1953 JEEP CJ steering
[x] Cancel search: steeringPage 217 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
H
cuit
lights,
the
signal switch
is
inoperative
and
must
be
replaced.
H-139.
Hazard
Warning Lights
All
current production vehicles
are
equipped with
a
four-way flasher warning system.
The
control switch
is
located
on the
instrument panel left
of
the steering column.
With
the
switch pulled
out,
the
two
front and
two
rear
turn
signal lights flash
on and
off
simultaneously,
as do
both
turn
signal
indicator
lights
on the
instrument clusters.
H-140.
Marker
Lights and Reflector Assembly
The
marker
lights
and
reflector assemblies
on
current
production vehicles
are
mounted
on the
side
of
the front fender and
on the
side
of
the
rear
quarter
panel.
The
spare wheel also mounts
a
marker
light. Some earlier production vehicles have
reflex reflectors mounted on the side of the hood and
on
the
side
of
the
rear
quarter panel. determine
if
dash wiper switch or wiring
is at
fault,
disconnect wiring harness from wiper motor
and
try
operating wiper independently
of
dash switch.
If
still
inoperative
see
procedure under
Par.
H-145.
b. Wiper
will
not
shut
off
— Determine
if
wiper
has both
low
and high speeds, slow speed only,
or
high speed only.
It is
important that
the
wiper
operates
at low
speed during parking cycle.
Dis
connect wiring harness from wiper motor
and try
operating wiper independently
of
dash switch.
If
wiper
shuts
off
correctly with
crank
arm
in
park
position and wiper has both speeds, check
the
lead
between
terminal
and
dash switch ground
and
check
for
defective dash switch.
If
wiper shuts
off
correctly,
but has
high speed only, check lead
be
tween wiper terminal and dash switch
for an
open
circuit
and check
for
defective dash switch.
If
still
inoperative,
see
Par. H-145.
c. Wiper
has
only fast speed.
Check
for
defective dash switch
or
open lead
between
terminal
and
dash switch.
H-141.
Windshield Wiper System
Early
production vehicles equipped with
the
Dauntless V-6
engine
have
two
single speed wind
shield wiper motors mounted above
the
windshield inside
the
vehicle. The wiper motors
are
operated
and
controlled
by a
switch located
on the
instru
ment panel.
Current
production vehicles with stationary wind
shield have
a
two-speed
electric windshield wiper motor mounted below
the
windshield outside
the
vehicle on the driver's side. The wiper motor switch is located
on the
instrument panel
to the
left
of
the steering column.
H-142.
Two-Speed Wiper Motor
The
two-speed
electric wiper motor
is
operated and
controlled
by a
turn
type, three poled, dash switch,
containing
a 6
amp. circuit breaker.
Current
flow
is directed from
the
battery through
the
ignition
switch
to the
wiper dash switch assembly
to the
two-speed
wiper motor, which passes current from the designated motor brush (high,
low or
park)
to
the armature circuit
to
ground.
H-143.
Troubleshooting Procedure
Troubleshooting procedures
are
divided into
two
categories: wiper troubleshooting
in
vehicle; wiper
troubleshooting
on
bench.
Fig. H-65 and H-66
illustrates connecting leads
of the
two-speed
wiper for either bench operation
or to run
wiper inde
pendently
of
dash switch and vehicle wiring when
installed
in the
vehicle.
H-144. Wiper Troubleshooting
in
Vehicle
Typical
wiper troubles and remedies are
as
follows
:
a.
Wiper
is
inoperative
—
Check
wiper switch
cir
cuit
breaker; wiring harness connection
at
wiper
motor
and
wiper switch; wiper motor
feed
wire
from
ignition starter switch
to
wiper switch;
and
check wiper
on
switch
to be
securely mounted.
With
ignition switch
on,
check
for 12
volts
at
har
ness
terminal that connects
to
wiper terminal.
To
BLACK
PARK
GREEN *-
RED m~
LOW
PARKING
<^^>
SWITCH
V^-O*'
HIGH
FIG.
H-64—WIRING
DIAGRAM
FIG.
H-65—WINDSHIELD
WIPER
SWITCH
ASSEMBLY
(EARLY)
1.
Park
(black)
2. Low (green)
3.
High (red)
d.
Wiper
has
only slow speed
and
shuts
off
with
dash switch in high speed position. Reverse harness
leads that connect
to
wiper terminals.
e. If
blades
do not
return
to
park
position when
wiper
is
turned
off,
check wiper ground connection
to vehicle body. Remove wiper from vehicle
and
check
for
dirty, bent,
or
broken
park
switch con
tacts.
f.
If
wiper speed
is
normal
in
slow,
but too ex
cessive
in
fast speed, check for an open terminal. 217
Page 239 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
J
THREE-SPEED
TRANSMISSION
Contents
SUBJECT
PAR.
GENERAL
J-l
TRANSMISSION
SHIFTING
CONTROL.
. J-2
TRANSMISSION
REMOTE
CONTROL
ADJUSTMENT
J-3
REMOTE
CONTROL
DISASSEMBLY
J-4
REMOTE
CONTROL
REASSEMBLY.
. . . . J-5
TRANSMISSION
REMOVAL
J-6
SEPARATING
TRANSMISSION
AND
TRANSFER
CASE
J-7
SUBJECT
PAR.
DISASSEMBLY
OF
CANE
SHIFT
TRANSMISSION
J-8, J-12, J-16
Transmission
Cleaning and
Inspection J-10, J-18
Transmission
Interlocking Sleeve Inspection J-9
REASSEMBLY
OF
CANE
SHIFT
TRANSMISSION
J-ll,
J-14, J-19
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS
J-20
TRANSMISSION
SPECIFICATIONS
J-21
J-1.
GENERAL
A
three speed synchromesh transmission is standard
equipment on all 'Jeep' Universal vehicles.
The
models T90 and T96 transmissions are used
with
the
Hurricane
F4 engine, and models
T86AA
and
T14A transmissions are used with the Daunt
less
V-6 engine. All model transmissions are similar
in
design with exception of the T14A which is a
fully
synchronized (all forward gears) transmission
with
helical drive gears throughout.
The
transmission assembly is attached to the
rear
face of the flywheel bell housing and is supported on a rubber insulator at the frame center cross member which forms the
rear
engine
support.
All
4-wheel-drive vehicles are equipped with a
transfer
case attached to the
rear
of the transmission.
Transfer
case service and repair procedures
are
described in Section
K.
Models
CJ-5A,
and
CJ-6A
are equipped with the
same transmission, but with a remote control shift.
Models DJ-5 and DJ-6 are equipped with a similar
transmission,
however, the construction is
some
what different because it is not designed to receive a transfer case for four-wheel drive.
For
DJ-5 and DJ-6 2WD vehicles, the trans mission repair procedures begin with Par. J-12.
J-2.
TRANSMISSION SHIFTING CONTROL
The
shift of the three-speed transmission is smooth
and
positive. The cane control lever shifts the trans
mission gears direct from the shift control housing
mounted to the top side of the transmission housing.
The
remote control lever shifts the transmission
gears through remote control rods attached to the
adjusting
levers of the shift shafts protruding from the left side of the transmission housing. Poppet
balls and springs retain the transmission gears in mesh and an interlocking mechanism prevents
shifting into two gears at the same time.
J-3.
Transmission Remote Control Adjustment
•
Early
CJ-5A,
CJ-6A
First
disconnect the transmission shift rods from the remote control levers.
Check
for binding of
the remote control shaft on the steering column
and
make the necessary corrections to eliminate any binding condition.
If
the shift is not smooth and positive, first make
sure
the gears are in neutral position then remove
the shift rods at the transmission by removing
clevis pins, Fig. J-l No. 17, and slip a short piece
of snug fitting 34" [6,35 mm.] aligning rod, through
the gearshift levers and housing as shown in insert
drawing.
This
places the clutch and shift lever assemblies
in
the neutral position. Adjust the shift rod yokes
at the transmission end, so clevis pins can be in stalled freely without moving the shift levers on the
transmission after which remove alignment pin.
If
shifting from first to second is difficult or trans
mission hangs in first gear, shorten the low and
reverse shift rod one
turn
at a time until the con
dition is corrected. Usually three turns are re
quired.
Should
the fault continue after completing the above adjustment, check further as outlined below.
First
remove the lubricating fitting. Use a narrow
feeler
gauge
which
will
enter the opening for the
lubricator
and check the clearance
between
the
faces of the shifting clutches.
This
clearance should
be .015" to .031", [W to W]
[0,397-0,794
mm.]. If
this clearance is greater the assembly must be removed for adjustment. The shift dog, which
engages
the clutch slots, should not have more than .009" [0,229 mm.] clearance in the slots. If the clear
ance
between
the clutch
grooves
and cross pins is
too great,
these
parts must be replaced.
J-4.
Removal
of
Remote Control
m
Early
CJ-5A,
CJ-6A
•
Refer to Fig. J-l
To
remove the remote control the following pro cedure is
suggested:
a.
Remove shifting rods from the transmission
and
also from the steering remote control clutch levers. 239
Page 240 of 376

THREE-SPEED
TRANSMISSION
FIG.
J-l—TRANSMISSION
REMOTE
CONTROL
CJ-5
A,
CJ-6A
1— Stop Screw
2—
Bias
Spring
3—
Gearshift
Lever
4—
Lever
Ball
5—
Steering
Wheel 6—
Horn
Button 7—
Column
and Bearing
8—
End
Huts
9—
Shift
Rod
Ends
10—
Shift
Rod
11—
Shift
Rod
12—
Cross-Shift
Bracket
13—
Control
Shaft
14—
Lubrication
Fitting
15—
Lever
and
Clutch
16—
Adjusting
Yoke
17—
Aligning
Rod 11706
b.
Remove gearshift lever fulcrum pin and the
gearshift lever.
c.
Remove plates on the toe board at the steer
ing
post.
d.
Remove two screws holding remote control
housing to the steering
post
and lift the housing
from
the positioning pin.
e.
Remove the assembly down through the floor
pan.
f. Remove the lower clutch and shift lever from the housing by turning counterclockwise.
g. Remove upper clutch and shift lever in the same
manner.
h. Wash all parts in a suitable cleaning solution.
J-5.
Reassembly of
Remote
Control
•
Refer to
Fig.
J-l
Check
clearance of shift dog which
engages
in slot
of clutches, and if found to be greater than .009" [0,229 mm.] clearance, replace the worn parts.
Assemble upper clutch lever assembly in housing
making
sure that the alignment
hole
in the housing
faces toward the engine.
Turn
the upper lever as
sembly in as far as it
will
go and then back off one
full
turn
until the
hole
in the clutch lever aligns
with
hole
in the housing.
Assemble the lower clutch lever assembly in hous ing until faces of clutches contact then back off
not more than one-half
turn
which should bring
the aligning
hole
in the lever in line with the
hole
in
the housing. If the one-half
turn
does
not bring
the alignment
hole
in proper position, it
will
be
necessary to grind off (square with axis not to exceed .015") [0,397 mm.] the face of the lower
clutch;
in other words, backing off not more than
one-half
turn
from face to face contact
gives
the
proper
clearance of .015" to .031"
[0,397-0,794
mm.]
between
the two clutches.
Assemble the unit to the steering
post
in reverse
order
of dismantling and adjust remote control
rods.
After
assembly, if the shift dog catches on the
edge
of the slot in the clutch when moving the lever up
and
down, disconnect the shift rod at the
transmission
end and either lengthen or shorten it
slightly to correct this condition.
J-6.
TRANSMISSION
REMOVAL
The
following repair procedures given in Par. J-7
through J-ll for the standard
3-speed
transmission
apply
in general to all models listed. Minor dif
ferences
between
models that affect the procedure
are
noted. Procedure for the optional
4-speed
transmission
begins
with Section
J-l.
Removal
is as follows:
a.
Drain
the transmission and transfer case. Re place the
drain
plugs.
b.
Remove the floor pan inspection plate.
c.
Remove the shift lever and shift housing as sembly and its gasket from the transmission. On 240
Page 277 of 376

'Jeep*
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
m
FRONT fiXLE
Contents
SUBJECT
PAR.
GENERAL.
M-l
4-WHEEL DRIVE FRONT
AXLE.
M-2
Maintenance
Requirements M-3
FRONT AXLE REMOVAL
.M-4
AXLE
SHAFT REMOVAL
M-5
REMOVING
AND
OVERHAULING
DIFFERENTIAL
.M-6
AXLE
SHAFT UNIVERSAL JOINT SERVICE
M-7
STEERING
KNUCKLE SERVICE
M-8
Replacing
Steering
Knuckle
Oil Seal M-10
M-1. GENERAL
The
front axle for all 'Jeep* Universal models,
which
have 4-wheel drive, is described in
Par.
M-2.
The
front axle for all DJ-5, DJ-6 models, which
have 2-wheel drive, is described in
Par.
M-l5.
M-2. 4-WHEEL-DRIVE FRONT AXLE
The
front axle is a live driving unit with hypoid
type
driving gears and spherical steering knuckles mounted m pivot pins which ride on tapered roller bearings for
ease
of steering. The drive is of the
full
floating
type
through axle shafts built integrally
with
cardan cross universal joints which revolve in the steering knuckles. The steering knuckle tie rod
arm
is made integrally with the knuckle. The
knuckles
are connected by a divided tie rod to a steering bell
crank.
A steering connecting rod con
nects
the bell
crank
to the steering gear arm. The
divided
tie rod is adjustable and the
toe-in
of each
front wheel is adjusted independently.
Camber
and
SUBJECT
PAR.
REASSEMBLY
AND
BEARING PRELOAD
M-9
AXLE
SHAFT INSTALLATION
M-ll
FRONT AXLE INSTALLATION........
.M-l2
Turning
Angle Adjustment . .M-14
Steering
Tie Rod and
Beilcrank
M-l3
2-WHEEL DRIVE FRONT AXLE
M-15
Removal
of Solid
Front
Axle M-l6
Steering
Knuckle
Service M-l7
Steering
Knuckle
Pin Replacement. ......M-l8
SERVICE
DIAGNOSIS
M-19
AXLE
SPECIFICATIONS.
M-20
caster
of the front
wheels
is preset.
Camber
cannot
be altered but caster can be adjusted by installing
caster
shims
between
the axle pad and the springs.
For
information on the steering
geometry
see
"Steering
Section."
Service
procedures given in this section include
the removal, installation, disassembly and assembly
of the Model
27AF
front axle assembly, the axle
shafts, steering knuckles, and
universal
joints.
Note:
All service replacement axle assemblies are
shipped from the factory without lubricant in the
differential.
Lubricant
must be added; use grade
and
quantity as specified in the lubrication chart (Section B).
M-3.
Maintenance Requirements
A
spring-loaded breather is located on the top of
the differential housing.
Each
time the differential
lubricant
is checked, the breather should be
Page 278 of 376
M
FRONT
AXLE
1— Nut
2—
Lock
Washer
3—
Bearing
Lock
Washer
4—
Wheel
Bearing Cup 5—
Cone
and Rollers
6—
Oil
Seal 7— Spindle
8— Spindle Bushing
9—
Filler
Plug
10—
Right
Knuckle and Arm
11— Shims
12— Pivot Pin
13—
Lock
Washer
14—
Cap
Screw
15— Nut
16—
Washer
17—
Universal
Joint Yoke
18—
Oil
Seal
19—
Oil
Slinger
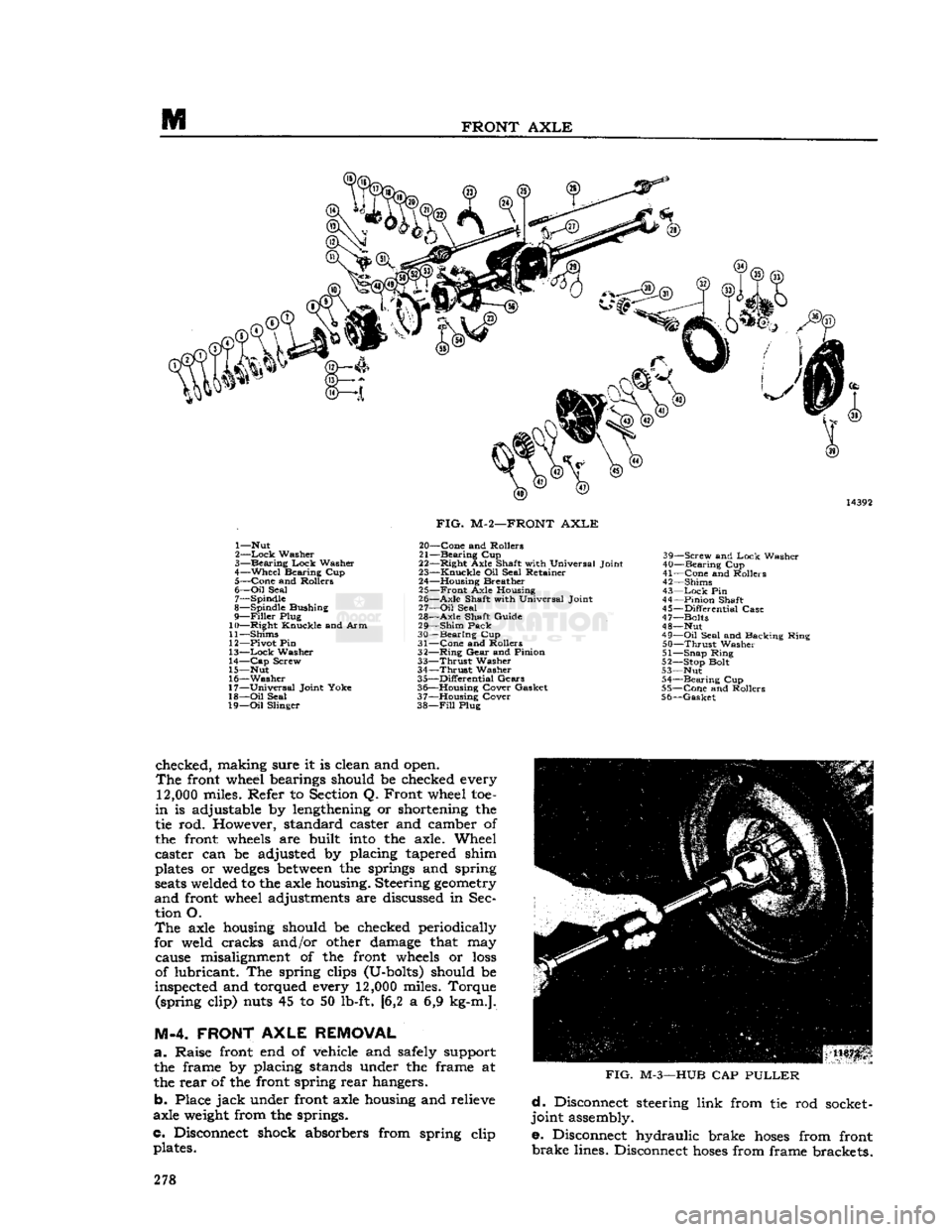
FIG.
M-2—FRONT
AXLE
20—
Cone
and Rollers
21—
Bearing
Cup
22—
Right
Axle Shaft with Universal Joint
23—
Knuckle
Oil Seal Retainer
24— Housing Breather 25—
Front
Axle Housing
26—
Axle
Shaft with Universal Joint
27—
Oil
Seal
28—
Axle
Shaft Guide
29—
Shim
Pack
30—
Bearing
Cup
31—
Cone
and Rollers
32—
Ring
Gear
and Pinion
33—
Thrust
Washer
34—
Thrust
Washer
35—
Differential
Gears
36— Housing Cover Gasket
37— Housing Cover
38—
Fill
Plug 39—
Screw
and
Lock
Washer
40—
Bearing
Cup
41—
Cone
and Rollers
42— Shims
43—
Lock
Pin
44—
Pinion
Shaft
45—
Differential
Case
47— Bolts
48— Nut
49—
Oil
Seal and Backing Ring
50—
Thrust
Washer
51— Snap Ring
52— Stop Bolt
53— Nut 54—
Bearing
Cup
55—
Cone
and Rollers
56—
Gasket
checked, making sure it is clean and open.
The
front wheel bearings should be checked every
12,000
miles. Refer to Section Q. Front wheel toe-
in
is adjustable by lengthening or shortening the
tie rod. However, standard caster and camber of
the front
wheels
are built
into
the axle. Wheel
caster can be adjusted by placing tapered shim
plates or
wedges
between
the springs and spring
seats
welded to the axle housing. Steering
geometry
and
front wheel adjustments are discussed in Sec tion O.
The
axle housing should be checked periodically
for weld cracks and/or other damage that may cause misalignment of the front
wheels
or
loss
of lubricant. The spring clips (U-bolts) should be
inspected and torqued every
12,000
miles. Torque (spring clip) nuts 45 to 50 lb-ft. [6,2 a 6,9 kg-m.].
M-4. FRONT
AXLE
REMOVAL
a.
Raise front end of vehicle
arid
safely support the frame by placing stands under the frame at
the rear of the front spring rear hangers.
b. Place
jack
under front axle housing and relieve
axle
weight
from the springs.
c. Disconnect shock absorbers from spring clip plates.
FIG.
M-3—HUB
CAP
PULLER
d.
Disconnect steering link from tie rod socket-
joint assembly.
e. Disconnect hydraulic brake
hoses
from front
brake
lines. Disconnect
hoses
from frame brackets. 278
Page 280 of 376
M
FRONT
AXLE
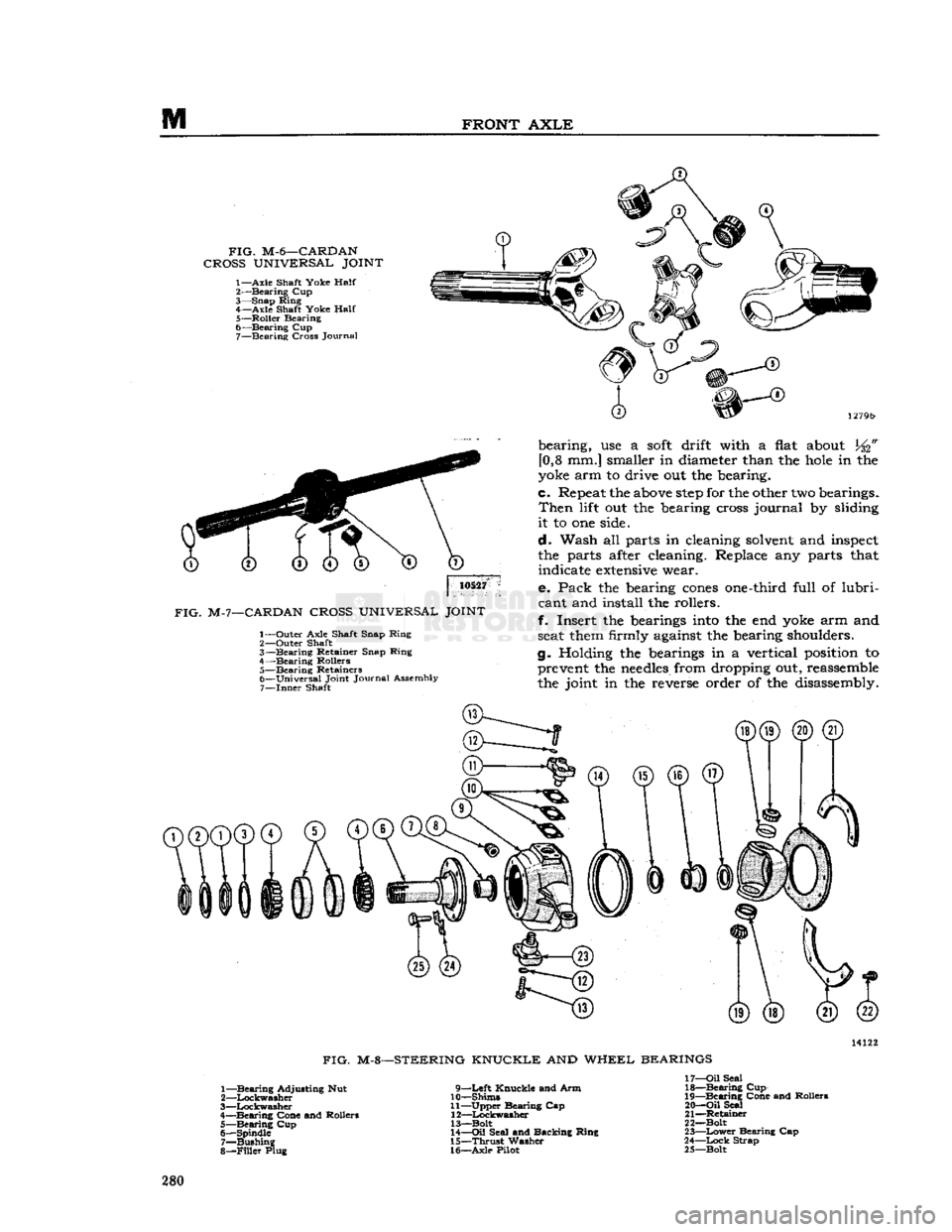
FIG.
M-6—CARDAN
CROSS
UNIVERSAL
JOINT
1—Axle
Shaft Yoke
Half
2-—Bearing Cup
3— Snap Ring 4— Axle Shaft Yoke
Half
5— Roller Bearing
6— Bearing Cup 7— Bearing Cross Journal
10527
FIG.
M-7—CARDAN
CROSS
UNIVERSAL
JOINT
1— Outer Axle Shaft Snap Ring
2— Outer Shaft
3— Bearing Retainer Snap Ring
4— Bearing Rollers 5— Bearing Retainers
6— Universal Joint Journal Assembly 7—
Inner
Shaft bearing, use a
soft
drift with a
flat
about
[0,8 mm.] smaller in
diameter
than the
hole
in the
yoke
arm to drive out the bearing.
c.
Repeat
the
above
step
for the
other
two
bearings.
Then
lift
out the
bearing
cross
journal by
sliding
it to one
side.
d. Wash all parts in
cleaning
solvent
and
inspect
the parts
after
cleaning.
Replace any parts
that
indicate
extensive
wear.
e. Pack the
bearing
cones
one-third
full of lubri
cant
and install the rollers.
f. Insert the
bearings
into
the end
yoke
arm and
seat
them
firmly
against
the
bearing
shoulders.
g.
Holding
the
bearings
in a vertical
position
to
prevent
the
needles
from
dropping
out,
reassemble
the joint in the
reverse
order of the
disassembly.
FIG.
M-8—STEERING KNUCKLE AND WHEEL BEARINGS
1— Bearing Adjusting Nut
2— Lockwasher
3— Lockwasher
4— Bearing Cone and Rollers 5— Bearing Cup
6— Spindle 7— Bushing
8—
Filler
Plug 9—Left Knuckle and Arm
10— Shims
11— Upper Bearing Cap 12— Lockwasher
13—Bolt
14—
Oil
Seal and Backing Ring
15—
Thrust
Washer
16— Axle Pilot 17—
Oil
Seal
18— Bearing Cup
19— Bearing Cone and Rollers
20—
Oil
Seal
21— Retainer
22— Bolt
23—
Lower
Bearing Cap
24—
Lock
Strap
25— Bolt 280
Page 281 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES
SERVICE
MANUAL
M
If
the joint binds when assembled, tap the yoke
lightly to relieve any pressure on the bearings at the end of the
journal.
M-8-
Steering
Knuckle
Service
The
steering knuckle pins pivot on tapered roller
bearings. Replacement of
these
bearings requires
removal
of the hub and brake drum assembly,
wheel bearings, axle shaft, spindle, steering tie rod,
and
steering knuckle. Disassemble the steering
knuckle
as follows:
Remove the
eight
screws which hold the oil seal
retainer
in place. Remove the four screws holding
the lower pivot pin bearing cap. Remove the four screws holding the upper bearing cap in place. Re
move
the bearing cap. The steering knuckle can
now be removed from the axle. Wash all parts in cleaning solvent. Replace any damaged or worn
parts.
Inspect the bearing and races for scores,
cracks,
or chips. Should the bearing cups be damaged,
they
may be removed and installed with
Special
Driver
W-138, as shown in Fig. M-9.
M-9.
Reassemble
and
Bearing Preload
Reverse
the procedure of Par. M-8 to reassemble
the unit. When reinstalling the steering knuckle, sufficient shims must be installed under the top
bearing
cap to obtain correct preload on the bear
ing.
Shims are available in
these
thicknesses: .003"
[0,076
mm.] .010"
[0,254
mm.] 005"
[0,127
mm.] .030"
[0,762
mm.]
Install
one each of the
above
shims at the top only.
Install
the bearing caps, lockwashers, and screws,
and
tighten securely.
Check
the preload on the bearings by hooking a
spring
scale, Tool C-690, in the
hole
in the knuckle
arm
for the tie rod socket.
Take
the scale reading when the knuckle has just started its
sweep.
The
kingpin bearing preload should be 12 to 16 lb. [5,43 a 7,24 kg.] with the oil seal removed. Remove
or
add shims to obtain a preload within
these
limits.
FIG.
M-9—SPINDLE
PIN
BEARING
CUP
DRIVER
1—Tool
W-138
FIG.
M-10—TURNING
ANGLE
STOP
SCREW
1—Stop
Screw
M-10.
Replacing Steering
Knuckle
Oil Seal
Remove the old steering knuckle oil seal by remov ing the
eight
screws which hold it in place.
Earlier
production vehicles are equipped with seals con sisting of two oil seal halves.
Later
production vehicles are equipped with oil seal assemblies con
sisting of a split oil seal and backing ring assembly,
an
oil seal felt, and two seal retainer plate halves.
Examine
the spherical surface of the axle for scores or scratches which could damage the seal.
Smooth any roughness with emery cloth. Before installing the oil seal felt, make a diagonal
cut across the top side of the
felt
so that it may be
slipped over the axle.
Install
the oil seal assembly
in
the
sequence
given above, making sure the
backing
ring (of the oil seal and backing ring as
sembly) is toward the wheel.
After
driving in wet, freezing weather swing the
front
wheels
from right to
left
to remove moisture
adhering
to the oil seal and the spherical surface of
the axle housing.
This
will
prevent freezing with
resulting
damage to the seals. Should the vehicle be
stored for any period of time, coat
these
surfaces
with
light grease to prevent rusting.
M-11.
AXLE
SHAFT
INSTALLATION
Refer
to Fig. M-2.
Installation
of the front right and
left
axle shaft
is the same and is given in the following
paragraphs.
a.
Clean
all parts of
dirt
and foreign matter.
b.
Enter
universal joint and axle shaft assembly
in
the axle housing, taking care not to knock out
the inner oil seal.
Enter
the splined end of the
axle shaft
into
the differential and push
into
place. 281
Page 282 of 376

FRONT
AXLE
FIG.
M-l
1—FRONT
STEERING
KNUCKLE
(With
Spicer Universal Joint)
1—
Wheel
Hub Cap
2—
Driving
Flange Cap Screw
3—
Axle
Shaft Drive Flange Gasket 4—
Wheel
Bearing Cup
5—
Front
Wheel Spindle
6—
Brake
Drum
7—
Front
Brake
Cylinder
8—
Brake
Backing Plate
9—
Pivot
Pin Bearing Cap
10—
Pivot
Pin Bearing Cap Nut
11—
Pivot
Pin 12—
Pivot
Bearing Adjusting Shims
13—
Pivot
Pin Cone and Rollers
14—
Steering
Knuckle
Oil Seal 15—
Front
Axle Universal Joint
16—
Thrust
Washer
17—
Brake
Backing Plate Screw
18—
Brake
Shoe and
Lining
19—
Hub
Oil Seal
20—
Wheel
Hub Bolt Nut
21—
Wheel
Bearing Cone and Rollers 22—
Wheel
Bearing Washer
23—
Wheel
Bearing Retaining Nut
24—
Wheel
Adjusting Nut
Lock
Washer
25—
Wheel
Bearing Retaining Nut
26—
Snap
Ring
c.
Install
the wheel bearing spindle and bushing.
d.
Install
brake backing plate.
e.
Grease and assemble wheel bearings and oil
seal.
Install
the wheel hub and drum on the wheel
bearing
spindle.
Install
the wheel bearing washer
and
adjusting nut. Tighten nut with
Wrench
W-144
as shown in
Fig.
M-5, until there is a slight drag on the bearings when the hub is turned.
Then
back off approximately one-sixth of a
turn.
Install
lock
washer
and nut, tightening nut
into
place, and then bend lip of lock washer over on the locknut.
f.
Install
drive
flange
and gasket on hub and attach
with
six cap screws and lock washers.
Install
snap
ring
on outer end of axle shaft.
g.
Install
hub cap.
h.
Install
the wheel, lug nuts, and wheel disc.
i.
If
tube
was installed with axle assembly on
vehicle, check front wheel alignment (Section O),
bleed brakes (Section P), and lubricate front axle
universal
joints (Section B).
M-12.
FRONT
AXLE
INSTALLATION
To
install the front axle, reverse the procedures described in
Par.
M-4 and then perform the follow
ing operations:
a.
Torque spring clip plate (U-bolt) nuts securing the axle to the front springs, (see Par. M-4).
b.
Adjust and bleed the brakes (see Section P).
c.
Check
axle lubricant level and
fill
as necessary, (see Section B).
d.
Check
front end wheel alignment (see Section
O).
e.
Check
wheel turning angle. Refer to Par. M-14.
M-13.
Steering
Tie Rod and
Bell Crank
These
parts of the front axle are covered in Sec
tion O.
M-14.
4-Wheel Drive
Turning
Angle
Adjustment
and service information regarding
turning
angles
is covered in Section O.
M-15.
2-WHEEL-DRIVE
FRONT
AXLE
The
front axle is of the reverse
Elliot
type. It is a
steel forging, heat treated for strength and ma
chined
to
close
limits. The steering knuckles are
mounted on pins which pass through
openings
at each end of the
"I"
beam and are locked securely
in
position with tapered pins and nuts. The knuckles
ride
on
ball
thrust bearings for
ease
of steering. See
Figs.
M-12, M-13.
The
knuckles are connected by a tie rod which is
mounted on
ball
and socket connections. The tie
rod
is adjustable to secure correct
toe-in
of the front wheels. A steering connecting rod
connects
the
left
knuckle arm with the steering gear arm.
Standard
caster and camber of the front
wheels
are
built
into
the front axle. Wheel camber cannot
be changed however, caster can be adjusted by
placing
tapered shims or
wedges
between
the
springs and spring seats. For
complete
information
regarding
the steering
geometry
refer to the
Section O.
M-16.
Removal of Solid
Front
Axle
Note:
The procedure for removing the solid front
axle varies slightly, depending on whether the
springs are slung under or over the axle. These
variations
are
noted
in the following procedure.
a. -
Raise the front end of the vehicle and safely support the frame behind the springs.
b.
Remove the
wheels
by removing the wheel
discs and lug nuts.
c.
Disconnect the steering connecting rod at the
ball
and socket connection on the steering knuckle. 282