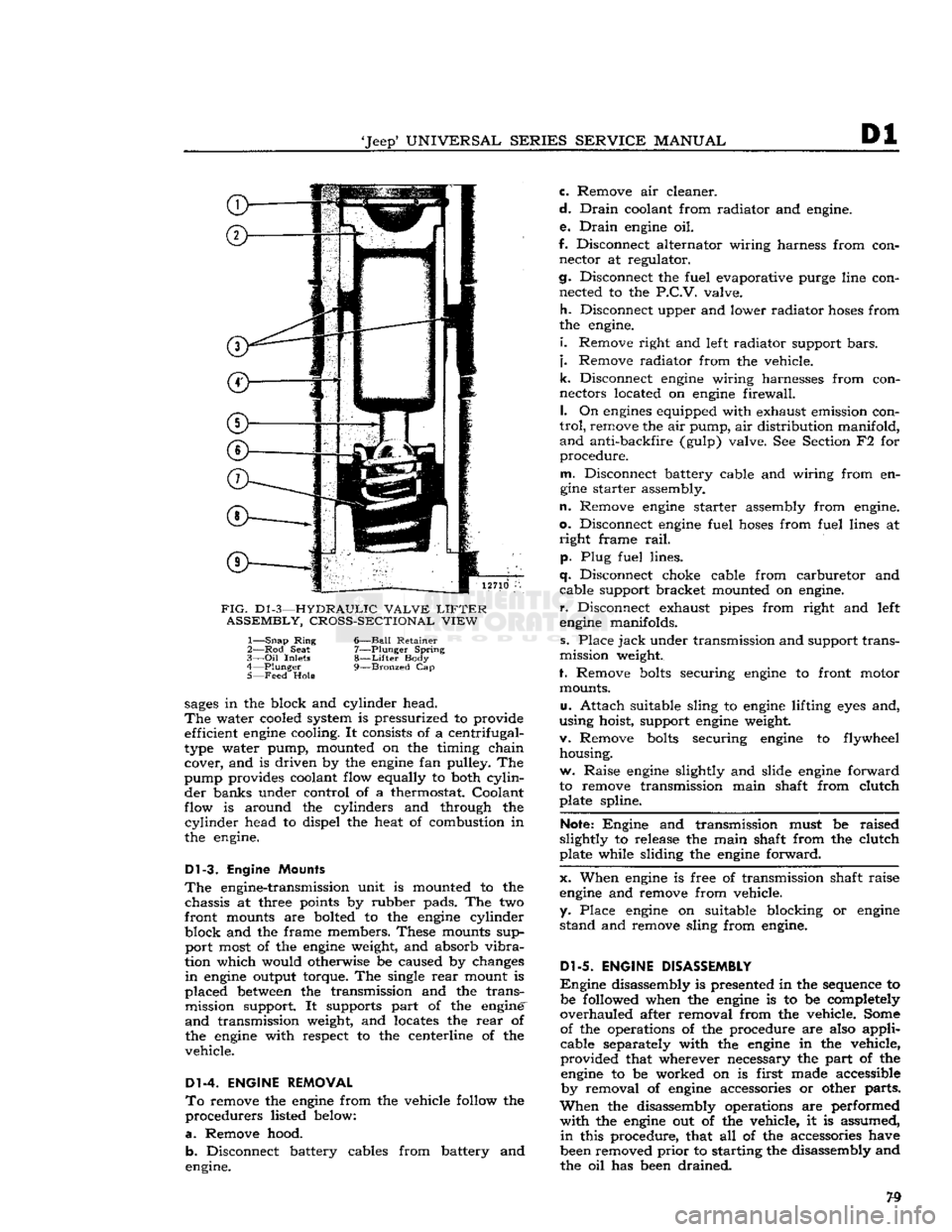
'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
12710
FIG.
D1
-3—HYDRAULIC VALVE
LIFTER
ASSEMBLY, CROSS-SECTIONAL VIEW
1—
Snap
Ring
6—Ball Retainer
2— Rod
Seat
7—Plunger Spring
3—
Oil
Inlets
8—Lifter
Body
4—
Plunger
9—Bronzed
Cap
5— Feed
Hole
sages
in the block and cylinder head.
The
water cooled system is pressurized to provide efficient
engine
cooling. It consists of a centrifugal-
type water pump, mounted on the timing chain cover, and is driven by the
engine
fan pulley. The
pump provides coolant flow equally to both
cylin
der banks under control of a thermostat. Coolant
flow is around the cylinders and through the
cylinder
head to dispel the heat of combustion in
the engine.
Dl-3.
Engine Mounts
The
engine-transmission unit is mounted to the chassis at three points by rubber pads. The two
front mounts are bolted to the
engine
cylinder
block and the frame members. These mounts sup port most of the
engine
weight, and absorb
vibra
tion which would otherwise be caused by changes
in
engine
output torque. The single
rear
mount is
placed
between
the transmission and the trans mission support. It supports part of the engine'
and
transmission weight, and locates the
rear
of
the
engine
with respect to the centerline of the
vehicle.
Dl-4. ENGINE REMOVAL
To
remove the
engine
from the vehicle follow the
procedurers listed below:
a.
Remove hood. b. Disconnect battery cables from battery and
engine. c. Remove air cleaner.
d.
Drain
coolant from radiator and engine.
e.
Drain
engine
oil.
f. Disconnect alternator wiring harness from con nector at regulator.
cj.
Disconnect the fuel evaporative purge line con nected to the
P.C.V.
valve.
h.
Disconnect upper and lower radiator
hoses
from
the engine.
i.
Remove right and left radiator support
bars,
j.
Remove radiator from the vehicle.
k.
Disconnect
engine
wiring harnesses from con
nectors located on
engine
firewall.
I.
On
engines
equipped with exhaust emission con
trol,
remove the air pump, air distribution manifold,
and
anti-backfire (gulp) valve. See Section F2 for
procedure.
m.
Disconnect battery cable and wiring from en
gine
starter assembly.
n.
Remove
engine
starter assembly from engine,
o.
Disconnect
engine
fuel
hoses
from fuel lines at
right
frame
rail,
p. Plug fuel lines.
q.
Disconnect choke cable from carburetor and cable support bracket mounted on engine,
r.
Disconnect exhaust pipes from right and left
engine
manifolds.
s. Place
jack
under transmission and support trans
mission weight.
f. Remove
bolts
securing
engine
to front motor mounts.
u.
Attach suitable sling to
engine
lifting
eyes
and,
using hoist, support
engine
weight.
v. Remove
bolts
securing
engine
to flywheel housing.
w. Raise
engine
slightly and slide
engine
forward
to remove transmission main shaft from clutch plate spline.
Note:
Engine and transmission must be raised
slightly to release the main shaft from the clutch
plate while sliding the
engine
forward.
x. When
engine
is free of transmission shaft raise
engine
and remove from vehicle,
y. Place
engine
on suitable blocking or
engine
stand and remove sling from engine.
Dl-5.
ENGINE DISASSEMBLY
Engine
disassembly is presented in the sequence to be followed when the
engine
is to be completely
overhauled after removal from the vehicle. Some of the operations of the procedure are also applicable separately with the
engine
in the vehicle,
provided that wherever necessary the part of the
engine
to be worked on is first made accessible by removal of
engine
accessories or other parts.
When
the disassembly operations are performed
with
the
engine
out of the vehicle, it is assumed,
in
this procedure, that all of the accessories have
been removed
prior
to starting the disassembly and
the oil has been drained.
Page 85 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
12713
FIG.
Dl-11—MEASURING
TELESCOPE GAUGE
1—
Telescope
Gauge
2—
Micrometer
may
be measured with an inside micrometer or
by setting the cylinder
gauge
dial
at zero and meas
uring
across the
gauge
contact points with an outside micrometer while the
gauge
is at same zero
setting. Refer to
Figs.
Dl-10 and Dl-11.
b.
If a cylinder bore is moderately rough or slightly
scored,
but is not out-of-round or tapered, it is
usually
possible to remedy the situation by honing
the bore to fit a standard service piston, since
standard
service pistons are high-limit production
pistons. If cylinder bore is very rough or deeply
scored,
it may be necessary to rebore the cylinder
to fit an oversize piston in order to ensure satisfac
tory
results.
c.
If cylinder bore is tapered .005" [0,127 mm.]
or
more or is out-of-round .003" [0,076 mm.] or
more,
it is advisable to rebore for the smallest possible oversize piston and rings.
d.
Carefully
inspect the cylinder block for small
cracks
or fractures, and for porosity.
Rust
in any
cylinder
bore may indicate a leak.
e.
Inspect all machined surfaces for scoring and
burrs.
With
a straight
edge
and feeler
gauge,
check
each
machined surface for distortion.
D1-37.
Cylinder Block Repair
If
one or more cylinder bores are rough, scored, or
worn
beyond prescribed limits, it
will
be necessary
to correct bores and fit new pistons.
If
relatively few bores require correction, it
will
not be necessary to rebore all cylinders to the same
oversize in order to maintain
engine
balance, since
all
oversize pistons are held to the same weights as
standard-size
pistons. If conditions justify replace
ment of all pistons, however, all new pistons should
be the same nominal size.
Standard-size
service pistons are high-limit, or
maximum
diameter; therefore, they can usually be installed after a slight amount of honing has
been
done
to correct slight scoring or excessive
clearances.
This
applies
primarily
to
engines
which
have relatively low mileage. Service pistons are also furnished in .010"
[0,254
mm.] oversize. All
service
pistons are diamond bored, and selectively
fitted with piston pins; pistons are not furnished
without pins.
Caution:
Do not attempt to cut down oversize pis
tons
to fit cylinder bores as this
will
destroy the
surface
treatment and affect the weight. The small
est possible oversize service pistons should be used
and
the cylinder bores should be honed to size
for
proper clearance.
Before
honing or reboring cylinders, measure all new pistons with a micrometer, on an axis perpen
dicular
to the piston pin. Select the smallest piston
for
the first fitting. The slight variation usually
found between pistons in a set may provide for
correction
in case the first piston tried is too
small.
If
wear at top of cylinder
does
not exceed .005" [0,127 mm.]
excess
diameter, or exceed .003"
[0,076 mm.] out-of-round, honing is recommended.
If
wear or out-of-round
exceeds
these
limits, the
bore should be reground with a boring bar of the
fly
cutter type, then finish-honed.
When
reboring cylinders, all crankshaft bearing caps must be in place and tightened to proper
torque to avoid distortion of bores in
final
assem
bly.
Always be sure the crankshaft is out of the
way
of the boring cutter when boring each cylinder.
When
boring, leave the diameter .001" [0,025 mm.]
undersize,
then finish hone to obtain the required
clearance.
When
honing cylinders, use clean sharp
stones
of
proper
grade for the amount of metal to be re
moved. Refer to instructions supplied by the hone
manufacturer.
Dull
or dirty
stones
cut unevenly
and
generate excessive heat. When using coarse
or
medium grade
stones,
leave sufficient metal so
that all
stone
marks can be removed with the fine
stones
used to finish-hone to proper clearance.
When
finish-honing, pass the hone through the entire length of cylinder at a rate of approximately 60 cycles per minute.
This
should produce the
desired
45-degree
cross hatch pattern on cylinder
walls.
A proper pattern
will
ensure maximum
ring
life and minimum oil consumption.
After
final
honing and before the piston is checked
for
fit, each cylinder bore must be washed thor oughly to remove all traces of abrasive, then dried completely. The dry bore should be brushed clean
with
a power-driven fibre
brush.
If all traces of
abrasive
are not removed,
rapid
wear of new pistons
and
rings
will
result.
Note:
Wipe cylinder bores with a clean white
cloth,
moistened with SAE 10 oil. Cleaning should
continue until this
test
shows no sign of
dirt.
It
is of the greatest importance that refinished
cylinder
bores be true, with .0005" [0,013 mm.]
or
less out-of-round or taper.
Each
bore must have
a
smooth surface, without
stone
or cutter
marks.
After
final
honing and cleaning, each piston must be fitted individually to the bore in which it
will
be installed. Once fitted, each piston should be
marked
with its cylinder number to assure correct
installation.
85
Page 87 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
A 8
j
13415
FIG.
Dl-13—USING
PLASTIGAGE
TO
MEASURE
BEARING CLEARANCE
1— Plastigage
A—Start
2—
Scale
B—Flattened
install
cap with shell and tighten
bolts
80 to 110 lb-ft. [11,1 a 15,2 kg-m.] torque.
Caution:
Do not turn crankshaft with Plastigage
in
bearing.
b.
Remove bearing cap with bearing half. The
flattened Plastigage
will
adhere either to the bear ing half or the
journal.
Do not remove it.
c. Using the scale printed on the Plastigage en
velope,
measure Plastigage width at its widest
point. The number within the graduation which
most
closely corresponds to the width of Plasti
gage
indicates the bearing clearance in thousandths
of an inch.
DI-43.
Main Bearing
Fitting,
Feeler or
Shim
Stock
A
small strip of feeler or shim stock can be used
to check main bearing clearance. The method is
simple, but care must be taken to avoid damage
to the bearing surface from excessive pressure against the strip.
a.
Cut a rectangular piece of feeler or shim stock, .001"
[.0254
mm.] thick,
i/2"
[12,70
mm.] wide, and
Vs"
[3,175 mm.] shorter than the bearing width.
Position the bearing cap to the crankshaft journal
and
cylinder block, and install two cap
bolts
loosely.
b.
Tighten alternate cap bolts, a little at a time,
until
both have
been
tightened to 35 to 45 lb-ft. [4,8 a 6,2 kg-m.] torque.
c.
Turn
the crankshaft by hand, no more than one
inch
[2,5 cm.] in either direction.
Caution:
If the crankshaft is turned too far, it
will
embed the strip in the bearing surface.
This
will
damage the bearing and also cause a false indication of bearing clearance.
If
bearing clearance is correct, the strip should cause a light to heavy drag, or resistance to rotation.
If
there is little or no drag, clearance is too great;
if
the crankshaft cannot be turned, clearance is
insufficient. In either case, a different main bear ing must be
selected
to obtain proper clearance.
d.
Repeat
steps
a, b, and c, as necessary, to
select
proper main bearing size. After a bearing has
been
selected, remove the
test
strip from bearing on
crankshaft
journal surface; wipe both surfaces care
fully,
and apply clean
engine
oil to both surfaces. Position the bearing cap to the crankshaft journal
and
cylinder block, and install two cap
bolts
loosely.
Tighten
alternate cap bolts, a little at a time, to
final
specified torque of 80 to 110 lb-ft. [11,1 a 15,2 kg-m.]. The crankshaft should now rotate
freely.
Dl-44.
Piston
and
Connecting
Rod
Disassembly
a.
Remove two compression rings with a piston
ring
expander. To remove oil ring, remove the two
rails
and spacer-expander, which are separate
pieces
in
each piston third
groove.
b.
From
Tool Set W-338 use support base J-6047-1
with collar J-6047-5 and driver J-6047-4 with an
arbor
press to press piston pin from piston and con
necting rod. Mount support base and collar in press. Set driver in position and press out pin. Refer to
Fig.
Dl-14.
FIG.
Dl-14—PISTON
PIN
REMOVAL
1—
Arbor
Press
2—
Driver
3—
Piston
and Rod Assembly
4—
Collar
•
5—Support Base Dl-45.
Piston
and
Connecting
Rod
Cleaning
and Inspection
a.
Clean
carbon from piston surfaces and under
side of piston heads, and remove all pistons rings.
Clean
carbon from ring
grooves
with a suitable tool.
Remove any gum or varnish from piston skirts with a suitable solvent.
b.
Carefully examine pistons for rough or scored
bearing surfaces, cracks in
skirt
or head, cracked
or
broken ring lands, chipping and uneven wear 87