1953 JEEP CJ ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 86 of 376

Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
Dl-38.
Crankshaft
Cleaning
Clean
the crankshaft thoroughly with a suitable
cleaning solvent.
Clean
drilled oil
passages
in its
journals
with a small rifle brush to remove all
sludge
or gum deposits; dry
passages
with com
pressed air.
Dl-39.
Crankshaft
Inspection
and
Repair
If
the crankshaft has not
been
removed from the
cylinder
block for inspection, disconnect two con necting rods at a time from crankshaft. Inspect
the bearings and crankpin journals. While turning
crankshaft,
it is necessary to temporarily reconnect
the rods to crankshaft to avoid possibility of dam aging the journals through contact with uncon
nected rods.
Inspect the crankpins visually for excessive or ir
regular
wear, and for scoring. Use an
outside
micrometer to check crankpins for out-of-round.
Standard
crankpin
diameter is
2.0000"
[5,080
cm.].
If
crankpins are more than .0015"
[0,0381
mm.]
out-of-round, new bearings cannot be
expected
to
have satisfactory life.
If
the crankshaft has
been
removed from the
cyl
inder
block for inspection support it on V-blocks
at its main bearing journals 1 and 4. Inspect the
main
bearing journals visually for excessive or ir
regular
wear, and for scoring. Standard main bear
ing
journal
diameter is 2.4995"
[6,349
cm.].
Total
indicator readings at each
journal
should not ex
ceed .003"
[0,076
mm.].
Check
run out at all four journals and
note
high
spot
(maximum eccentricity) of each
journal.
High
spot
of each
journal
should
come
at the same
angular
location. If high
spots
do not coincide,
crankshaft
is misaligned and unsatisfactory for
service.
If
crankpin or main bearing journals are scored,
ridged, or out-of-round, the crankshaft must be replaced or reground to a standard undersize bear
ing diameter to ensure satisfactory life of bearings. Slight roughness can be removed with a fine grit
polishing cloth thoroughly
wetted
with
engine
oil.
Burrs
can
be
honed with a fine oil
stone,
so long as
bearing clearances
will
remain within specified
limits.
Dl-40.
Crankshaft
Main
Bearings
A
crankshaft bearing consists of two halves which
are
neither alike nor interchangeable. One half is
carried
in the corresponding main bearing cap; the
other half is located
between
the crankshaft and
cylinder
block. The upper (cylinder block) half
of the bearing is grooved to supply oil to the con necting rod bearings, while the lower (bearing cap)
half
of the bearing is not grooved. The two bearing
halves must not be interchanged. All crankshaft
bearings
except
the thrust bearing and the
rear
main
bearing are identical. The thrust bearing (No. 2) is longer and it is flanged to take
crank
shaft end thrust. When the bearing halves are
placed in cylinder block and bearing cap, the
ends
extend slightly beyond the parting surfaces. When
cap
bolts
are tightened, the halves are clamped
tightly in place to ensure positive seating and to
prevent turning. The
ends
of bearing halves must never be filed flush with parting surface of
crank
case or bearing cap.
Crankshaft
bearings are the precision type which
do not require reaming to size or other fitting.
Shims
are not provided for adjustment since worn
bearings are readily replaced with new bearings of proper size. Bearings for service replacement are
furnished
in standard size and undersizes. Under no circumstances should crankshaft bearing caps
be filed to adjust for wear in old bearings.
Dl-41.
Crankshaft
Main
Bearing
Cleaning
and
Inspection
Clean
main bearing surfaces. Inspect the bearings
visually
for excessive or uneven wear, scoring, and
flaking.
Visibly worn or damaged bearings must
be replaced. It is necessary to check
radial
clear ance of each new or used crankshaft main bearing
before installation.
This
can be
done
by either of two methods, which are described in
Pars.
Dl-42
and
Dl-43.
a.
The desired
radial
clearance of a new bearing
is .0005" to .0021"
[0,0127
a
0,0534
mm.].
b. Replacement bearings are furnished in standard
size, and in several undersizes, including undersizes
for reground journals. If a new bearing is to be installed, try a standard size; then try each under
size in turn until one is found that
meets
the
specified clearance limits.
Note:
Each
undersize bearing half has a number
stamped on its outer surface to indicate amount of undersize. Refer to Fig. Dl-12. 14288
FIG.
Dl-12—LOCATION
OF
UNDERSIZE
MARK
ON
BEARING
SHELL
1—
Tang
2—
Undersize
Mark
Dl-42.
Main
Bearing
Fitting,
Plastigage
Bearing
clearance can be checked by use of Plasti
gage,
Type PG-1 (green) which has a range of
.001" to .003" [0,025 a
0,076
mm.]. Refer to
Fig.
Dl-13.
a.
Place a piece of Plastigage lengthwise along the
bottom
center of the lower bearing half, then 86
Page 87 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
A 8
j
13415
FIG.
Dl-13—USING
PLASTIGAGE
TO
MEASURE
BEARING CLEARANCE
1— Plastigage
A—Start
2—
Scale
B—Flattened
install
cap with shell and tighten
bolts
80 to 110 lb-ft. [11,1 a 15,2 kg-m.] torque.
Caution:
Do not turn crankshaft with Plastigage
in
bearing.
b.
Remove bearing cap with bearing half. The
flattened Plastigage
will
adhere either to the bear ing half or the
journal.
Do not remove it.
c. Using the scale printed on the Plastigage en
velope,
measure Plastigage width at its widest
point. The number within the graduation which
most
closely corresponds to the width of Plasti
gage
indicates the bearing clearance in thousandths
of an inch.
DI-43.
Main Bearing
Fitting,
Feeler or
Shim
Stock
A
small strip of feeler or shim stock can be used
to check main bearing clearance. The method is
simple, but care must be taken to avoid damage
to the bearing surface from excessive pressure against the strip.
a.
Cut a rectangular piece of feeler or shim stock, .001"
[.0254
mm.] thick,
i/2"
[12,70
mm.] wide, and
Vs"
[3,175 mm.] shorter than the bearing width.
Position the bearing cap to the crankshaft journal
and
cylinder block, and install two cap
bolts
loosely.
b.
Tighten alternate cap bolts, a little at a time,
until
both have
been
tightened to 35 to 45 lb-ft. [4,8 a 6,2 kg-m.] torque.
c.
Turn
the crankshaft by hand, no more than one
inch
[2,5 cm.] in either direction.
Caution:
If the crankshaft is turned too far, it
will
embed the strip in the bearing surface.
This
will
damage the bearing and also cause a false indication of bearing clearance.
If
bearing clearance is correct, the strip should cause a light to heavy drag, or resistance to rotation.
If
there is little or no drag, clearance is too great;
if
the crankshaft cannot be turned, clearance is
insufficient. In either case, a different main bear ing must be
selected
to obtain proper clearance.
d.
Repeat
steps
a, b, and c, as necessary, to
select
proper main bearing size. After a bearing has
been
selected, remove the
test
strip from bearing on
crankshaft
journal surface; wipe both surfaces care
fully,
and apply clean
engine
oil to both surfaces. Position the bearing cap to the crankshaft journal
and
cylinder block, and install two cap
bolts
loosely.
Tighten
alternate cap bolts, a little at a time, to
final
specified torque of 80 to 110 lb-ft. [11,1 a 15,2 kg-m.]. The crankshaft should now rotate
freely.
Dl-44.
Piston
and
Connecting
Rod
Disassembly
a.
Remove two compression rings with a piston
ring
expander. To remove oil ring, remove the two
rails
and spacer-expander, which are separate
pieces
in
each piston third
groove.
b.
From
Tool Set W-338 use support base J-6047-1
with collar J-6047-5 and driver J-6047-4 with an
arbor
press to press piston pin from piston and con
necting rod. Mount support base and collar in press. Set driver in position and press out pin. Refer to
Fig.
Dl-14.
FIG.
Dl-14—PISTON
PIN
REMOVAL
1—
Arbor
Press
2—
Driver
3—
Piston
and Rod Assembly
4—
Collar
•
5—Support Base Dl-45.
Piston
and
Connecting
Rod
Cleaning
and Inspection
a.
Clean
carbon from piston surfaces and under
side of piston heads, and remove all pistons rings.
Clean
carbon from ring
grooves
with a suitable tool.
Remove any gum or varnish from piston skirts with a suitable solvent.
b.
Carefully examine pistons for rough or scored
bearing surfaces, cracks in
skirt
or head, cracked
or
broken ring lands, chipping and uneven wear 87
Page 90 of 376

DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
Note:
The rib on
edge
of cap and the conical
boss
on web of connecting rod must be toward
rear
of
engine
in all connecting rod assemblies of left
cyl
inder
bank and toward front of
engine
in all connecting rod assemblies of right cylinder bank.
Dl-50.
Oil
Pump Intake
and
Screen Cleaning
a.
Pry screen from housing and examine for clog
ging due to deposit of sludge or other foreign
material.
b.
Clean
the screen and housing thoroughly in sol
vent; dry with compressed air.
c.
Install
screen in housing.
Dl-51.
Oil Pan Cleaning and Inspection
Inspect
the oil pan for corrosion, dents, leaks, and
other damage. Inspect its mounting flange carefully
for damage or distortion to be certain that it
will
give
a
good
seal.
Dl-52.
Flywheel Cleaning
and
Inspection
Clean
the flywheel with suitable cleaning solvent;
dry
with compressed air. Inspect clutch face for
burned
or scuffed condition and for rivet grooves.
Inspection
for run out or improper mounting is de
scribed
in installation procedure.
Inspect
teeth
of the flywheel
ring
gear for
burrs,
nicks,
and minor distortion. If necessary and pos
sible, use a small emery wheel to remove
burrs
and
reshape teeth. If gear
teeth
are broken,
cracked,
seriously
burred
or deformed, the
ring
gear must be replaced.
Dl-53.
Ring Gear Replacement
a.
Drill
a
hole
between
two
ring
gear teeth; then
split
the gear with a cold chisel. Be careful not to
damage
ring
gear shoulder or seat surfaces of fly
wheel.
b.
Polish several
spots
on the new
ring
gear to be
installed.
With
a hot plate or slowly moving torch,
heat the new
ring
gear until polished
spots
become
blue, about
600°F.
[312°C.].
Caution:
Do not heat the
ring
gear to a temperature
greater than
800°F.
[424°C.].
Excessive heat
will
destroy heat treatment given to
ring
gear during
manufacture.
c.
Quickly
install
ring
gear on flywheel. Chamfered
edge
of
ring
gear must be toward
ring
gear shoulder
of flywheel. Be certain that
ring
gear is seated prop
erly.
Allow
ring
gear to cool slowly, so that it
will
be held tightly in place.
Dl-54.
Flywheel Housing Cleaning and Inspection
Both
flywheel and clutch are enclosed by a fly
wheel housing. Its front surface is bolted to the
engine
cylinder block, and its
rear
surface acts as
front
support to the transmission.
Clean
the fly wheel housing with a suitable cleaning solvent; dry
with
compressed air. Inspect front and
rear
surfaces
for distortion and improper alignment with each
other;
these
planes must be
parallel
to assure
proper
alignment
between
engine
and transmission.
Dl-55.
Camshaft Cleaning
and
Inspection
Clean
both camshaft and camshaft bearing surfaces
with
a suitable cleaning solvent; dry with com
pressed air.
Note:
The steel-backed babbitt-lined camshaft
bearings are pressed into the crankcase.
From
front
to
rear,
each bearing is .030" [0,76 mm.] smaller
in
diameter than the preceding bearing.
From
front
to
rear,
each camshaft
journal
is correspondingly
smaller
in diameter.
The
camshaft bearings must be line reamed to
proper
diameter after being pressed into crankcase.
Since
this operation requires special reaming equip
ment, the original bearings should be retained un
less
they are severly damaged. Slightly scored cam
shaft bearings are satisfactory if the surfaces of camshaft journals are polished, bearings are
polished to remove
burrs,
and
radial
clearance
between
camshaft and bearings is within .0015"
to .004" [0,038 a 0,102 mm.].
Dl-56.
Valve Lifter
and
Push
Rod
Cleaning and Inspection
a.
Examine the cam contact surface at lower end of each valve lifter body. If surface is excessively
worn,
galled, or otherwise damaged, discard the
valve lifter. Also examine the mating camshaft
lobe
for excessive wear or damage.
b.
Disassemble one or two valve lifters, as de
scribed
below, and inspect them for
dirt
or
varnish.
If
they are dirty or have a varnish deposit, clean
and
inspect all twelve valve lifters. Otherwise,
service
only
those
valve lifters which do not operate
properly.
c.
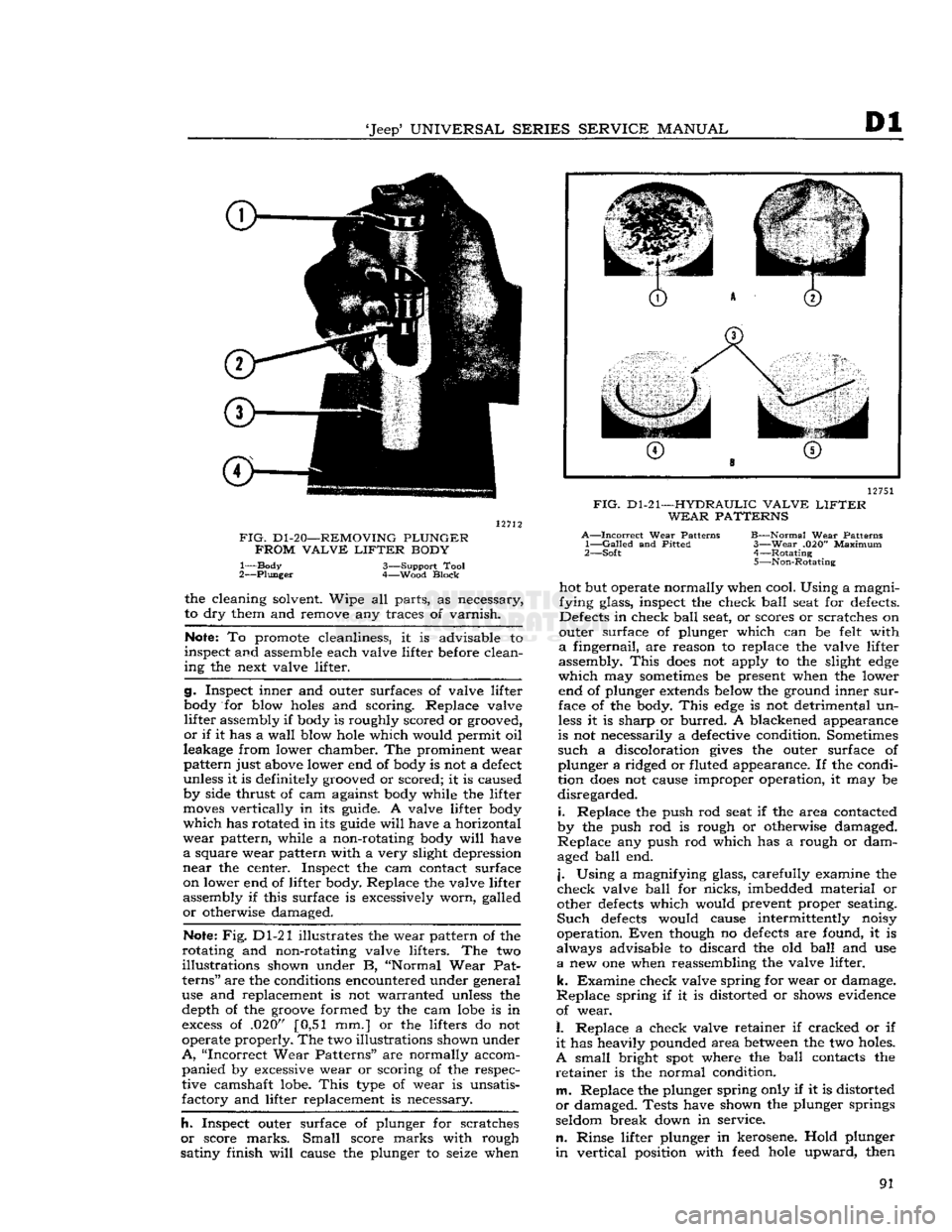
To disassemble each valve lifter, depress the
push
rod seat with a push rod, and remove the
plunger retainer from the valve lifter body with
a
retainer remover. Remove push rod seat and
plunger from valve lifter body. If plunger sticks
in
valve lifter body, place body in large end of
a
plunger remover tool, with plunger downward.
While
holding lifter with thumb, rap the open end
of remover against a block of wood with just enough force to jar the plunger from body. Refer to
Figs.
Dl-20, Dl-22 and Dl-23.
d.
Drain
oil from valve lifter and remove the check
valve retainer,
ball,
valve spring, and plunger
spring.
e. Keep all parts of each valve lifter separated
during
part cleaning and inspection. The valve
lifter
body and plunger are selectively fitted to each other and must not be interchanged with parts
of other valve lifters.
f. Rinse all valve lifter parts in kerosene to remove as much oil as possible.
This
will
reduce contamina
tion of the cleaning solvent. Immerse all parts in cleaning solvent for approximately one hour. The
time required
will
depend on varnish
deposits
and
effectiveness
of the solvent. After the varnish has
dissolved or has
softened
sufficiently to permit re
moval
by wiping, allow parts to
drain.
Varnish
can
then be cleaned from the valve lifter body
with
a
brush.
Rinse the parts in kerosene to dissolve 90
Page 91 of 376
'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
12712
FIG.
D1-20—REMOVING
PLUNGER
FROM
VALVE
LIFTER
BODY
1— Body 3—Support Tool
2—
Plunger
4—Wood Block the cleaning solvent. Wipe all parts, as necessary,
to dry them and remove any traces of varnish.
Note:
To promote cleanliness, it is advisable to
inspect and assemble each valve lifter before clean
ing the next valve lifter.
g. Inspect inner and outer surfaces of valve lifter
body for blow
holes
and scoring. Replace valve lifter assembly if body is roughly scored or grooved,
or
if it has a wall blow
hole
which would permit oil
leakage from lower chamber. The prominent wear
pattern just above lower end of body is not a
defect
unless it is definitely grooved or scored; it is caused
by side thrust of cam against body while the lifter
moves
vertically in its guide. A valve lifter body
which
has rotated in its guide
will
have a horizontal
wear
pattern, while a non-rotating body
will
have
a
square wear pattern with a very slight depression
near
the center. Inspect the cam contact surface on lower end of lifter body. Replace the valve lifter
assembly if this surface is excessively worn, galled
or
otherwise damaged.
Note:
Fig. Dl-21 illustrates the wear pattern of the
rotating and non-rotating valve lifters. The two
illustrations shown under B, "Normal Wear Pat
terns"
are the conditions encountered under general
use and replacement is not warranted unless the depth of the
groove
formed by the cam
lobe
is in
excess
of .020" [0,51 mm.] or the lifters do not
operate properly. The two illustrations shown under
A,
"Incorrect Wear Patterns" are normally accom panied by excessive wear or scoring of the respec
tive camshaft lobe.
This
type of wear is unsatis
factory and lifter replacement is necessary.
h.
Inspect outer surface of plunger for scratches
or
score marks.
Small
score marks with rough
satiny finish
will
cause the plunger to seize when 12751
FIG.
D1-21—HYDRAULIC
VALVE
LIFTER
WEAR PATTERNS
A—Incorrect
Wear Patterns B—Normal Wear Patterns
1—
Galled
and Pitted 3—Wear .020" Maximum
2— Soft 4—Rotating
5—Non-Rotating
hot but operate normally when cool. Using a magni
fying glass, inspect the check ball seat for defects.
Defects in check ball seat, or scores or scratches on
outer surface of plunger which can be felt with
a
fingernail, are reason to replace the valve lifter
assembly.
This
does
not apply to the slight
edge
which
may
sometimes
be present when the lower end of plunger
extends
below the ground inner
sur
face of the body.
This
edge
is not detrimental un
less
it is sharp or burred. A blackened appearance
is not necessarily a defective condition. Sometimes
such
a discoloration
gives
the outer surface of
plunger a ridged or fluted appearance. If the condi
tion
does
not cause improper operation, it may be
disregarded.
i.
Replace the push rod seat if the area contacted
by the push rod is rough or otherwise damaged.
Replace
any push rod which has a rough or dam
aged ball end.
j.
Using a magnifying glass, carefully examine the
check valve ball for nicks, imbedded material or
other
defects
which would prevent proper seating.
Such
defects
would cause intermittently noisy
operation.
Even
though no
defects
are found, it is
always advisable to discard the old ball and use
a
new one when reassembling the valve lifter,
k.
Examine check valve spring for wear or damage.
Replace
spring if it is distorted or shows evidence
of wear.
I.
Replace a check valve retainer if cracked or if
it
has heavily pounded area
between
the two holes.
A
small bright
spot
where the ball contacts the
retainer
is the normal condition.
m.
Replace the plunger spring only if it is distorted
or
damaged. Tests have shown the plunger springs
seldom break down in service.
n.
Rinse lifter plunger in kerosene. Hold plunger
in
vertical position with
feed
hole
upward, then 91
Page 94 of 376

Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
FIG.
D1-28—CLEANING
OR
ENLARGING
VALVE
GUIDE
1—Reamer
d.
Measure clearance of each valve stem in cor
responding valve guide. For intake valves, this
clearance
should be .0012" to .0032" [0,0305 a
0,0813
mm.]. For exhaust valves, this clearance should be .0015" to .0035"
[0,0381
a
0,0889
mm.]
at top of guide and .002" to .004"
[0,051
a 0,102 mm.] at bottom of guide. If this clearance is exces
sive, valve guides must be reamed with .004" [0,102 mm.] oversized reamer J-5830-1 and valves
replaced
by new valves with oversize stems.
Dl-63.
Cylinder
Head
and Valve
Repair
a.
If a valve stem has excessive clearance in its
guide, the guide must be reamed .004" [0,102 mm.]
oversize. Valves are available with oversize stems
to fit this valve guide diameter.
b.
Grind
valve faces or replace valves if necessary.
Valve
faces must be ground at an angle of 45 degrees. If a valve head must be ground to a
knife
edge
to obtain a true face, the valve should
be replaced.
c.
If necessary, grind valve seats at an angle of 45 degrees.
Grinding
a valve seat decreases valve
spring
pressure and increases the width of the seat.
The
nominal width of the valve seat is
[
1,59
mm.].
If a valve seat is wider than %" [1,98 mm.]
after grinding, it should be narrowed to specified
width
by the use of 20-degree and 70-degree stones.
Improper
operation of a hydraulic valve lifter may
result
if valve and seat are refinished to the extent
that the valve stem is raised more than .050" [1,27 mm.] above normal height. In this case, it
is necessary to grind off the end of the valve stetti or replace parts.
Note:
The normal height of the valve stem above
the valve spring seat surface of the head is
1.925"
[4,889 cm.].
d.
Lightly
lap the valves into seats with fine grind
ing compound. The refacing and reseating should
leave the refinished surfaces smooth and true so that a minimum of lapping
will
be required. Ex
cessive lapping
will
groove the valve face and pre
vent
good
valve seating.
e. Test valve seats for concentricity with guides,
and
for proper valve seating. Coat a small segment
of the valve face lightly with Prussian blue pig ment.. Insert the valve stem into its guide and
turn
the valve face against the seat. If the valve seat is concentric with the valve guide, a
mark
will
be made all around the seat. If the seat is not concentric with the guide, a
mark
will
be made
on only one side of the seat.
Clean
all pigment from both valve and seat. .Next,
coat a small segment of the valve seat lightly with
Prussian
blue pigment. Again insert the valve stem into its guide and rotate the valve face against the
seat. If the valve face is concentric with the valve
stem, and if the valve is seating all the way around,
pigment
will
coat the valve face with a uniform
band
around its entire perimeter. Both of
these
tests
are necessary to prove that proper valve seat
ing is obtained.
f. Inspect the valve springs visually for corrosion,
breaks,
and distortion.
With
a valve spring tester
check
each valve spring for proper tension. When
a
valve spring is compressed to a length of
1.640"
[4,166 cm.] (closed-valve condition), it should
have a tension of 64 lb. [29,03 kg.]. When a valve
spring
is compressed to a length of
1.260"
[3,200
cm.] (open-valve condition), it should have ten sion of 168 lb. [76,205 kg.]. Replace any valve
spring
which is visibly damaged or
does
not
meet
tension specifications.
Dl-64.
Valve Installation
Lubricate
valve stems with engine oil.
Install
valves, valve springs, spring retainers, and valve
retainers
on the cylinder head. Use the same equipment and reverse procedure used for removal.
Install
valve springs with closely wound coils to
ward
the cylinder head. Refer to Fig. Dl-29.
FIG.
Dl-29—VALVE
SPRING
1—
Spring
2—
Close
Wound
Coils
Toward
Head
94
Page 96 of 376

Dl
DAUNTLESS
V-6
ENGINE
Note:
During
engine
reassembly, use Perfect Seal
Aerosol
Spray Sealer
Part
No.
994757
on all en
gine
gaskets to ensure against vacuum, oil, gasoline
and
water leaks. Apply to head gaskets, valve covers, water pumps, oil pan gaskets, radiator and
heater
hose
connections, felt gaskets, gasoline and
oil
line connections, stud bolts, spark plug threads,
and
grease retainer washers. Refer to manufac
turer's
instructions on container for proper appli
cation procedure.
Dl-72.
Cylinder
Block
and Crankshaft
Rear
Oil Seals
Braided
fabric seals are pressed into
grooves
of
cylinder
block and
rear
main bearing cap, to
rear
of the oil collecting groove, to seal against oil leak age at the crankshaft. Refer to Fig. Dl-32.
FIG.
Dl-32—INSTALLING
CRANKSHAFT REAR
OIL
SEAL
1—Neoprene
Seal
2—Fabric
Seal
A
neoprene composition (stick) seal is installed in
grooves
in the sides of the
rear
main bearing cap
to seal against leakage in the joints
between
the
cap and cylinder block. The neoprene composition
expands in the presence of oil and heat.
This
seal
is undersize when newly installed. Refer to Fig.
Dl-32.
a.
The braided fabric seal can be installed in the
cylinder
block only when the crankshaft is re moved; however, the seal in the cap can be replaced
whenever the cap is removed. Remove oil seal and place new seal in groove, with both ends projecting
above parting surface of cap. Force seal into
groove
by rubbing down with hammer handle or smooth
stick
until seal projects above the
groove
not more
than
[1,59 mm.]. Cut ends off flush with
sur
face of cap, using sharp knife or razor blade.
Lubricate
the seal with heavy
engine
oil just before
installation.
Caution:
The
engine
must be operated at slow
speed when first started after new braided seal
has been installed.
b. The neoprene composition seal is slightly longer
than
the
grooves
in the bearing cap. The seal must
not be cut to length. The seals are installed after the bearing cap is installed in the block and torqued
firmly
in place. Dip the neoprene seals in kerosene
approximately IV2 minutes, then install seals into
bearing cap grooves. The protruding ends of the seals are, again, squirted with kerosene, wiped off,
and
peaned over with a hammer to be sure of a
seal
at the upper parting line
between
the cap and
cylinder
block.
Dl-73.
Main
Bearing and Crankshaft
Installation
Refer
to Fig. Dl-6.
This
procedure assumes that crankshaft main bear
ings have been inspected and proven satisfactory,
or
that new crankshaft main bearings of appropriate size have been selected. If necessary, check or select
main
bearings as described in Par. Dl-41 and
Pars.
Dl-42 and Dl-43.
a.
Install
four upper main bearing halves in
seats
of cylinder block so that prong of each bearing half
fits into corresponding notch of seat. Flanged thrust
bearing must be installed in the second seat from
front of engine.
Install
a new upper crankshaft
rear
oil seal in the cylinder block as described in
Par.
Dl-72.
Caution:
Upper main bearing halves have an oil groove, while lower halves are plain. They must
not be interchanged.
b. Apply
engine
oil to upper bearing surfaces.
Install
the crankshaft so that its four journals rest
in
the upper bearing halves.
c. Seat all four lower main bearing halves in cor
responding bearing caps.
Install
a new lower
crank
shaft
rear
oil seal and cylinder block
rear
oil seal
described in
Par.
Dl-72, a and b.
Lubricate
all lower
main
bearing surfaces with
engine
oil. Position bear ing caps to cylinder block and crankcase journals.
Install
two cap bolts,
loosely,
at each cap.
d.
It is necessary to align thrust surfaces of the
second main bearing whenever it has been removed
from
the engine. To do this, pry the crankshaft
back
and forth several times, throughout its entire end travel, with cap
bolts
of second main bearing
only finger tight.
e. Tighten alternate cap
bolts
of each main bearing
cap,
a little at a time, until they have been tight ened to 80 to 110 lb-ft. [11,1 a 15,2 kg-m.] torque.
D1-74. Crankshaft End Play Check
To
measure crankshaft end play, mount a dial
indicator
on the cylinder block and index its plung
er
to either a front or
rear
face of one crankshaft
counterweight. Pry the crankshaft to one limit
of its end travel and adjust the dial indicator to
zero. Pry the crankshaft to its
opposite
end travel
limit
and
note
end play as indicated by the dial
indicator.
Crankshaft end play tolerances are .004"
to .008" [0,102 a
0,204
mm.]. If end play is too great, it can be corrected only by replacement of
the second main (thrust) bearing.
Dl-75.
Piston and Connecting Rod
Installation
This
procedure assumes that connecting rod bear ings have been inspected and proven satisfactory,
or
that new connecting rod bearings of appropriate 96
Page 97 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL
SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
size have
been
selected. If necessary, check or
select
connecting rod bearings as described in Par. Dl-49.
Note:
When a piston and connecting rod assembly
is properly installed, the oil spurt
hole
in the con necting rod
will
face the camshaft. The rib on the
edge
of the bearing cap
will
be on the same side
as the conical
boss
on the connecting rod web;
these
marks (rib and boss)
will
be toward the other
connecting rod on the same crankpin. The notch
on the piston
will
face the front of the
engine.
a.
Be certain that cylinder bores, pistons, connect
ing rod bearings and crankshaft journals are absolutely clean. Coat all bearing surfaces with
engine
oil.
b. Before installing a piston and connecting rod as
sembly into its bore, rotate the crankshaft so that
the corresponding crankpin is moved downward, away from the cylinder bore.
c. Remove bearing cap from connecting rod. With
upper bearing half seated in connecting rod, install connecting rod guides. These
guides
hold the upper
bearing half in place and prevent damage to the
crankshaft
crankpin during installation of the con
necting rod and piston assembly.
d.
Be certain that the gap in the oil ring rails faces
upward,
toward center of
engine.
Gaps of the com
pression rings shall not be aligned with each other
or
with the oil ring
rails.
e. Lubricate the piston and rings. Compress the
rings with a suitable piston ring compressor; install
the piston and connecting rod assembly from top of cylinder bore. Refer to Fig. Dl-33.
f.
Install
bearing cap, with lower bearing half, on connecting rod. Torque bolt nuts to 30 to 40 lb-ft. [4,1 a 5,5 kg-m.].
g.
Install
all other piston and connecting rod as
semblies in same manner.
h.
Check
end clearance
between
connecting rods
on each crankpin with a feeler
gauge.
Clearance should be .005,/ to .012" [0,127 a
0,305
mm.].
Dl-76.
Install
Oil
Pump
Intake
Pipe
and
Screen Assembly
Check
mating surfaces of oil pump intake pipe
and
engine
cylinder block to be certain that they
are
clean. Secure the pipe and screen assembly,
with a new gasket, to
engine
cylinder block with two attaching screws. See Fig. Dl-34. Torque screws 6 to 9 lb-ft. [0,83 a 1,24 kg-m.].
Dl-77.
Install
Oil Pan
Refer
to Fig. Dl-35.
Be
certain the flange surface of oil pan and cor
responding surface of
engine
cylinder block are
clean.
Install
a new oil pan gasket on the cylinder
block.
Secure
oil pan to cylinder block with mount ing bolts. Torque
bolts
10 to 15 lb-ft [1,4 a 2,1
kg-m.].
Dl-78.
Install
Flywheel
Refer
to Fig. Dl-7.
a.
Check
flywheel flange of
engine
crankshaft and corresponding surface of flywheel to
be
certain that
FIG.
Dl-33—INSTALLING
PISTON
AND
CONNECTING
ROD
ASSEMBLY
1—Ring
Compressor
FIG.
Dl-34-^-OIL
PUMP
INTAKE PIPE
AND
SCREEN
INSTALLATION
1—Pipe and Screen
97
Page 99 of 376

'Jeep'
UNIVERSAL SERIES SERVICE
MANUAL
Dl
both are clean. Any foreign material on either of
these
surfaces
will
cause flywheel run out and en
gine
vibration. Position flywheel to crankshaft and
secure with six mounting bolts. Torque mounting
bolts
50 to 65 lb-ft. [6,91 a 8,98 kg-m.].
Note:
Flywheel mounting
bolts
are unevenly
spaced so that flywheel can be installed in only
one position.
This
assures correct balance of fly
wheel and crankshaft.
b.
Mount a
dial
indicator on flywheel housing
flange of cylinder block and index its plunger to
the flywheel surface. Measure flywheel run out.
Maximum
allowable run out is .015"
[0,381
mm.].
Dl-82.
Install
Cylinder
Head Assembly
Refer
to Fig. Dl-9.
a.
Wipe cylinder head face of
engine
cylinder
block, and be certain no foreign material has fallen
into the cylinder bores, bolt holes, or in the valve
lifter
area.
It is
good
practice to clean out bolt
holes
with compressed air.
b.
Install
a new cylinder head gasket on the
cylin
der
block. Dowels in the block
will
hold the gasket
in
position. Always handle gaskets carefully to
avoid
kinking or damage to the surface treatment
of the gasket. Apply Perfect Seal Aerosol
Spray
Sealer
Part
No.
994757
on cylinder head gaskets.
Dl-79.
Install
Clutch
and Flywheel Housing
a.
Note
marks made on clutch assembly and fly
wheel during
engine
disassembly. Position clutch
assembly to flywheel, according to
marks,
and
fasten
loosely
with six attaching bolts. Torque
bolts
in rotation, one
turn
at a time, to 30 to 40 lb-ft. [4,1 a 5,5 kg-m.].
b.
Engage fork of clutch linkage to clutch and
position flywheel housing to
engine
cylinder block.
Secure
housing to block with six mounting bolts.
Torque
bolts
30 to 40 lb-ft. [4,1 a 5,5 kg-m.].
D1-80.
Install
Camshaft
Insert
camshaft into camshaft bearings of
engine
cylinder
block carefully to avoid damage to bear
ing surfaces. Make certain camshaft journals are
properly
seated in bearings.
12695
FIG.
D1-36—CAMSHAFT
AND
VALVE LINKAGE
1—
Rocker
Arm
2—
Push
Rod 3—
Valve
Lifter
4—
Camshaft
14203
FIG.
Dl-37—CYLINDER
HEAD
BOLT TIGHTENING SEQUENCE c.
Clean
gasket surface of cylinder head and care
fully
place on the
engine
block dowel pins.
d.
Clean
and lubricate the cylinder head
bolts
with
a
sealing compound
(Part
No. 994757, or equiv
alent).
e.
Install,
and alternately tighten the head bolts,
a
little at a time, in the sequence shown in Fig.
Dl-37.
Torque
bolts
65 to 85 lb-ft. [9,0 a 11,8
kg-m.].
f.
Tilt
the rocker arms toward the push rods and locate the top of each push rod in its rocker arm
seat.
g.
Mount the rocker arm and shaft assembly, tightening the bracket
bolts
a little at a time.
Torque
the bracket
bolts
25 to 35 lb-ft. [3,5 a 4,8
kg-m.].
Do not overtighten.
h.
See Section Fl and F2 for
engines
equipped
with
exhaust emission control.
D1-81.
Install
Valve Lifter
and Push Rod
Make
certain valve lifter guide
holes
and adjacent
area
of cylinder block are clean.
Liberally
lubricate
the camshaft and valve lifter bores with
engine
oil,
and install valve lifters.
Each
valve lifter must slide freely in its guide hole. See Fig. Dl-36.
Dl-83.
Install
Rocker Arm Cover
Install
a new gasket on each rocker arm cover.
Secure
each rocker arm cover to corresponding
cylinder
head with four attaching screws.
Install
the positive crankcase ventilation valve on right
rocker
arm cover. 99